This article mainly explains “ How do you use it? Python operation Redis database ”, Interested friends might as well come and have a look . The method introduced in this paper is simple and fast , Practical . Now let Xiaobian take you to learn “ How do you use it? Python operation Redis database ” Well !
Redis Is an open source, memory based and persistent Key-Value database , use ANSI C Language writing . It has a rich data structure , Have transaction function , Ensure the atomicity of the command . Because it's an in memory database , Reading and writing is very fast , Can be up to 10w/s Evaluation rate of , Therefore, it is generally applied to data that changes rapidly 、 Real time communication 、 Cache, etc . But memory database usually needs to consider the memory size of the machine .
Redis Yes 16 A logical database (db0-db15), Each logical database project is isolated , By default db0 database . If you choose the second 2 A database , Through the command select 2 ,python You can specify the database when connecting to .
String- character string
List- list
Hash- Hash
Set- aggregate
ZSet- Ordered set
Bitmap- Bitmap
python We use redis-py Library to operate Redis database , The following will focus on .
Premise : To be installed Redis database , If there is no installation point here
pip3 install redis
The first way : Ordinary
import redis redis_conn = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1', port= 6379, password= 'your pw', db= 0)
The second way : Connection pool
import redis redis_pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port= 6379, password= 'your pw', db= 0)redis_conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool= redis_pool)
redis The return value types of Chinese characters are bytes (bytes) type
stay redis in , A key corresponds to a value
1.String set Set a single key value
set(name, value, ex=None, px=None, nx=False, xx=False)
ex: Expiration time ( second ), When it's time redis It will be deleted automatically
px: Expiration time ( millisecond ), When it's time redis It will be deleted automatically .ex、px One out of two
nx: If set to True, only name When there is no , At present set Operation before execution
xx: If set to True, only name In existence , At present set Operation before execution
redis_conn.set('name_2', 'Zarten_2')2.String get Get a single value
v = redis_conn.get('name_1')print(v)3.String mset Set multiple key values
mset(*args, **kwargs)
redis_conn.mset(name_1= 'Zarten_1', name_2= 'Zarten_2')
perhaps
name_dict = { 'name_4' : 'Zarten_4', 'name_5' : 'Zarten_5'}redis_conn.mset(name_dict)4.String mget Get multiple values
mget(keys, *args)
m = redis_conn.mget('name_1', 'name_2')#m = redis_conn.mget(['name_1', 'name_2']) It's OK print(m)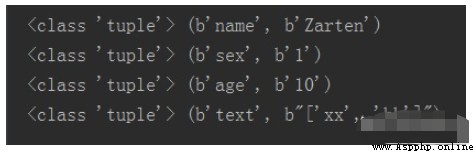
5.String getset Set new values for existing keys , And return the original value
getset(name, value)
When the given key does not exist , Will set its new value , But the return value is None
v = redis_conn.getset('name_1', 'hi')6.String setrange Modify a key according to the index value value
setrange(name, offset, value)
The return value is : Modified string length
name: key , Automatically add when the given does not exist
offset: Offset , With 0 Start
value: Modified character or string , String with offset Go backwards
length = redis_conn.setrange('name_2', 1, 'zhihu')print(length)
7.String getrange Get the part of a key according to the index value value
If the given key does not exist , Returns a null value b''
getrange(key, start, end)
v = redis_conn.getrange('name_4', 0, 2)The result is :
8.String strlen obtain value The length of
strlen(name)
When the given key does not exist , The return value is 0
