leetCode The first 88 topic Merge two ordered arrays
Here are two buttons Non decreasing order Array of arranged integers nums1 and nums2, There are two other integers m and n , respectively nums1 and nums2 The number of elements in .
Would you please Merge nums2 To nums1 in , Make the merged array press Non decreasing order array .
Be careful : Final , The merged array should not be returned by the function , It's stored in an array nums1 in . In response to this situation ,nums1 The initial length of is m + n, The top m Elements represent the elements that should be merged , after n Elements are 0 , It should be ignored .nums2 The length of is n .
Example 1:
Input :nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output :[1,2,2,3,5,6]
explain : Need merger [1,2,3] and [2,5,6] .
The combined result is [1,2,2,3,5,6] , In which, bold italics indicates nums1 The elements in .
Example 2:
Input :nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
Output :[1]
explain : Need merger [1] and [] .
The combined result is [1] .
Example 3:
Input :nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
Output :[1]
explain : The array to be merged is [] and [1] .
The combined result is [1] .
Be careful , because m = 0 , therefore nums1 No elements in .nums1 The only remaining 0 Just to ensure that the merged results can be successfully stored in nums1 in .
Tips :
nums1.length == m + n
nums2.length == n
0 <= m, n <= 200
1 <= m + n <= 200
-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
Advanced :
You can design and implement a time complexity of O(m + n) Does the algorithm solve this problem ?
The problem is not complicated ,nums1 The total length of is m+n, front m Yes nums The elements of , after n The element is 0, Just put the back n One element changed to nums2 The elements of , Right again nums1 Just sort it out .
But I would like to share with you my problems
## Error code The first edition
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
nums1 = nums1[:m]
nums1 = nums1+nums2
nums1.sort()
print(nums1)

python Of print() The function outputs the list with a space , At first I didn't think so WA, It is presentation error
So the output format is changed
## Error code The second edition
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
nums1 = nums1[:m]+nums2
nums1.sort()
print("[",end="")
print(",".join(str(x) for x in nums1),end='')
print("]",end='')
After the change, the space is really gone , But still wrong 
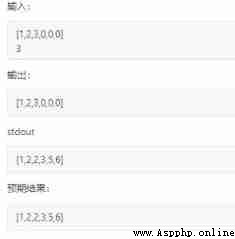
Only then did I notice that the output was [1,2,3,0,0,0], But I will nums1 The output is the correct result .
At first I thought it was nums1.sort() There is a problem , So I changed it to nums1 = sorted(nums1), And test
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
print(id(nums1))
nums1 = nums1[:m]+nums2
print(id(nums1))
nums1 = sorted(nums1)
print(id(nums1))
''' Running results 2550904029568 2550904029312 2550904029248 '''
Look at the address of the variable , Found in python in , Each time the list is nums1 = ‘’’ Assignment of ,nums1 Your address will be changed . use sorted(nums1) and nums1.sort() But it won't change nums1 The address of .
take nums1 = nums1[:m]+nums2 This kind of writing is wrong in this question . It should be m The elements after are changed directly , Instead of merging the list and assigning values to nums1.
## Correct code
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
for i in range(n):
nums1[m+i] = nums2[i]
nums1.sort()
This kind of writing is really simple , But it's not efficient . The title says that the two lists are orderly , Merge the two lists into an unordered table , Sorting later does not make good use of the condition of ordered table , So it can be optimized .
stay n1 and n2 Set up a pointer on the , Compare the size of two values , Store smaller elements in a temporary list , Then move the pointer , Continue to compare . Finally, the values of the temporary list are assigned to one by one n1.
This method only n1 and n2 I went through it , The time complexity is O(m+n)
# python3
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
k = m+n
temp = [0]*k # Temporary list
n1Index = 0 # Define two pointers
n2Index = 0
for i in range(k):
if n1Index >= m: # nums1 The element of has been fetched , Put... Directly nums2 Fill in the elements of
temp[i] = nums2[n2Index]
n2Index += 1
elif n2Index >= n: #nums2 The element of has been fetched , Put... Directly nums1 Fill in the elements of
temp[i] = nums1[n1Index]
n1Index += 1
elif nums1[n1Index] < nums2[n2Index]:
temp[i] = nums1[n1Index]
n1Index += 1
else:
temp[i] = nums2[n2Index]
n2Index += 1
nums1[:] = temp
In the above practice , Temporary lists are introduced temp, But in nums1 Some of them 0 Element takes up space , Not used .
This means that you can optimize , There is no need to introduce a temporary list temp.
In two ordered tables ,6 Than 3 Big , That means 6 It should be placed last , Then the pointer 2 Move forward ,5 Than 3 Big ,5 It should be the penultimate ,2 Than 3 Small , The penultimate should be 3,2 And 2 The same big as that , The penultimate should be 2.. This eliminates the need to introduce temporary lists .Insert picture description here ">
class Solution2:
def merge(self, nums1: [int], m: int, nums2: [int], n: int) -> None:
""" Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead. """
k = m + n
n1Index = m-1
n2Index = n-1
for i in range(k-1,-1,-1):
if n1Index < 0: #n1 I have finished taking , Fill in the remaining blank n2
nums1[i] = nums2[n2Index]
n2Index -= 1
elif n2Index < 0: # n2 I have finished taking ,n1 There is no need to change
break
elif nums1[n1Index] > nums2[n2Index]:
nums1[i] = nums1[n1Index]
n1Index -= 1
else:
nums1[i] = nums2[n2Index]
n2Index -= 1