We will share at one time 6 An immortal built-in function . In many computer books , They are also commonly used as Higher order function To introduce . And myself in my daily work , Often use them to make code faster , Easier to understand .
Lambda The function is used to create anonymous functions , That is, functions without names . It's just an expression , Function volume ratio def Simple a lot . When we need to create a function to perform a single operation and write it on one line , You can use anonymous functions .
lambda [arg1 [,arg2,.....argn]]:expressionlambda The subject of is an expression , Not a block of code . Only in lambda Expressions encapsulate limited logic . for example :
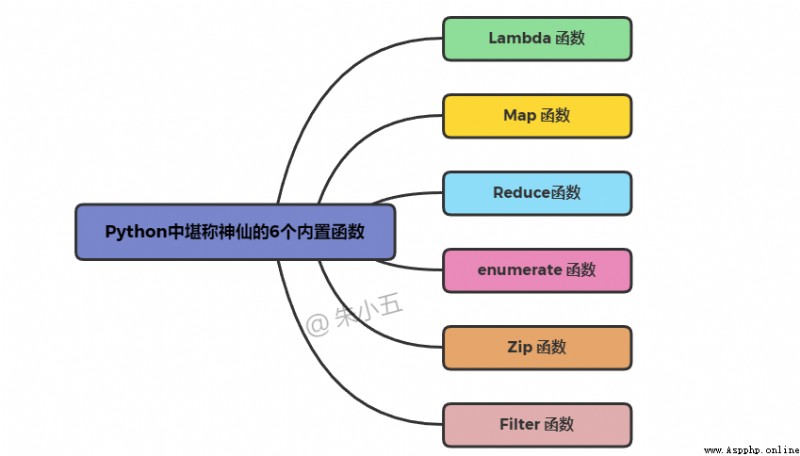
lambda x: x+2 If we also imagine def The defined function is called at any time , Can be lambda function Assigned to such a function object .
add2 = lambda x: x+2
add2(10)Output results :
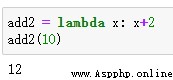
utilize Lambda function , You can simplify the code a lot , Take another example .
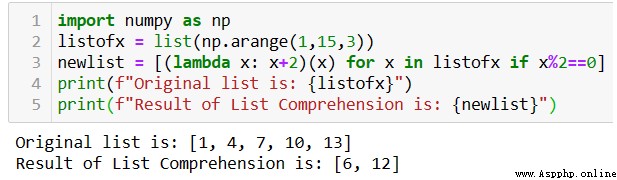
As shown in the figure above , Result list newlist It's using lambda The function is generated in one line of code .
map() The function maps a function to all elements of an input list .
map(function,iterable) For example, we first create a function to return an uppercase input word , Then add this function to the list colors All elements in .
def makeupper(word):
return word.upper()
colors=['red','yellow','green','black']
colors_uppercase=list(map(makeupper,colors))
colors_uppercaseOutput results :

Besides , We can also use Anonymous functions lambda To match map function , This can be more streamlined .
colors=['red','yellow','green','black']
colors_uppercase=list(map(lambda x: x.upper(),colors))
colors_uppercaseIf we don't Map Function words , You need to use for loop .
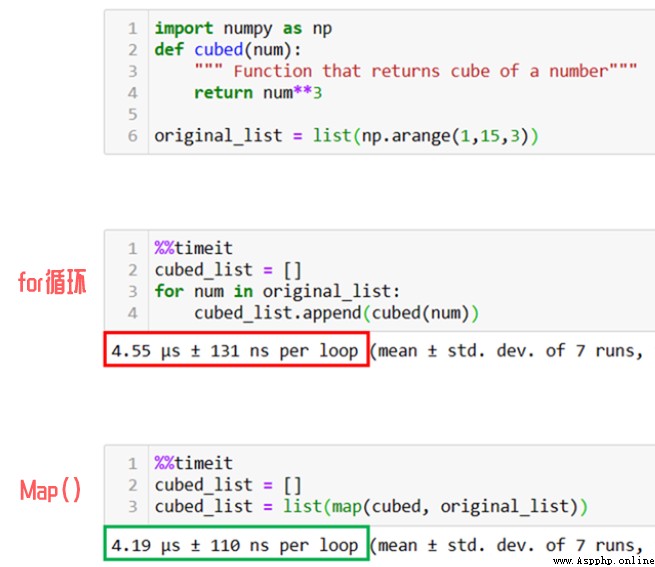
As shown in the figure above , In practical use Map The function will compare with for The method of looping through list elements in turn is fast 1.5 times .