length = redis_conn.strlen('name_2')9.String incr int Type of value Self increasing ( Self reduction )
Empathy : Self reduction ,decr(name, amount=1)
The value corresponding to the given key must be an integer or string value , Otherwise, it will report a mistake . The default auto increment is 1
incr(name, amount=1)
The return value is : Modified value ,int type
redis_conn.set('num_2', 2)#redis_conn.set('num_2', '2') Will do v = redis_conn.incr('num_2')10.String incrbyfloat Floating point number type value Self increasing
incrbyfloat(name, amount=1.0)
The return value is : Floating point type float
v = redis_conn.incrbyfloat('num_2')11.String append value Back up
append(key, value)
If given key does not exist , Then set a new value
The return value is the length of the modified string
length = redis_conn.append('name_5', '666')The result is :

stay redis in , A key corresponds to a list
12.List lpush Add values to the left of the list rpush( On the right )
lpush(name, *values)
value When there are multiple values , Add... To the left of the list from left to right , The types can be different
When the given key does not exist , Create a new list
Return value : The size of the list
v = redis_conn.lpush('Zarten', 1,2,3,4,5)#v = redis_conn.lpush('Zarten', 6)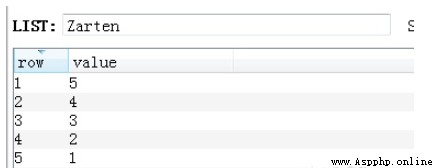
13.List lpushx When the bond exists , Add to the left of the list rpushx( Far right )
lpushx(name, value)
When only keys exist , Just add . If the key does not exist, do not add , Or create a new list
The return value is : List size
v = redis_conn.lpushx('Zarten_1', 'hehe')14.List llen Get the list size of the given key
llen(name)
v = redis_conn.llen('Zarten')15.List linsert Insert a new value in the middle of the list
linsert(name, where, refvalue, value)
name: Key name
where: Location , front (BEFORE) Or behind (AFTER)
refvalue: Specify which value to insert before and after
value: Insert new value
Return value : The length of the list after insertion , If returns -1, be refvalue non-existent
Data before insertion :

v = redis_conn.linsert('Zarten', 'AFTER', 6, 'b')The inserted data :
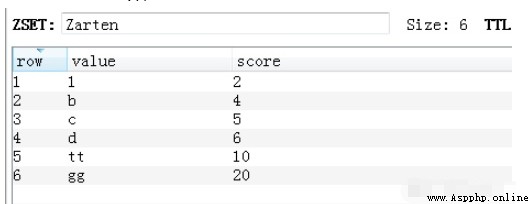
16.List lset The list is assigned by index
lset(name, index, value)
Return value : success True otherwise False
v = redis_conn.lset('Zarten', 2, 'cc')17.List lindex Get list values by index
lindex(name, index)
v = redis_conn.lindex('Zarten', 2)18.List lrange Get a piece of data from the list
lrange(name, start, end)
Return value :List A piece of data of type
v = redis_conn.lrange('Zarten', 2, 5)19.List lpop Delete the first value on the left rpop( On the right )
lpop(name)
Return value : The value of the deleted element
v = redis_conn.rpop('Zarten')20.List lrem Delete... From the list N Two identical values
lrem(name, value, num=0)
name: Key name
value: Values to be deleted
num: Number of deletions An integer indicates left to right Negative numbers indicate right to left for example :2 -2
Return value : Return the number of deletions
v = redis_conn.lrem('Zarten', 'hehe', -2)21.List ltrim Delete all values outside the range in the list
ltrim(name, start, end)
Return value : success True
v = redis_conn.ltrim('Zarten', 5, 10)22.List blpop Delete and return the leftmost value in the list brpop( Far right )
blpop(keys, timeout=0)
keys: Given key
timeout: Waiting timeout , The default is 0, To wait for
Return value :tuple type Form like : ( Key name , Deleted values ) (b'Zarten', b'hehe')
v = redis_conn.blpop('Zarten')23.List rpoplpush The rightmost value in one list is taken out and added to the leftmost value in another list brpoplpush Blocking version
rpoplpush(src, dst)
brpoplpush(src, dst, timeout=0) by rpoplpush Blocking version of ,timeout by 0 when , Always block
Return value : Extracted element value
