Mysql Study ---Python operation Mysql 1231
install PyMysql:Py3 Default by oneself pip3 install ,Py2 The default is no pip command
cmd Get into PyCharm To complete the installation pip3 install pymysql
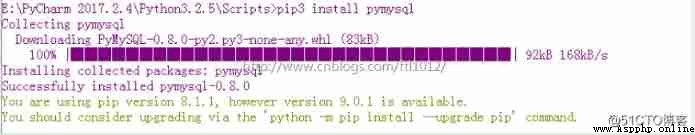
Where the installation is complete :E:\PyCharm 2017.2.4\Python3.2.5\Lib\site-packages

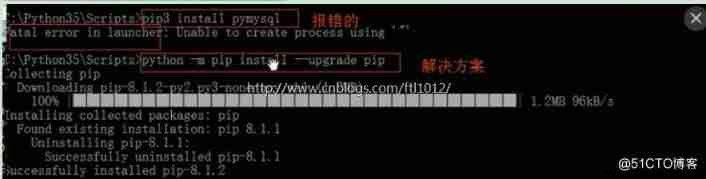
Fault handling : Update the default Python install
PyMySQL - Dedicated to the operation of MySQLpython modular , Py2 and Py3 Compatible with
- MySQLdb(py3 Temporarily not supported MySQLdb)
Basic operation : Add information ——Insert
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor() # Default is tuple , Can be changed to dictionary type
# The first one is : Directly inserted into the
# perform SQL, And return the number of affected rows
insert_effect_row = cursor.execute("insert into course(cname, teacher_id) VALUES ('hhhh43hhkkhh', '2')")
inp = input(' Please enter a name :')
inp2 = input(' Please enter the teacher ID:')
# The second kind : String splicing
# sql = 'insert into course(cname) VALUES ("%s")' %inp
# cursor.execute(sql) # String splicing can be used , But it's easy to cause sql Injection is not recommended
# The third kind of : Parameter passing , utilize %s Make a placeholder , Pass in parameters ,PyMysql Internal help us transform
insert_effect_row_sec = cursor.execute("insert into course(cname, teacher_id) VALUES (%s, %s)", (inp, inp2)) # Parameter passing
# A fourth : Insertion of multiple messages
li = [
(' WOW! 1', 1),
(' WOW! 2', 2),
(' WOW! 3', 3),
]
executmany = cursor.executemany("insert into course(cname, teacher_id) VALUES (%s, %s)", li) # Pass in an iteratable type
print('executmany:', executmany) # executmany: 3 , Modification successful 3 strip
# Submit , Otherwise, new or modified data cannot be saved
conn.commit()
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()

Basic operation : find information ——Select
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor()
ret = cursor.execute('select * from student') # Only data is loaded into memory , need fetch Value
print(ret) # Number of results found
# The first one is : Print directly , When there is a large amount of data, it is easy to run out of memory ( There is a pointer index inside )
# r = cursor.fetchall()
# print(' Take out all the values \n', r) # Print the results , The result is a tuple
# The second kind : Take it out of memory 1 Data , At this point, the data has been loaded into memory
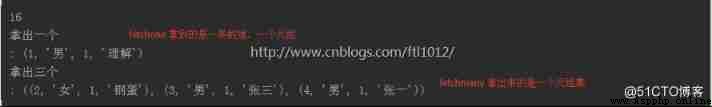
r1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(' Take out one \n:', r1)
# The third kind of : Take it out of memory 3 Data , At this point, the data has been loaded into memory
r3 = cursor.fetchmany(3)
print(' Take out three \n:', r3)
# A fourth : Operation pointer fetches data
# cursor.scroll(0, mode='relative') # The relative position , Pointer index regression 0, +1/-1 It means up / Down
# r4 = cursor.fetchmany(3)
# print(' The relative index takes out three \n:', r4) # From 5 Starting value : ((5, ' Woman ', 1, ' Zhang Er '), (6, ' male ', 1, ' Zhang Si '), (7, ' Woman ', 2, ' Hammer '))
cursor.scroll(0, mode='absolute') # Absolute position , Pointer index regression 0
r5 = cursor.fetchmany(3)
print(' The absolute index takes out three \n:', r5) # From 0 The first position starts to take values : ((1, ' male ', 1, ' understand '), (2, ' Woman ', 1, ' Steel egg '), (3, ' male ', 1, ' Zhang San '))
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()
Basic operation : Change information ——Update
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor()
inp = input(' Please enter the updated information :')
ret = cursor.execute("update course set cname = %s where cname = ' WOW! 4'", inp)
ret2 = cursor.execute("update course set cname = %s where cname = ' WOW! 1'", inp)
# Submit , Otherwise, new or modified data cannot be saved
conn.commit()
print(' Does not exist and updates the result :', ret, '\r\n Exists and updates the result :', ret2)
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()

Basic operation : Delete the information ——Delete
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor()
inp = input(' Please enter the updated information :')
ret = cursor.execute("update course set cname = %s where cname = ' WOW! 4'", inp)
ret2 = cursor.execute("update course set cname = %s where cname = ' WOW! 1'", inp)
# Submit , Otherwise, new or modified data cannot be saved
conn.commit()
print(' Does not exist and updates the result :', ret, '\r\n Exists and updates the result :', ret2)
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()

Other operating : Change the return value of the cursor to dictionary
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute('select cid as id , cname as name from course') # You can change the... Of the principle dictionary key[cname] by name
print(cursor.fetchall()) # You can take values according to the dictionary
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()

Other operating : Gain self increase ID
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.executemany("insert into course(cname, teacher_id)values(%s,%s)", [(" Pepsi Cola ", 1), (" Coca Cola ", 2)])
conn.commit()
# Get the latest self increment ID
new_id = cursor.lastrowid
print(new_id)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
prevent SQL Method of injection :
1. stored procedure
2. Place holder stitching Remember to use string concatenation
SQL Inject : Changed the original sql sentence , Splicing is not recommended , Recommended parameter transfer
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql
# Create connection
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='test_python', charset='utf8')
# Create cursors
cursor = conn.cursor()
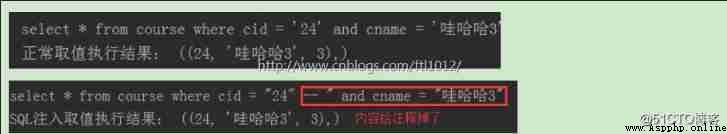
sql = 'select * from course where cid = "%s" and cname = "%s"'
# sql = sql % ('24', ' WOW! 3') # normal
sql = sql % ('24"-- ', ' WOW! 3') # SQL Injection value , Comment out the following content
# sql = sql % ('24" or 1=1 -- ', ' WOW! 3') # SQL Injection value , The latter condition is always true , All results can be queried
print(sql)
ret = cursor.execute(sql);
r = cursor.fetchall()
print(' Execution results :', r)
# Close cursor
cursor.close()
# Close the connection
conn.close()
author : Small a ninety-seven
-------------------------------------------
Individuality signature : Everything is good in the end , If it's not good , That means things haven't come to the end yet ~
The copyright of this article belongs to the author 【 Small a ninety-seven 】, Welcome to reprint , However, this statement must be retained without the consent of the author , And in the article page obvious position gives the original link , Otherwise, the right to pursue legal responsibility is reserved !