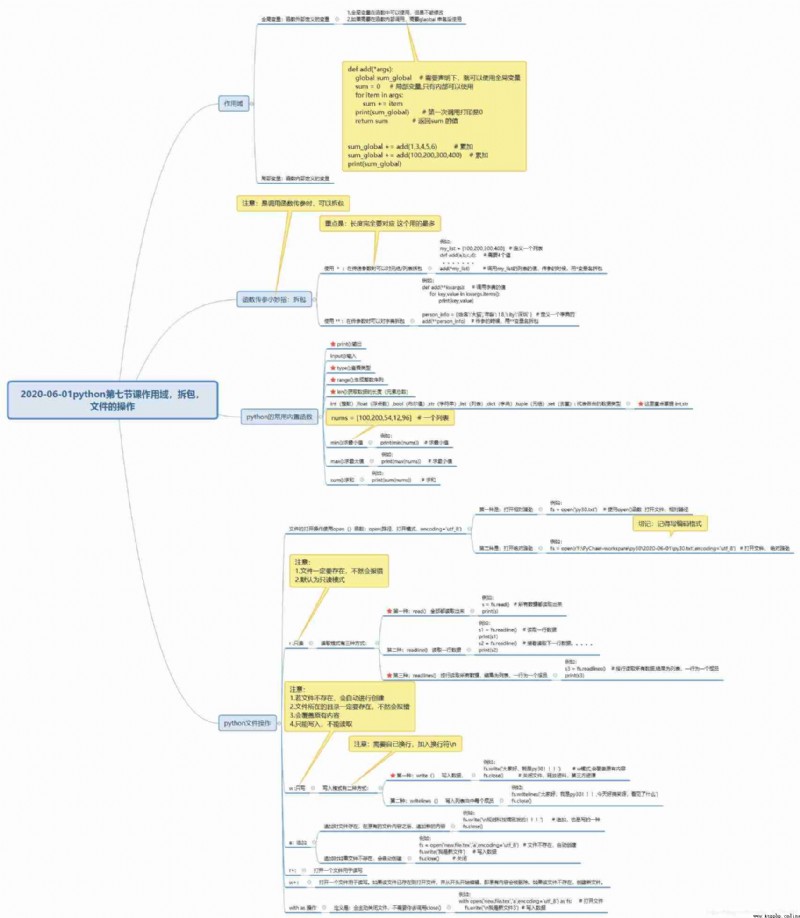
"""
When calling a function to pass parameters , Detachable bags
1、*: When passing parameters, you can set the / List unpacking
2、**: You can unpack the dictionary when passing parameters
example :
data=[1,2,3] Call function :func(*data) => func(1,2,3)
data={"aa"=11} Call function :func(**data) => func(aa=11)
"""
# 1、*: When passing parameters, you can set the / List unpacking
# num_list = [1,2,3]
# def add(*args):
# for item in args:
# print(item)
#
# add(*num_list) # Remove the list
# my_list = [1,2,3,4]
# def add (a,b,c,d): # Add the numbers in the list after unpacking
# sum = a+b+c+d # The calculation and
# print(sum)
#
# add(*my_list)
# 2、**: You can unpack the dictionary when passing parameters
# num_dict = {"name":"XX","age":20,"city":" Shenzhen "}
# def add_dict(**kwargs): # Pass on dictionary values
# for key,value in kwargs.items():
# print(key,value)
#
# add_dict(**num_dict) # call
print("*********** Built in functions ****************")
# id() # View data address
# a = " Shenzhen "
# print(id(a))
# print(): Output
# input(): Input
# type(): View type
# range(): Generating a sequence of integers
# len(): Get the length of the data ( The total number of elements )
# int,float,bool,str,list,dict,tuple,set: Represents the data type for
# Here we focus on int,str
# nums = [100,200,300,400]
# print(min(nums)) # For the minimum
# print(max(nums)) # For maximum
# print(sum(nums)) # Sum up
print("************ File operations *************")
"""
The file is read-only :r
1、 The file must exist , Otherwise, it will report a mistake
2、 The default is read-only mode
3、 Coding format :encoding='utf-8'
There are three ways to read mode :
a:read() All read out , Display as usual
b:readline() The first item reads the first line , The second item reads the second line
c:readlines() Read all lines , The result is in the form of a list
"""
# fs = open(r'C:\down\day10\1- Extended learning \py30.txt',encoding='utf-8') # The absolute path to the open file
# s = fs.read() # All the data is read out
# print(s)
#
# s1 = fs.readline() # Read a row of data
# print(s1)
# s2 = fs.readline() # Then read the next row of data .....
# print(s2)
# s3 = fs.readlines() # Read all data by line , The result is a list
# print(s3)
"""
File write only :w
1、 file does not exist , Automatically created
2、 The directory where the file is located must exist , Otherwise, it will report a mistake
3、 It will cover the original content
4、 Write only , Cannot read
5、 Be sure to close the release after writing
There are two ways to write . Be careful : I need to change my career , Add line breaks \n
a、write()
b、writelines()
"""
fs = open(r'C:\down\day10\1- Extended learning \py31.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') # Absolute path
# # fs.write(" Hello everyone !A") # Method 1 ,w The schema will overwrite the original content
fs.writelines(" Hello, everyone ! My name is XX, From Wuhan ") # Method 2 , Set each member in the list , It will cover the original content
# fs.close()
""""
files were added :a
After the original file contents , Add new content
Write 、 Append if the file does not exist , Automatically created
If the original directory of the file is incorrect , Will report a mistake
"""
# fs = open(r'C:\down\day10\1- Extended learning \py31.txt','a',encoding='utf-8') # Absolute path , You can also use relative paths
# fs.write("\n I use a What the pattern adds ") # Addition is also a kind of fixed input
# fs.close()
"""
Can read but write
r+ Readable and appendable
w+ Clear contents first
with as operation , Will shut down , Unwanted close()
"""
# with open(r'C:\down\day10\1- Extended learning \py31.txt','a',encoding='utf-8') as fs:
# fs.write("\n use with Added content , Automatically shut down ")