v = redis_conn.rpoplpush('Zarten', 'Zhihu')It is internally stored as key value pairs
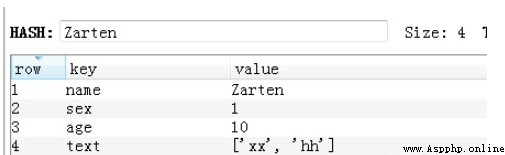
24.Hash hset Add a key value pair to the hash
hset(name, key, value)
key There is , The modified , Otherwise, add
Return value : Return the number of successful additions int
v = redis_conn.hset('Zarten', 'age', 10)25.Hash hmset Set multiple key value pairs in the hash
hmset(name, mapping)
mapping:dict type
Return value : success True
v = redis_conn.hmset('Zarten', {'sex':1, 'tel':'123'})26.Hash hmget Get multiple key value pairs in the hash
hmget(name, keys, *args)
Return value : List of values list Form like : [b'1', b'123'] <class 'list'>
v = redis_conn.hmget('Zarten', ['sex', 'tel'])#v = redis_conn.hmget('Zarten', 'sex', 'tel') also ok27.Hash hget Get specified key Value
hget(name, key)
v = redis_conn.hget('Zarten', 'age')28.Hash hgetall Get all key value pairs in the hash
hgetall(name)
Return value :dict type
v = redis_conn.hgetall('Zarten')29.Hash hlen Get the number of key value pairs in the hash
hlen(name)
v = redis_conn.hlen('Zarten')30.Hash hkeys Get all the keys in the hash key
hkeys(name)
Return value :list type
v = redis_conn.hkeys('Zarten')31.Hash hvals Get all the values in the hash value
hvals(name)
Return value :list type
v = redis_conn.hvals('Zarten')32.Hash hexists Check if there is a key in the hash key
hexists(name, key)
Return value : Yes True ; otherwise False
v = redis_conn.hexists('Zarten', 'b')33.Hash hdel Delete key value pairs in hash (key-value)
hdel(self, name, *keys)
Return value :int Number of deletions
v = redis_conn.hdel('Zarten', 'age')34.Hash hincrby Auto incrementing hash key Corresponding value value ( Must be integer numeric type )
hincrby(name, key, amount=1)
If given key Create if it does not exist ,amount Default increase 1, Can be negative
Return value :int Increased value
v = redis_conn.hincrby('Zarten', 'sex', -3)35.Hash hincrbyfloat Self-incremented floating point number ditto hincrby
hincrbyfloat(name, key, amount=1.0)
36.Hash expire Set the expiration time of the entire key
expire(name, time)
time: second , Time is up. , Automatically delete immediately
v = redis_conn.expire('Zarten', 10)37.Hash hscan Incrementally iterate to get the data in the hash
hscan(name, cursor=0, match=None, count=None)
name:redis Of name
cursor: The cursor ( Fetch data in batches based on cursors )
match: Matching the specified key, Default None Represents all key
count: Minimum number of slices per slice , Default None Said the Redis The default number of slices
Return value :tuple type ;( Scanning position , all dict data )
v = redis_conn.hscan('Zarten')38.Hash hscan_iter return hscan The generator
hscan_iter(name, match=None, count=None)
Refer to the above function hscan
v = redis_conn.hscan_iter('Zarten')for i in v: print(type(i), i)
The elements in the set do not repeat , Generally used to filter elements
39.Set sadd Add elements to the collection
sadd(name, *values)
If you insert an existing element , Will not be inserted automatically
v = redis_conn.sadd('Zarten', 'apple', 'a', 'b', 'c')40.Set scard Returns the number of elements in the collection
scard(name)
v = redis_conn.scard('Zarten')41.Set smembers Get all the elements in the collection
smembers(name)
Return value :set type , Form like : {b'a', b'apple', b'c', b'b'}
v = redis_conn.smembers('Zarten')42.Set srandmember Get one or at random N Elements
srandmember(name, number=None)
name: Key name
number: One or more N individual , The default is to return a . If returns N individual , Then return to List type
Return value : Return a value or a list
v = redis_conn.srandmember('Zarten', 2)43.Set sismember Determine whether a value is in the set
sismember(name, value)
Return value :True stay False be not in
