First , Why learn python Well ?
There is only motivation when there is a goal !
The goal is : Learn the basics python, Learn to crawl , You can climb down a novel or poem on Baidu .
Python download
cmd perform python Check whether the installation is successful , If version number appears, the installation is successful .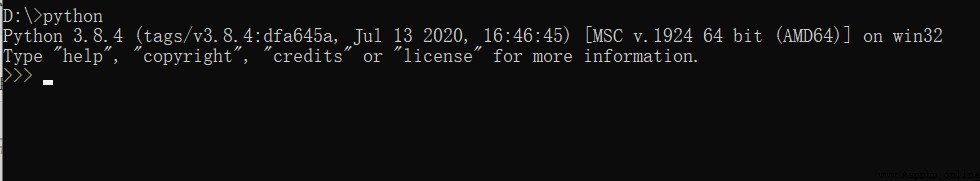
I followed teacher liaoxuefeng's tutorial ,Python course by Liao Xuefeng .
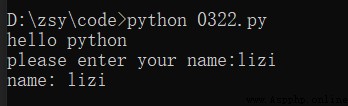
VSCode establish 0322.py file .
cmd In the implementation of . find 0322.py The catalog of ,python 0322.py Execute code .
# Output
print("hello python")
# Input
name = input("please enter your name:")
print("name:", name)
Integers 、 Floating point numbers 、 character string 、 Boolean value (True、False)、 Null value (None)、 Variable ( The variable name must be case English 、 Numbers and _ The combination of , And can't start with a number )、 Constant ( stay Python in , We usually use all uppercase variable names to represent constants )
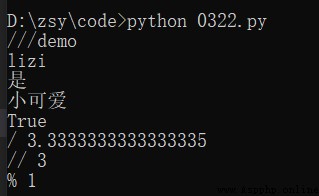
# r'' Indicates that the escape character is not escaped
print(r"///demo")
# '''...''' Represent multiline content
print('''lizi yes Cutie ''')
# Boolean judgment
print(5 > 3)
# division
print("/", 10/3)
# Floor removal , integer
print("//", 10//3)
# Remainder
print("%", 10%3)
print("abcde The length of ", len('abcde'))
# abcde The length of 5
print("hello, %s" %"world")
# hello, world
print('%.2f%%' % 24.2455)
# 24.25%
Built in data types
Element types can be different , You can also nest , Such as :["apple", "orange", "sweets", 2, [True, "22"]]
food = ["apple", "orange", "sweets"]
print("list The length of ", len(food))
# list The length of 3
print("list first 、 the second 、 The penultimate element ", food[0], food[1], food[-1])
# list first 、 the second 、 The penultimate element apple orange sweets
# Insert the element at the end append()
food.append("banana")
print(food)
# ['apple', 'orange', 'sweets', 'banana']
# Inserts the element at the specified location insert()
food.insert(2, "bread")
print(food)
# ['apple', 'orange', 'bread', 'sweets', 'banana']
# Delete last element pop()
print(food.pop())
print(food)
# banana
# ['apple', 'orange', 'bread', 'sweets']
# Delete the specified location element pop(i)
print(food.pop(1))
print(food)
# orange
# ['apple', 'bread', 'sweets']
# Element substitution
food[0] = "peach"
print(food)
# ['peach', 'bread', 'sweets']
tuple nothing append()、insert()、pop() Other methods , Once defined, it cannot be changed .
When there is only one element , Omit parentheses , Not tuple type . You can add a comma , representative tuple type .
people = ("Liz", "Andy", "Bob")
print(people)
# ('Liz', 'Andy', 'Bob')
test = ("Jim")
print(test)
# Jim
test2 = ("Jim", )
print(test2)
# ('Jim',)
Use if...:...else:...
height = 24
if height > 30:
print("1")
elif height > 5:
print("2")
else:
print("3")
# 2
# as long as x Yes no zero value 、 Non empty string 、 Non empty list etc. , Judge as True, Otherwise False.
if x:
print('True')
# Input
input()
# String to integer
int()
food = ["apple", "nut", "coke"]
for item in food:
print(item)
# apple
# nut
# coke
# 0-num Integer sequence of
range(num)
num = 2
all = 3
while all > 0:
num = num * num
all = all - 1
print(num)
# 256
num = 2
all = 3
while all > 0:
num = num * num
all = all - 1
if all < 2:
break
print(num)
# 16
n = 0
while n < 5:
n = n + 1
if n%2 == 0:
continue
print(n)
# 1
# 3
# 5
dict Full name dictionary, Same as map, Use the key - value (key-value) Storage , Easy and quick to find information .
info = {
"name": "Liz", "age": "18", "weight": "44kg"}
print(info["name"])
# Liz
info["height"] = "160cm"
print(info)
# {'name': 'Liz', 'age': '18', 'weight': '44kg', 'height': '160cm'}
print(info.get("height"))
# 160cm
print(info.pop("name"))
# Liz
print(info)
# {'age': '18', 'weight': '44kg', 'height': '160cm'}
A group of key Set , But no storage. value, Elements cannot be repeated .
s = set([1, 2, 3, 2])
print(s)
# {1, 2, 3}
s.add(4)
s.remove(1)
print(s)
# {2, 3, 4}
a = set([1, 2, 5])
print(a & s)
# {2}
print(a | s)
# {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
python Built-in methods official
# python Built in functions ,abs(), Find the absolute value
print(abs(-10))
# 10
Custom function : stay Python in , Define a function to use def sentence , Write the function names in turn 、 Brackets 、 Parameters and colons in brackets :, then , Write function bodies in indented blocks , The return value of the function is return Statement returns .
def my_abs(x):
# isinstance() Type error report
if not isinstance(x, (int, float)):
raise TypeError('bad operand type')
if x >= 0:
return x
else:
return -x
print(my_abs(-2))
# 2
# Empty function pass, Function placeholder
if a > 10:
pass
def power(x, n):
s = 1
while n > 0:
n = n - 1
s = s * x
return s
print(power(5, 2))
# 25
The required parameters are in front , The default parameter is after .
