Django Usually called “ Frame containing battery ”, Because it has default settings for everything , And it has the function of helping anyone to develop the website quickly . Talking about forms , stay HTML in , Form is <form>...</form> A collection of elements within , Allows visitors to perform tasks such as entering text 、 Select options 、 Operate on objects or controls , Then send the information back to the server . Basically , It is a collection of data for any purpose , Including saving it in the database or getting data from the database .Django Support all types HTML Forms and render data from them into views , In order to use various logical operations for processing .
To learn about HTML More information about the form , Please visit How to use Django Forms create form ?.Django It also provides Django Forms Built in features of , It's like Django Models equally . Can be in Django Create forms in and use them to get data from users in a convenient way . To start using forms , You need to be familiar with the GET and POST request .
- GET: by comparison ,GET Bind the submitted data into a string , And use it to form a URL.URL Contains the address where data must be sent , And data keys and values . If you are in Django Search in the document , You can see this , This will result in a https://docs.djangoproject.com/search/?q=forms&release=1 Of URL.
- POST: Any request that can be used to change the state of the system ( for example , Requests to make changes in the database ) Should be used POST.
stay Django Medium rendering HTML Form description
Use examples to illustrate Django Forms . Consider a person named geeksforgeeks Project , It has a name called geeks Applications for .
Let's create a simple HTML Form to show how to enter data from the user and use it in the view . stay geeks > templates > home.html Enter the following code in
<form action = "" method = "get">
<label for="your_name">Your name: </label>
<input id="your_name" type="text" name="your_name">
<input type="submit" value="OK">
</form> Now we're going to render it in our view , We need to modify... For geek apps urls.py. stay geeksforgeeks > urls.py Enter the following code in
from django.urls import path
# importing views from views..py
from .views import geeks_view
urlpatterns = [
path('', home_view ),
] Now? , Let's switch to home_view And start checking how we will get the data . come from Django in HTML All the data of the form is used as JSON Object transfer , It's called a request . Let's first create a view , Then we will try all the ways to get data from the form .
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your view here
def home_view(request):
# The logic of the view will be implemented here
return render(request, "home.html") When everything is in place , Let's run Python manage.py run server And check if the form exists on the home page .
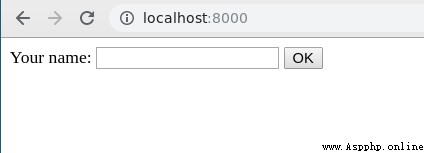
By default , Each uses HTML Written forms are sent to the back end of the application GET request ,GET Requests typically use URL To work with queries in . Let's use the table above to demonstrate , Fill out the form in your name , Let's see what happens .
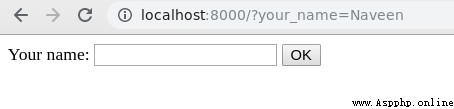
above URL With input tag attached Name attribute and the name entered in the form . This is it. GET How the request works , Whether they will be attached to URL To send data to the back end of the application . Let's examine how we finally get this data in our view , So that the logic can be applied according to the input . stay views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your view here
def home_view(request):
print(request.GET)
return render(request, "home.html") Now? , When we fill out the form , We can see the following output in the terminal :
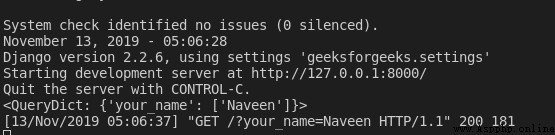
request.GET Return a query Dictionary , It can be like any other python Access it like a dictionary , Finally, use its data to apply some logic . Again , If the transmission mode is POST, You can use request.POST As a query Dictionary , Render the data in the form to the view . stay home.html in
<form action = "" method = "POST">
{% csrf_token %}
<label for="your_name">Your name: </label>
<input id="your_name" type="text" name="your_name">
<input type="submit" value="OK">
</form> Please note that , Whenever we create a form request , For safety's sake ,Django Will ask you to add {% csrf_token %} Now? , stay views.py in , Let's check request.POST what are you having? .
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your view here
def home_view(request):
print(request.POST)
return render(request, "home.html") Now? , When we submit the form , It will display the following data .
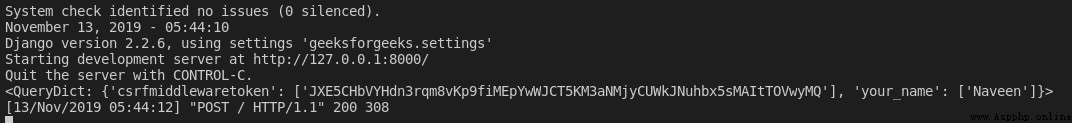
such , People can use this data to query the database or use some logical operations to process , And use the context dictionary to pass it to the template .