v = redis_conn.sismember('Zarten', 'appl')44.Set spop Randomly delete and return the elements in the collection
spop(name)
v = redis_conn.spop('Zarten')45.Set srem Delete one or more elements in the collection
srem(name, *values)
Return value : Return the number of deletions int
v = redis_conn.srem('Zarten', 'c', 'a')46.Set smove Move values from one set to another
smove(src, dst, value)
if value When there is no , return False
Return value : success True
v = redis_conn.smove('Zarten', 'Fruit', 'apple')47.Set sdiff Returns all elements in one collection but not in other collections ( Difference set )
sdiff(keys, *args)
stay keys Collection , Elements that are not in other collections
Return value :set type {b'2', b'4', b'3', b'1'}
v = redis_conn.sdiff('Zarten', 'Fruit')48.Set sdiffstore above sdiff The return value of ( Difference set ) Save in another collection
sdiffstore(dest, keys, *args)
stay keys Collection , Elements that are not in other collections are saved in dest Collection
dest: New collection , New set of settings , The old collection will be overwritten
Return value :int Returns the number of actions
v = redis_conn.sdiffstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')49.Set sinter Returns the intersection of a set and other sets
sinter(keys, *args)
Return value :set type
v = redis_conn.sinter('Zarten', 'Fruit')50.Set sinterstore Returns the intersection of a set and other sets , And save it in another set
sinterstore(dest, keys, *args)
dest: Another collection , Set up a new set , The old collection elements will be overwritten
v = redis_conn.sinterstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')51.Set sunion Returns the union of a set and other sets
sunion(keys, *args)
v = redis_conn.sunion('Zarten', 'Fruit')52.Set sunionstore Returns the union of a set and other sets , And save it in another set
sunionstore(dest, keys, *args)
dest: Another collection , Set up a new set , The old collection elements will be overwritten
Return value : Number of new collection elements
v = redis_conn.sunionstore('Left', 'Zarten', 'Fruit')An ordered set has one more fractional field than a set , Fractions can be sorted in ascending and descending order
53.Zset zadd Add elements to an ordered set
zadd(name, *args, **kwargs)
When adding an element, you need to specify the score of the element
Return value : Returns the number of additions
2 The ways are as follows :
v = redis_conn.zadd('Zarten', 'a', 3, 'b', 4)#v = redis_conn.zadd('Zarten', c= 5, d= 6)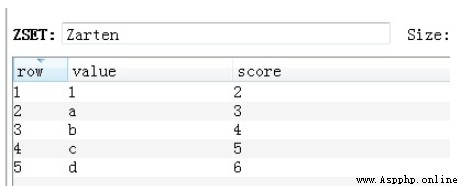
54.Zset zcard Returns the number of elements in an ordered collection
zcard(name)
v = redis_conn.zcard('Zarten')55.Zset zcount Returns the number of elements within the fractional range in an ordered set
zcount(name, min, max)
contain min max
Return value : Number int
v = redis_conn.zcount('Zarten', 3, 5)56.Zset zscore Returns the fraction of a specified value in an ordered set
zscore(name, value)
Return value :float Score of type ; Form like : -5.0 <class 'float'>
v = redis_conn.zscore('Zarten', 'zhi')57.Zset zincrby Increase the score of a value in an ordered set
zincrby(name, value, amount=1)
value: If exist , Increase its amount fraction ; If it does not exist , Then add the new value and the corresponding score
amount: Increased value , Can be negative
Return value : Increased score float type ; Form like : -5.0 <class 'float'>
v = redis_conn.zincrby('Zarten', 'zhi', -5)58.Zset zrem Delete one or more values in an ordered set
zrem(name, *values)
Return value : Return the number of deletions
v = redis_conn.zrem('Zarten', 'zhi', 'a')59.Zset zremrangebyrank Delete the ordered collection elements according to the sorting range
zremrangebyrank(name, min, max)
Return value : Delete the number int

