# List operation - Sort , reverse ( The interview may ask )
# From small to large , Sort from large to small - Ascending , Descending operation
numb_list = [11, 19, 78, 456, 230, 56, 41, 350]
# sort() The function is used to sort in ascending order
numb_list.sort() # Ascending , From small to large
print(numb_list) # Changes have been made to the list itself
# sort(reverse=True) In descending order
numb_list.sort(reverse=True) # Descending , From small to large
print(numb_list)
# Inversion of the list
# Format : list .reverse()
print(numb_list[::-1]) # How slices are read
numb_list.reverse() # Modify the original list
print(numb_list)
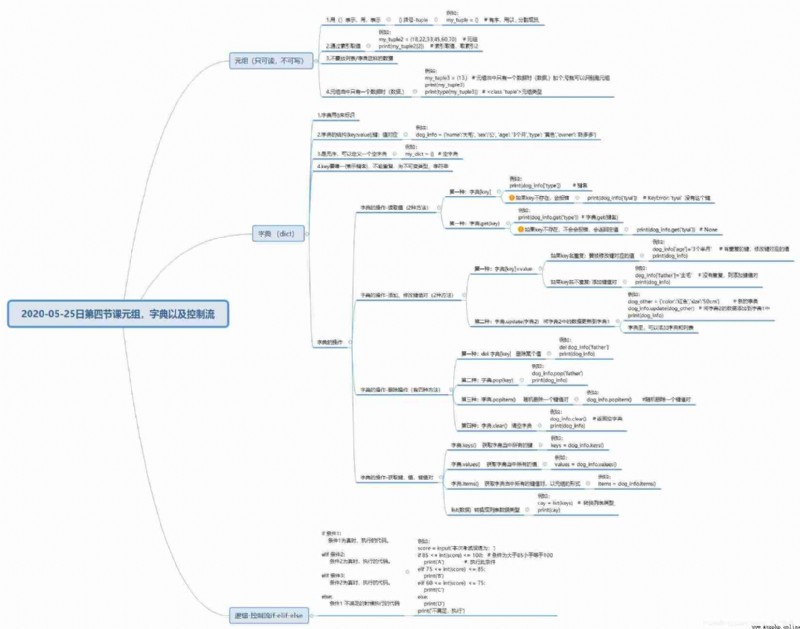
# Tuples - Read only , Don't write
# 1. use () Express , use , Express
# 2. Take value through index
# 3. Don't put a list / Data like dictionaries
# 4. When there is only one data in a tuple ( data ,)
# () Brackets -tuple
# my_tuple = () # Orderly , With , Split members ,
my_tuple2 = (18, 22, 33, 45, 60, 70) # Tuples
print(my_tuple2[2]) # Index value , Index 2
#
my_tuple3 = (13,) # When there is only one data in a tuple ( data ,) Add one , No
print(my_tuple3)
print(type(my_tuple3)) # <class 'tuple'> A tuple type
# Dictionaries dict
# 1. Dictionary use {} To mark
# 2. Structure of dictionary {key:value}, key : Value correspondence
# 3. It's disorder
# 4.key Only one , Can't repeat , Is immutable type , character string
dog_info = {
'name': ' Big wool ',
'sex': ' Male ',
'age': '3 Months ',
'type': ' yellow ',
'owner': ' Chen Duoduo '
}
my_dict = {} # You can define an empty dictionary
print(dog_info)
# Dictionary operation - Read the values (2 Methods )
# The first one is : Dictionaries [ Key name ] If key non-existent , Will report a mistake
print(dog_info['type']) # Key name
# print(dog_info['tyui']) # KeyError: 'tyui' Without this key
# The first one is : Dictionaries .get( Key name ) If key non-existent , No mistake.
print(dog_info.get('type')) # Dictionaries .get( Key name )
print(dog_info.get('tyui')) # None
# Dictionary operation - add to 、 Modify key value pair (2 Methods )
# The first one is : Dictionaries [key]=value If key There is , Then modify the value . If key non-existent , Then add key-value
# key The first name is repeated : Replace the value corresponding to the modification key
dog_info['age'] = '3 Months and a half ' # There are duplicate keys , Modify the value of the key
print(dog_info)
# key Name does not repeat : Add key value pair
dog_info['father'] = ' Golden hair ' # No repetition , Then add a key value pair
print(dog_info)
