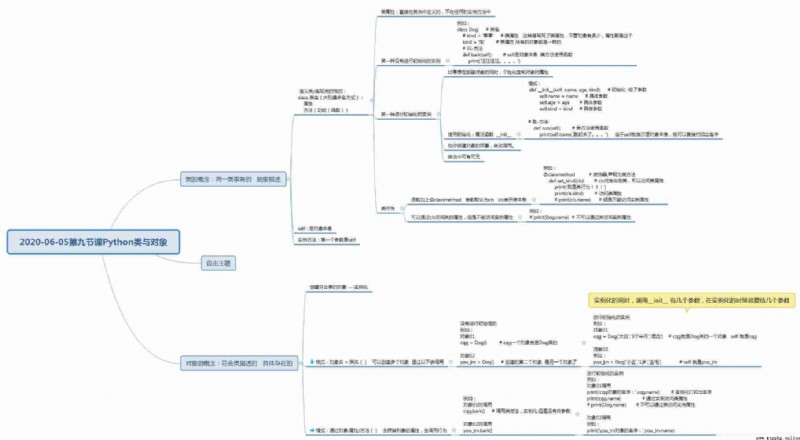
'''
Classes and objects
I understand. , But it's a little hard to use
Concepts of classes and objects
class : Of the same kind of transaction Abstract description
object : Conforming to class description Concrete existence
Functional encapsulation function -
Why should we encapsulate it into a function class ? --- whole : Properties and functions ( Behavior )
First of all Defining classes / Implementation class
Generating objects
'''
class Class name ( Hump ):
attribute
Method ( function ( function ))
self : It's the object itself
Example method : The first parameter is self
If you want to create objects at the same time , Customize the properties of the object
initialization : Magical function __init__
When you create objects for colleagues , Automatically call .
Class is optional
Class properties : Defined directly in the class , Not in any instance method
Class behavior : Function plus @classmethod The parameter defaults to cls cls Represents the class itself
Can pass cls Access the properties of a class , But you cannot access instance properties
# Instance properties are preferred
Instance attributes :self. Property name
Example method : The first parameter is self
Instances can access class properties , Class method
'''
# The second instance is initialized
# Defining classes
class Dog: # Class name
# kind = None
# kind = ' String ' # Class properties In this way, class attributes are written to death , No matter how many objects , The attributes are all this
kind = ' Dog ' # Class properties All objects are the same
# name , Varieties , Age
def __init__(self, name, age, kind): # initialization Given the parameters
self.name = name # Specific parameters
self.age = age # Specific parameters
self.kind = kind # Specific parameters
@classmethod # Decorator , Declared as a class method
def set_kind(cls): # cls Represents the current class , You can access class properties
print(' I'm a kind of behavior !!!')
print(cls.kind) # Access class properties
# print(cls.name) # But you cannot access instance properties
# It's called - Method
def bark(self): # self It's the object itself Class methods use functions
print(' Wang Wang Wang Wang ....')
print(self.name)
# eat - Method
def eat(self): # Class methods use functions
print(' Dog food ...')
# run - Method
def run(self): # Class methods use functions
print(self.name,' Run up ...') #
# sleep - Method
def sleep(self): # Class methods use functions
print(' To go to sleep! ')
# At the same time of instantiation , call __init__ There are several parameters , When instantiating, you need to give several parameters
cqg = Dog(' String ','3 Months and a half ',' The half-blood ') # cqg Namely Dog An object of class self Namely cqg
print('cqg The name of the object :',cqg.name) # Instantiate and print out the name
cqg.run() # Direct call method
print(cqg.name) # Accessing class properties through instances
# print(Dog.name) # Instance properties cannot be accessed through classes
cqg.set_kind() # Instance calls class methods
Dog.set_kind() # Class calls class methods
print('**************************************************')
you_jm = Dog(' Small gold ','1 year ',' Golden hair ') # self Namely you_jm
print('you_jm The name of the object :',you_jm.name)
you_jm.run() # Direct call method
Homework after class
# 4、 Define a login test case class Case
# attribute : Use case name
# Use case step
# Expected results
# The actual result
# Method : Run case 、 Use case results ( Compare whether the expected result is equal to the actual result )
# Instantiation 2 Test cases , And run the use case , Present use case results
print('************************************* Fourth question **********************************************************')
class Case: # Define a class
use_account = 'woshijinyao300' # Define a class property - Account name
use_password = '12345678' # Define a class property - password
def __init__(self,case_name,account_name,password,expected): # Initialize instance properties
self.case_name = case_name # Specific instance properties - Use case name
self.account_name = account_name # Specific instance properties - Account name
self.password = password # Specific instance properties - password
self.expected = expected # Specific instance properties - Expected results
self.actual = None # Specific instance properties - The actual result is unknown , Empty first
# Method 1: Run case
def case(self): # Example method
print(' Run test cases :{}\n user name :{}, password :{}, The expected result is :{}'.
format(self.case_name,self.account_name,self.password,self.expected))
if self.use_account == self.account_name and self.use_password == self.password:
self.actual = ' Login successful !'
print(' The actual result is :',self.actual)
else:
self.actual = ' Login failed !'