v = redis_conn.zremrangebyrank('Zarten', 1, 3)Delete it as shown in the figure below :
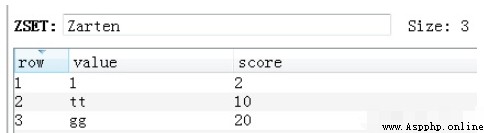
60.Zset zremrangebyscore Delete ordered set according to score range
zremrangebyscore(name, min, max)
Return value : Delete the number int
v = redis_conn.zremrangebyscore('Zarten', 8, 15)61.Zset zrank Returns the rank of a value in an ordered set ( From small to large ) zrevrank( From big to small )
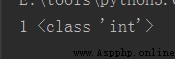
zrank(name, value)
Return value :value stay name Score ranking value in , Rank the scores from small to large , from 0 Start
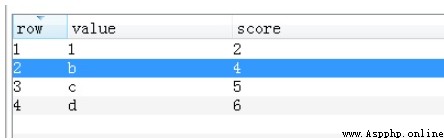
v = redis_conn.zrank('Zarten', 'b')The return value is shown in the following figure :
62.Zset zrange Returns a piece of data sorted by the scores of an ordered set
zrange(name, start, end, desc=False, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float)
name:redis Of name
start: An ordered collection index starting position ( The score )
end: End of index of ordered collection ( The score )
desc: Sort rule , By default, sort by score from small to large
withscores: Whether to get the score of the element , The default is to get only the values of the elements
score_cast_func: A function that converts data to scores
Return value :list type [(b'tt', 10.0), (b'd', 6.0), (b'c', 5.0)] <class 'list'>
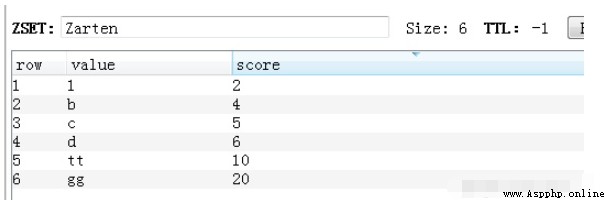
v = redis_conn.zrange('Zarten', 1, 3, True, True, score_cast_func=float)The result is shown in Fig. :

bitmap Bit in which binary is stored 0 and 1, Similar to digit group . Typical applications are based on redis The bloom filter .
Belong to String String data structure , solid bit The mapping is limited to 512 MB within (2^32)
63.Bitmap setbit Set the value of the bitmap
setbit(name, offset, value)
name:redis Key name
offset: Offset , Greater than or equal to 0. When offset stretches , Blank space to 0 fill
value: Binary value 0 or 1
v = redis_conn.setbit('Zarten_2', 100, 1)64.Bitmap getbit Returns the value of the specified offset of the bitmap
getbit(name, offset)
return 0 or 1
v = redis_conn.getbit('Zarten_2', 101)65.Bitmap bitcount The binary in the returned bitmap is 1 Total number of
bitcount(key, start=None, end=None)
start end Specify the start and end bits , Default entire bitmap
v = redis_conn.bitcount('Zarten_2', 100, 1000)Global functions apply to any data structure
66. Global function delete Delete redis All data for one or more keys in
delete(*names)
Return value :int Number of deletions
v = redis_conn.delete('name', 'name_1')67. Global function exists Judge redis Is there a key in
exists(name)
Return value : There is True; conversely False
v = redis_conn.exists('name')68. Global function rename rename redis Middle key name
rename(src, dst)
Return value : success True
v = redis_conn.rename('name_2', 'name_100')69. Global function move Move redis All data of a key in a key to a key db in
move(name, db)
Return value : success True
v = redis_conn.move('name_100', 12)70. Global function randomkey Random access redis A key name in
randomkey()
Return value : Form like : b'name_55'
v = redis_conn.randomkey()
71. Global function type see redis A key data structure type in
type(name)
Return value : character string ( Byte form ) Form like : b'hash'
none (key non-existent )
string ( character string )
list ( list )
set ( aggregate )
zset ( Ordered set )
hash ( Hashtable )
v = redis_conn.type('name_4')Here we are , I'm sure you're right “ How do you use it? Python operation Redis database ” Have a deeper understanding of , You might as well put it into practice ! This is the Yisu cloud website , For more relevant contents, you can enter the relevant channels for inquiry , Pay attention to our , Continue to learn !