Calculate the time required to create tuples and lists :ipython Use in timeit
In terms of memory occupation and operation time , Tuples have more advantages than lists .
When the content does not change , Tuples are preferred ; When the content needs to change , Priority list .
collections Module namedtuple function
namedtuple: Receive two parameters , The name of the first type created , Second list
from collections import namedtuple
Fruits = namedtuple('Fruits', ['name', 'color', 'size'])
f = Fruits('watermelon', 'green', '3')
print(f.name)
# The output is : watermelon
Dictionary derivation
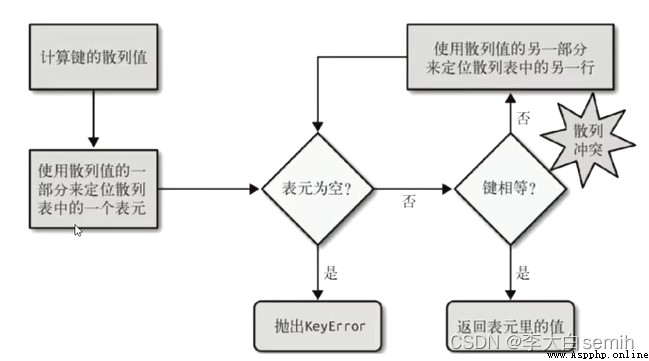
The process of looking up values in dictionaries
Performance analysis :
Compare... In terms of time : aggregate , Dictionaries , Tuples , list
Compare from memory : Dictionaries , aggregate , list , Tuples
3.1 List derivation
Take the traversed value to the front
lis_nu = [i for i in range(1,101)]
print(lis_nu)3.2 Dictionary derivation
dit_nu = {i: i+1 for i in range(10)}
print(dit_nu)
> {0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 4, 4: 5, 5: 6, 6: 7, 7: 8, 8: 9, 9: 10}
3.3 generator
3.3.1 ()
advantage : To save memory , Improve performance
ge = (i for i in range(100))
a = next(ge)
print(a)
> 03.3.2 yield
yield adopt next() Value
3.4 iterator
An iterator can pass through next() Value
Iteratable object : Sure for Loop traversal is an iterative object
Convert iteratable objects to iterators :iter( Iteratable object )
A generator is a kind of iterator

3.4.2 send() function
def s_d():
for i in range(6):
j = yield i
print(j)
# send: Interact with the generator
dd = s_d()
print(next(dd))
print(dd.send(10))
》 The output is :
0
10
1
send(num) function , amount to next() function , also send(num) Function passed in num The value is equal to yield i