# The second kind : Dictionaries .update( Dictionaries 2) Dictionary 2 Update the data in to the dictionary 1
dog_other = {'color': ' Red ', 'size': '50cm'} # New dictionary
# dog_info.update(dog_other) # Dictionary 2 Add data to the dictionary 1 in
# print(dog_info)
# In the dictionary , Can members be dictionaries , Can I make a list ?
dog_info['other_info'] = dog_other # Add a dictionary and add a dictionary to it
print(dog_info)
# Dictionary operation - Delete operation ( Yes 3 Methods )
# 1.del Dictionaries [key] Delete a value
# del dog_info['father']
# print(dog_info)
# 2. Dictionaries .pop(key)
dog_info.pop('father')
print(dog_info)
# 3. Dictionaries .clear() Empty dictionary
# dog_info.clear() # Return to empty dictionary
# print(dog_info)
# Dictionary operation - Get key , value , Key value pair
# 1. Dictionaries .keys() Get all the keys in the dictionary
keys = dog_info.keys()
# list() Convert to list data type
cay = list(keys) # Convert list types
print(cay)
# 2. Dictionaries .values() Get all the values in the dictionary
values = dog_info.values()
# list() Convert to list data type
cay = list(values) # Convert list types
print(cay)
# 3. Dictionaries .items() Get all the key value pairs in the dictionary , In the form of a tuple
items = dog_info.items()
# list() Convert to list data type
cay = list(items) # Convert list types
print(cay)
# aggregate - List to heavy ( understand )
# 1. It's the same as the list , take [] Switch to {}
# 2. List to heavy :s = set( list )
list_aa = ['aaa', 11, 12, 11, 12, 'hehhe']
# set duplicate removal
set_aa = set(list_aa)
# Transfer out list
print(list(set_aa))
# Logic - control flow
score = input(' The result of this examination is :')
# Judge If 100 branch , A meimoda
'''
if Conditions 1:
Conditions 1 To true , Executed code .
else:
Conditions 1 Code executed when not satisfied
if Conditions 1:
Conditions 1 To true , Executed code .
elif Conditions 2:
Conditions 2 To true , Executed code .
elif Conditions 3:
Conditions 2 To true , Executed code .
else:
Conditions 1 Code executed when not satisfied
'''
# if int(score) == 100:
# print(' Here's a tip for you ')
# print(' Well done ')
# if int(score) > 60:
# print(' You passed !')
# else:
# print(' Knock the code all night ')
# print(' dissatisfaction , perform ')
# ********************************************************
if 85 <= int(score) <= 100: # The condition is greater than 85 Less than or equal to 100
print('A') # Execute this condition
elif 75 <= int(score) <= 85:
print('B')
elif 60 <= int(score) <= 75:
print('C')
else:
print('D')
print(' dissatisfaction , perform ')
# Homework after class
# 1、 Reverse the word position in the string ,“hello xiao mi” Convert to “mi xiao hello”
# ( Tips : Split by string , Splicing , List reverse order and other knowledge points )
str = "hello xiao mi"
list1 = str.split(' ') # String entry segmentation
print(list1)
list1.reverse() # The list is in reverse order
print(list1)
aa = ' '.join(list1) # String splicing
print(aa)
# 2、 Adding, deleting, looking up and modifying dictionaries : A game needs to get your personal information , Writing a piece of code requires the following :
# 1、 When running, remind to input full name 、 Gender 、 Age , Input finished , Please store the data in a dictionary ,
my_dict1 = {} # Define an empty dictionary
my_dict1['name'] = input(' Please enter your name :') # Enter a name
my_dict1['gender'] = input(' Please enter your gender :') # Enter gender
my_dict1['age'] = input(' Please enter your age :') # Enter the age
print(my_dict1) # Print Dictionary
# 2、 The data is stored up , Then output personal introduction , The format is as follows : My name XXX, This year, XXX year , Gender XX, Like typing code
name = my_dict1['name'] # Take the value stored in the dictionary
gender = my_dict1['gender'] # Take the value stored in the dictionary
age = my_dict1['age'] # Take the value stored in the dictionary
print(' My name is {}, I this year {} year , Gender is {}, Like typing code '.format(name, age, gender)) # Use format function
# 3、 Someone is interested in you , The platform needs you to supplement your height and contact information ;
my_dict1['hignt'] = input(' Please enter your height :') # Add height to the dictionary
my_dict1['phone'] = input(' Please enter your contact information :') # Add contact information to the dictionary
print(my_dict1) # Print a new dictionary
# 4、 Platform to protect your privacy , Need you to delete your contact information ;
del my_dict1['phone'] # The first is to delete the contact information
# my_dict1.pop('phone') # The second way is to delete the contact information
print(my_dict1)
# 5、 In order to get better grades , You have added a skill you are good at .
my_dict1['sto_pig'] = ' Climbing the mountain '
print(my_dict1)
# 3、 Underline the list li=[“python”,“java”,“php”] The elements of are spliced into a string , Then convert all the letters to uppercase ,
li = ['python', 'java', 'php']
string = '_'.join(li) # Strings are spliced together
res = string.upper() # All capitals
print(res)
# 4、 Use slicing to 'http://www.python.org' Medium python Take out the string
pain_info = 'http://www.python.org'
print(pain_info[11:17]) # Subscript index value
# 5、 Here are some data ,
# t1 = ("aa",11) t2= (''bb'',22) li1 = [("cc",11)]
# Please pass the learned knowledge points , Perform relevant operations and change to the following dictionary : {"aa":11,"cc":11,"bb":22}
t1 = ('aa', 11) # A tuple type
t2 = ('bb', 22) # A tuple type
li1 = [('cc', 11)] # List the type
list2 = [t1, t2] + li1
guy = dict(list2) # Turn it into a dictionary
print(guy) # Print out the dictionary