Default parameters must point to immutable objects
def power(x, n=2):
s = 1
while n > 0:
n = n - 1
s = s * x
return s
print(power(5))
# 25
def calc(*numbers):
sum = 0
for x in numbers:
sum = sum + x*x
return sum
print(calc(1, 2, 3))
# 14
nums = [1, 2, 3]
print(calc(*nums))
# 14
def person(name, age, **kw):
print('name:', name, 'age:', age, 'other:', kw)
print(person("Liz", 18))
# name: Liz age: 18 other: {}
# None
extra = {
'city': 'Beijing', 'job': 'Engineer'}
print(person('Jack', 24, **extra))
# name: Jack age: 24 other: {'city': 'Beijing', 'job': 'Engineer'}
# None
Separator * The following parameters are named keyword parameters
def person(name, age, *, city, job):
print(name, age, city, job)
person('Jack', 24, city='Beijing', job='Engineer')
# Jack 24 Beijing Engineer
The order of number definitions must be : Required parameters 、 Default parameters 、 Variable parameters 、 Name keyword parameters and keyword parameters
def f1(a, b, c=0, *args, **kw):
print('a =', a, 'b =', b, 'c =', c, 'args =', args, 'kw =', kw)
f1(1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', x=99)
# a = 1 b = 2 c = 3 args = ('a', 'b') kw = {'x': 99}
Calculation 1x2x3x4x……n
def fact(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
return n * fact(n-1)
print(fact(3))
# 6
def fact(n):
return fact_iter(n, 1)
def fact_iter(num, product):
if num == 1:
return product
return fact_iter(num - 1, num * product)
print(fact(3))
# 6
Take object n-m,Obj[n:m:l]( It doesn't contain m, Every time l Take one of them ),n=0 You can omit .
people = ["Andy", "Lily", "Popi", "Uu", "Wendy"]
print(people[:4:2])
# ['Andy', 'Popi']
food = ("apple", "nuts", "banana", "strawberry", "chicken")
print(food[:3])
# ('apple', 'nuts', 'banana')
print("asdfghjkl"[::2])
# adgjl
Use for...in... Loop iteration ,in You need to decide whether it is a circulable iteration .
from collections.abc import Iterable
print(isinstance('asdf', Iterable))
# True
for Ahead if ... else Is an expression , and for hinder if It's filter conditions , You can't take else.
# Generate 1-4
print(list(range(1, 5)))
# [1, 2, 3, 4]
# Generate 1*1-4*4
print(list(i*i for i in range(1,5)))
# [1, 4, 9, 16]
# A lowercase letter 、 Remove non string
L1 = ['Hello', 'World', 18, 'Apple', None]
L2 = [x.lower() for x in L1 if isinstance(x, str)]
# ['hello', 'world', 'apple']
The mechanism of computing while cycling . There are the following ways to generate generators :
[] Change to ()g = (x * x for x in range(3))
print(g)
print(next(g))
# <generator object <genexpr> at 0x000001BD81FC1270>
# 0
for i in g:
print(i)
# 0
# 1
# 4
yield keyword The variable of a function can be a function , The return can also be a function .
def add(x, y, f):
return f(x) + f(y)
print(add(-5, 6, abs))
# 11
map( Conversion rules , Parameters to be converted )
def fn(x):
return x*x
print(list(map(fn, [1, 2, 3, 4])))
# [1, 4, 9, 16]
print(list(map(str, [1, 2, 3, 4])))
# ['1', '2', '3', '4']
from functools import reduce
def add(x, y):
return x + y
print(reduce(add, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
# 10
sorted( object ,key Function ,reverse=True),key The rules , Omission ,reverse=True Reverse sorting , Omission
print(sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21], key=abs))
# [5, 9, -12, -21, 36]
def calc_sum(*args):
def sum():
n = 0
for i in args:
n = n + i
return n
return sum
f = calc_sum(1, 2, 3, 4)
print(f)
# <function calc_sum.<locals>.sum at 0x0000018038F1E160>
print(f())
# 10
To form a closure , Be careful : Return functions do not reference any loop variables , Or variables that will change in the future .
Anonymous functions lambda Parameters : Return value # nothing return, Isn't there a name , Don't worry about function name conflicts .
f = lambda x: x * x
print(f)
# <function <lambda> at 0x000001BF94BFE0D0>
print(f(5))
# 25
def fn():
print('fn ah ')
fn()
# fn ah
print(fn.__name__) # function __name__ attribute , Get the name of the function
# fn
# Define a print log decorator
def log(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kw):
print('call %s():' % func.__name__)
return func(*args, **kw)
return wrapper
@log
def fn():
print('fn ah ')
fn()
# call fn():
# fn ah
https://github.com/ChestnutNeko/pythonStudy/blob/main/douban.py