
Pandas Yes 2 Data structures , Namely Series and DataFrame
Series Similar to a column in a table (column), Similar to one-dimensional arrays , You can save any data type
Series from Indexes (index) and Column form
Tips
Cause to explain 、 The role of location data ,Series yes Pandas The most basic data structure
grammar
import pandas as pd
pd.Series(data, index, dtype, name, copy)Parameter description
data: A set of data (ndarray type )
index: Data index label , If you don't specify , The default from the 0 Start
dtype: data type , By default, I will judge
name: Set the name
copy: Copy the data , The default is False
example
import pandas as pd
arr = [1, 2, 3]
res1 = pd.Series(arr)
# Read data according to index value
res1[1] # 2
# Specifies the index value
res2 = pd.Series(arr, index = ['x','y','z'])
# Read data according to index value
res2['y'] # 2
res1
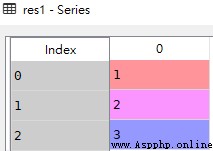
It can be seen from the figure above , If no index is specified , The index value is from 0 Start
res2
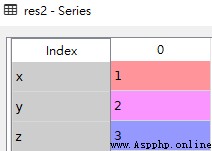
Use key/value object , Similar to a dictionary to create Series
import pandas as pd
dicts = {1: "Odin", 2: "Jack", 3: "Lee"}
res3 = pd.Series(dicts)res3
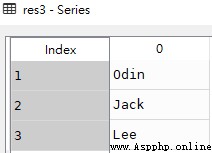
It can be seen from the figure above , Dictionary key Becomes an index value
If we only need part of the data in the dictionary , Just specify the index of the data you want
import pandas as pd
dicts = {1: "Odin", 2: "Jack", 3: "Lee"}
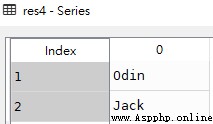
res4 = pd.Series(dicts, index = [1, 2])res4
Set up Series Name parameter
import pandas as pd
dicts = {1: "Odin", 2: "Jack", 3: "Lee"}
pd.Series(dicts, index = [1, 2], name='Hudas')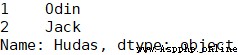
Not set Series Name parameter
import pandas as pd
dicts = {1: "Odin", 2: "Jack", 3: "Lee"}
pd.Series(dicts, index = [1, 2])
DataFrame It's a Tabular form Data structure of , It has an ordered set of columns , Each column can be of a different value type ( The number 、 character string 、 Boolean value )
DataFrame There are both row and column indexes , It can be seen as being composed of multiple Series A dictionary made up of ( Share an index )
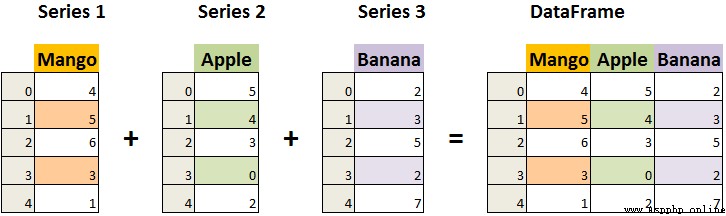
DataFrame yes Pandas Define a two-dimensional data structure
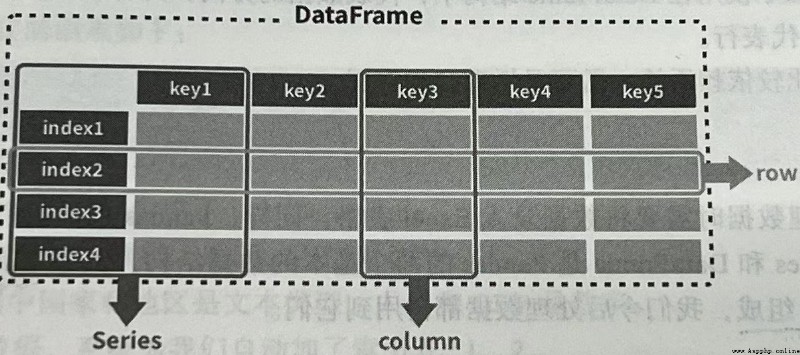
The horizontal is called That's ok (row), A piece of data is one of the rows
Vertical is called Column (column) or Field , Is a value of a piece of data
The first line is Header Or call it Field name , Be similar to Python The key in the dictionary , Represents the attributes of data
The first column is Indexes , This is the subject described by this line of data , It is also the key to this data
In some scenarios , The header is called Column index , The index is called Row index
grammar
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data, index, columns, dtype, copy)Parameter description
data: A set of data (ndarray、series, map, lists, dict Other types )
index: Index value , Or it can be called a line label
columns: Column labels , The default is RangeIndex (0, 1, 2, …, n)
dtype: data type
copy: Copy the data , The default is False
2.1 Create with list DataFrame
import pandas as pd
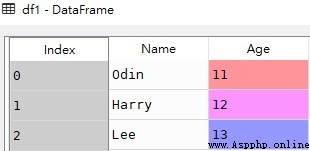
data = [['Odin',11],['Harry',12],['Lee',13]]
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'],dtype=float)df1
2.2 Use ndarrays establish DataFrame
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Hudas', 'Odin', 'Summer'], 'Age':[20, 21, 22]}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data)df2
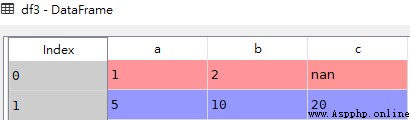
2.3 Using dictionaries key/value establish DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# Dictionary key Is the column name
data = [{'a': 1, 'b': 2},{'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}]
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data)df3
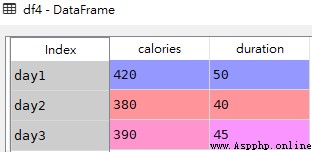
import pandas as pd
data1 = {
"calories": [420, 380, 390],
"duration": [50, 40, 45]
}
df4 = pd.DataFrame(data1, index = ["day1", "day2", "day3"])df4
