String encoding :Unicode
ord() Used to convert characters to Unicode code
chr() Is used to Unicode Code to character
Eg:
>>> ord(" high ")
>>> chr("39640")39640
' high '
String definition : Both single and double quotation marks can be defined ( Three continuous orders / Double quotation marks can be used for multi line input )
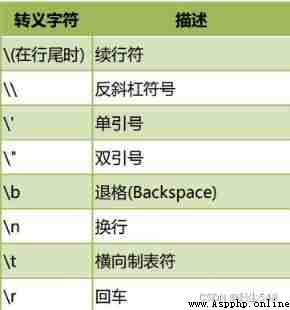
Escape character :
String splicing :
1. have access to + Concatenate multiple strings .
(1) If + Both sides are strings , Then splicing .( Efficiency join() faster )
(2) If + There are numbers on both sides , Then add .
(3) If + There are different types on both sides , Throw an exception .
String copy :
Use * You can copy strings .
Print without wrapping :end=""
print("abc",end="")
print("def")abcdef
Read the string from the console :input()
str() Realize digital transformation string :
>>> str(3.14e2)’314.0’
Use [] Extract characters :
Forward search :
The first character on the far left , The offset is 0, The second offset is 1, And so on . until len(str)-1
until .
Reverse search :
The first character on the far right , The offset is -1, The penultimate offset is -2, And so on , until -len(str)
until .
replace() Implement string substitution :
a=a.replace(" Character before change "," Changed character ")
replace Does not change the string itself
String slice slice operation :
[ Starting offset start: End offset end: step step]
When slicing , The start offset and end offset are not [0, String length -1] This range , No errors reported . start
Offset less than 0 Will be treated as 0, The end offset is greater than “ length -1” Will be treated as -1. for example :
>>> "abcdefg"[3:50]
'defg'
Tip: With a head and no tail
split() Divide and join() Merge :
a.split(" A partition ") That is, by what division
>>> a = "to be or not to be"
>>> a.split('be')
"'to ', ' or not to ', ''
a.join(" Merger ") That is to say, by what
>>> a = ['sxt','sxt100','sxt200']
>>> '*'.join(a)'sxt*sxt100*sxt200'
String resident mechanism : Legal identifiers are cached in the same location
>>> a = "abd_33"
>>> b = "abd_33"
>>> a is b
True
>>> c = "dd#"
>>> d = "dd#"
>>> c is d
False
Common search methods :
len(a) String length
a.startswith('') Starts with the specified string
a.endswith('') Ends with the specified string
a.find('') The first occurrence of the specified string position
a.rfind('') The last occurrence of the specified string
a.count("") The specified string appears several times
a.isalnum() All characters are letters or numbers
Remove the front and back information :
a.strip(" Specify the characters ") Remove the left and right specified characters
a.lstrip(" Specify the characters ") Remove the specified characters on the left
a.rstrip(" Specify the characters ") Remove the specified characters on the right
toggle case :
a.capitalize() Generate a new string , title case
a.title() Generate a new string , Every word is capitalized
a.upper() Generate a new string , All characters are capitalized
a.lower() Generate a new string , All characters are converted to lowercase
a.swapcase() Generate new , Case conversion of all letters
Other methods :
isalnum() Is it a letter or a number
isalpha() Checks whether a string is made up of only letters ( With Chinese characters ).
isdigit() Checks whether a string is made up of numbers only .
isspace() Check for white space
isupper() Is it a capital letter
islower() Lowercase or not
format() Basic usage :
>>> a = " The name is :{name}, Age is :{age}"
>>> a.format(name="giaohu",age=18)
' The name is :giaohu, Age is :18'Fill and align :
^、<、> They're centered 、 Align left 、 Right alignment , Width of back band
: Number followed by a filled character , It can only be one character , If it is not specified, it is filled with spaces by default
>>> " I am a {name}, I like numbers {num:*^8}".format(name="giaohu",num="666")
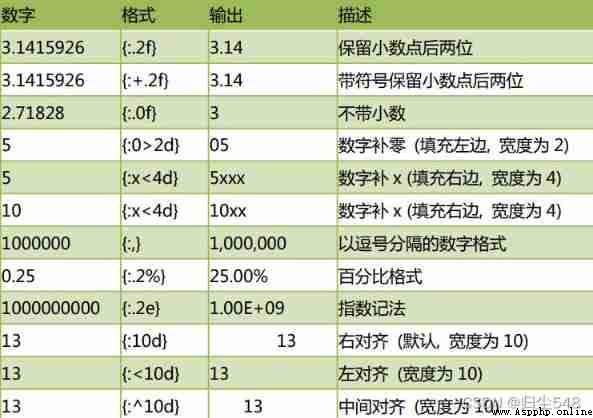
' I am a giaohu, I like numbers **666***' Number formatting :
Variable string : io.StringIO()
import io
s="Hello,world?"
sio=io.StringIO(s)
sio.seek(11)
sio.write("!")
s=sio.getvalue()
print(s)'Hello,world!'