import time
time.time() What you can get is Time stamp . namely 1970 year 1 month 1 Japan 0 when 0 branch 0 The offset from seconds to the present time s
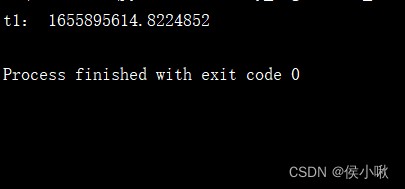
t1 = time.time()
print('t1:', t1)
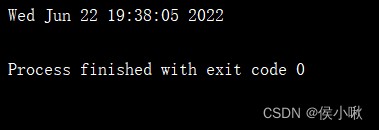
Convert timestamps to A fixed format String , have access to time.ctime() Method .( But not very often )
t = time.ctime(time.time())
print(t)
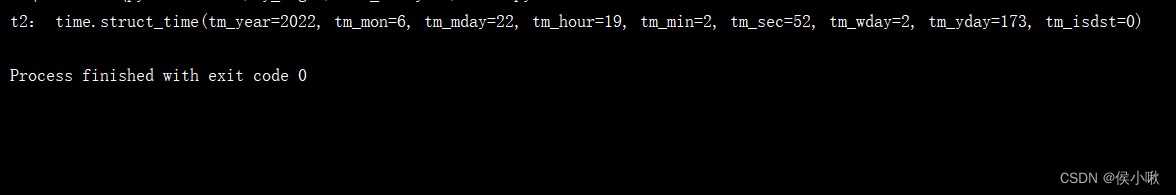
It is easier for us to use structured time
Local time is related to time zone .
t2 = time.localtime(time.time())
print("t2:", t2)
Greenwich mean time (0 The time zone ) Later than Beijing time 8 Hour only ( Global benchmarks , Using this time can eliminate the impact of writing code in different places )
t3 = time.gmtime(time.time())
print("t3:", t3)

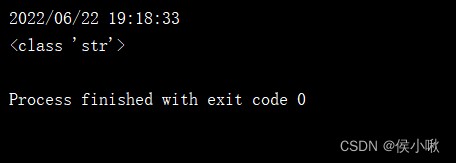
String form is generally accepted by human beings
t4 = time.strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S", t2)
print(t4)
print(type(t4))
Reverse operation of the above operation
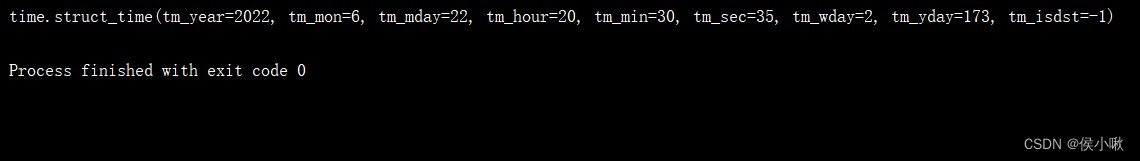
t5 = time.strptime('2022/06/22 20:30:35', "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")
print(t5)
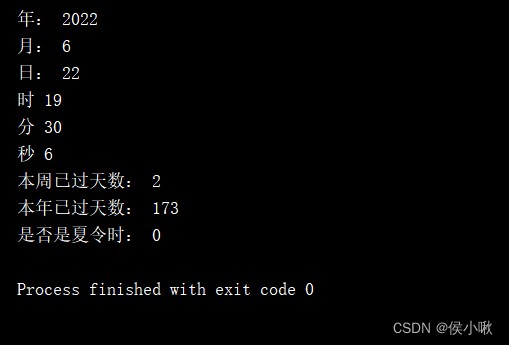
print(" year :", t2.tm_year)
print(" month :", t2.tm_mon)
print(" Japan :", t2.tm_mday)
print(" when ", t2.tm_hour)
print(" branch ", t2.tm_min)
print(" second ", t2.tm_sec)
print(" Days of the week have passed :", t2.tm_wday)
print(" This year has passed :", t2.tm_yday)
print(" Is it daylight saving time ", t2.tm_isdst)
t7 = time.mktime(t2)
print(t7)