print(' The actual result is :', self.actual)
# Method 2: Use case results ( Compare whether the expected result is equal to the actual result )
def Compare(self): # Example method
if self.actual == self.expected: # If the actual result be equal to Expected results
print(' Use case pass ') # Then the use case passes
else: # conversely If the actual result It's not equal to Expected results
print(' Use case failure ') # The use case fails
# Instantiation 2 Test cases , And run the use case , Present use case results
print('******************************************** The first use case *****************************************************')
test01 = Case(' Normal login ','woshijinyao300','12345678',' Login successful !') # Login with the correct account password
test01.case() # Object name (test01) Invoking an instance method (case), Give execution
test01.Compare() # Object name (test01) Invoking an instance method (Compare), Give execution
print('******************************************** The second use case *****************************************************')
test02 = Case(' Wrong password login ','woshijinyao300','123458',' Login failed !') # Wrong password login
test02.case() # Object name (test02) Invoking an instance method (case), Give execution
test02.Compare() # Object name (test02) Invoking an instance method (Compare), Give execution
# 5、 Encapsulate a student class Student,( Determine whether it is defined as a class attribute or an instance attribute , Methods are defined as instance methods )
# - attribute : identity ( Student ), full name , Age , Gender , English scores , Math scores , Chinese achievement ,
# - Method 1 : Calculate the total score , Method 2 : Calculate the average score of the three subjects , Method 3 : Print student's personal information : My name is XXX, Age :xxx, Gender :xxx.
# Instantiation 1 A student , And print students' personal information , Calculate the total score .
print('************************************* Fifth question **********************************************************')
print('************************************ The first method ********************************************************')
class Student: # Define a student class name
def __init__(self,student,name,age,gender,English_results,math_results,chinese_results): # Initialize parameters 7 Instance properties
self.student = student # Specific parameter name
self.name = name # Specific parameter name
self.age = age # Specific parameter name
self.gender = gender # Specific parameter name
self.English_results = English_results # Specific parameter name
self.math_results = math_results # Specific parameter name
self.chinese_results = chinese_results # Specific parameter name
# Calculate the total score - Method 1
def sum_score(self): # Class methods use functions
return self.English_results + self.math_results + self.chinese_results # return 3 The total value of academic achievements
# Calculate the average score of the three subjects - Method 2
def average_score(self): # Class methods use functions
return (self.English_results + self.math_results + self.chinese_results) / 3 # return 3 The average grade of a subject
# Print student's personal information : My name is XXX, Age :xxx, Gender :xxx - Method 3
def personal_info(self): # Class methods use functions
print(' My identity is :{}, My name is :{}, Age :{}, Gender is :{}, The English score is :{}, What's the math score :{}, The grade of Chinese is :{}, The total score is :{}, The average is :{:.2f}'.
format(self.student,self.name,self.age,self.gender,self.English_results,self.math_results,
self.chinese_results,member.sum_score(),member.average_score())) # Print personal information , Using functions
# instantiate , call __init__ Yes 7 Parameters , At the time of instantiation 7 Parameters
member = Student(' Student ',' Little ',20,' male ',97,57,60) # member Namely Studer An object of class self Namely member
member.personal_info() # Call object (member) To access class properties (personal_info)
print('************************************ The second method ********************************************************')
class Student: # Define a class
student = ' Student ' # Define a class property - Student
def __init__(self,name,age,gender,English_results,math_results,chiese_results): # Initialize instance properties
self.name = name # Define instance properties - full name
self.age = age # Define instance properties - Age
self.gender = gender # Define instance properties - Gender
self.English_results = English_results # Define instance properties - English scores
self.math_results = math_results # Define instance properties - Math scores
self.chiese_results = chiese_results # Define instance properties - Chinese achievement
# Method 1 : Calculate the total score -- Example method
def sum_score(self):
total_score = self.English_results + self.math_results + self.chiese_results
print(' My total score is :{}'.format(total_score))
# Method 2 : Calculate the average score of the three subjects -- Example method
def average_score(self):
ave = (self.English_results + self.math_results + self.chiese_results) / 3
print(' My average score of three subjects is :{}'.format(ave))
# Method 3 : Print student's personal information : My name is XXX, Age :xxx, Gender :xxx-- Example method
def personal_info(self):
print(' My personal information : My name is :{}, Age is :{}, Gender is :{}'.format(self.name,self.age,self.gender))
# Instantiation 1 A student , And print students' personal information , Calculate the total score .
# instantiate , call __init__ Yes 6 Instance properties , At the time of instantiation 6 Attributes
member = Student(' Little ','25',' male ',90,85,86)
member.personal_info() # Object name (member) Invoking an instance method (personal_info), Give execution
member.sum_score() # Object name (member) Invoking an instance method (sum_score), Give execution
member.average_score() # Object name (member) Invoking an instance method (average_score), Give execution
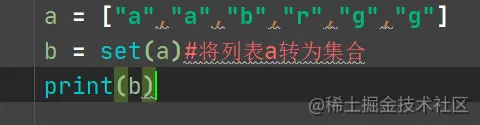 Enumerate usage and zip usage in Python: parallel traversal, collection usage and characteristics
Enumerate usage and zip usage in Python: parallel traversal, collection usage and characteristics
p{margin:10px 0}.markdown-body
 python報錯xml.etree.ElementTree.ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token): line 3, column 50
python報錯xml.etree.ElementTree.ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token): line 3, column 50
一、錯誤描述錯誤很簡單,就是xml裡面有非法字符(有的說是編
 Python crawler series of get things web page version details page sign signature algorithm
Python crawler series of get things web page version details page sign signature algorithm
Python Crawler series of the c