When you need to do some calculations on a list and return results ,reduce() It's a very useful function . for instance , When you need to calculate the product of all elements of an integer list , You can use reduce Function implementation .[1]
It is associated with map The biggest difference between functions is ,reduce() Mapping function in (function) Receive two parameters , and map Receive a parameter .
reduce(function, iterable[, initializer]) Next, we use an example to demonstrate reduce() Code execution process .
from functools import reduce
def add(x, y) : # Addition of two numbers
return x + y
numbers = [1,2,3,4,5]
sum1 = reduce(add, numbers) # Calculation list and Get the results sum1 = 15, The code execution process is shown in the following square diagram .
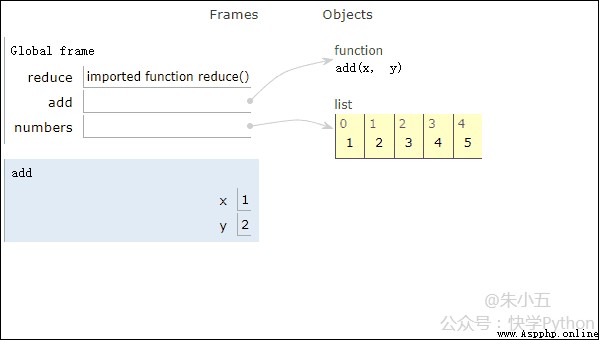
Combined with the above figure, we will see ,reduce Add an addition function add() Act on a list [1,2,3,4,5] On , The mapping function receives two parameters ,reduce() Continue to accumulate the result with the next element of the list .
Besides , We can also use it Anonymous functions lambda To match reduce function , This can be more streamlined .
from functools import reduce
numbers = [1,2,3,4,5]
sum2 = reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, numbers) Get the output sum2= 15, Consistent with previous results .
We need to pay attention to :Python3.x Start
reduce()Has been moved to functools In the module [2], If we want to use , Need to usefrom functools import reduceImport .
enumerate() Function is used to traverse a data object ( As listing 、 Tuples or strings ) Combined into an index sequence , List both data and data index , Generally used in for Cycle of . Its syntax is as follows :
enumerate(iterable, start=0)Its two parameters , One is the sequence 、 Iterators or other objects that support iteration ; The other is the starting position of the subscript , The default is from 0 Start , You can also customize the starting number of the counter .
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black']
result = enumerate(colors)If we have a store colors A list of colors , After running, you will get a enumerate( enumeration ) object . It can be directly in for Use in loop , It can also be converted to a list , The specific usage is as follows .
for count, element in result:
print(f" Iteration number :{count}, The corresponding element :{element}")
zip() Function to take iteratable objects as parameters , Package the corresponding elements in the object into tuples , Then return a list of these tuples [3].
Let's still use two lists as examples :
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black']
fruits = ['apple', 'pineapple', 'grapes', 'cherry']
for item in zip(colors,fruits):
print(item)Output results :

When we use zip() Function time , If the number of elements in each iterator is inconsistent , Returns a list of the same length as the shortest object .
prices =[100,50,120]
for item in zip(colors,fruits,prices):
print(item)
filter() Function to filter the sequence , Filter out the elements that do not meet the conditions , Returns a new list of eligible elements , The syntax is as follows [4].
filter(function, iterable) For example , We can first create a function to determine whether the data is odd , And then use filter() Function to filter out all odd numbers in the list :
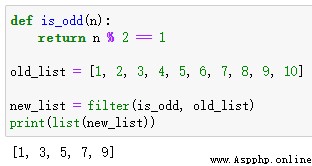
def is_odd(n):
return n % 2 == 1
old_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
new_list = filter(is_odd, old_list)
print(newlist)Output results :
Today's share of this 6 Built in functions , In the use of Python It is very convenient for data analysis or other complex automation tasks .
[1]
Books : Mechanical industry press -《Python Programming based 》
[2]Novice tutorial : https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-reduce.html
[3]Novice tutorial : https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-zip.html
[4]towardsdatascience: https://towardsdatascience.com/