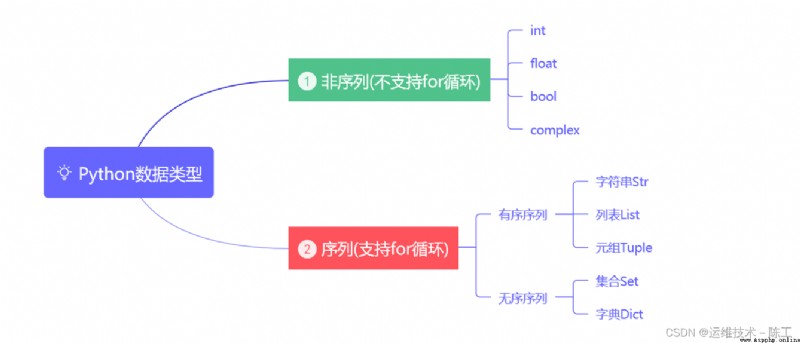
#1、創建集合
示例1:創建
s = {
1,2,3,1,2,3}
print(s,type(s))
#結果
{
1, 2, 3} <class 'set'>
示例2:集合裡面不能有其他變量
s = {
1,2,3,[1,2,3]}
print(s,type(s))
#結果
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
注意:空集合得用set
s={
}
print(s,type(s)) 其結果為字典
k=set()
print(k,type(k)) set的結果才是集合
#結果
{
} <class 'dict'>
set() <class 'set'>
因為集合是無序,不重復的,所以
不支持連接,重復,索引,切片
支持成員操作符(in ,not in)
1、add增加一個
s = {
1,2,3}
s.add(100)
print(s)
#結果
{
1, 2, 3, 100}
2、update一次增加多個
s = {
1,2,3}
s.update({
4,5,6})
print(s)
#結果
{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
1、remove:刪除(如果刪除的數字沒有則會報錯)
s = {
1,2,3}
s.remove(3)
print(s)
#結果
{
1, 2}
2、discard:刪除(如果數字沒有則不進行操作)
s = {
1,2,3}
s.discard(3)
print(s)
#結果
{
1, 2}
3、pop:任意刪除一個值(集合為空則刪除)
s = {
1,2,3,4,5}
s.pop()
print(s)
#結果
{
2, 3, 4, 5}
1、差集
s1={
1,2,3,4}
s2={
3,4}
print(s1-s2)
#結果
{
1, 2}
2、交集
s1={
1,2,3,4}
s2={
3,4}
print(s1-s2)
print(s1 & s2)
#結果
{
3, 4}
3、對稱差分
s1={
1,2,3}
s2={
1,2,4}
print(s1^s2)
#結果
{
3, 4}
4、並集
s1={
1,2,3}
s2={
1,2,4}
print(s1|s2)
#結果
{
1, 2, 3, 4}
5、判斷子集
s1={
1,2,3}
s2={
1,2,4}
print(s1.issubset(s2)) s1是s2的子集合嗎
#結果
False
6、判斷交集
s1={
1,2,3}
s2={
1,2,4}
print(s1.isdisjoint(s2)) s1與s2沒有交集對嗎
#結果
False
7、拓展:frozenset
不能增加,刪除
s = frozenset({1,2,3})
print((s,type(s)))
#結果
(frozenset({1, 2, 3}), <class ‘frozenset’>)

import random
NUMBER=set()
print(NUMBER,type(NUMBER))
for x in range(100):
num = random.randint(1,1000)
NUMBER.add(num)
print(NUMBER)
print(sorted(NUMBER,reverse=True))
1、字典的創建
key-value對或者鍵值對
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
print(d,type(d))
#結果
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安'} <class 'dict'>
2、創建空字典
d={
}
print(d,type(d))
#結果
{
} <class 'dict'>
和集合類似,不支持拼接,重復等
1、判斷成員操作符
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
print('name' in d)
print('westos' in d)
#結果
True 是判斷key值的,因此答案是ture
False 是westos不是key值的,因此答案是false
1、查看
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
print(d.keys()) 查看所有可以、值
print(d.values()) 查看所有value
print(d.items()) 查看所有元素
print(d['name']) 查看name對應的value值
print(d.get('province')) 查看省份、對應返還value值,如果存在則返還,如果不存在則返還為None
print(d.get('province','陝西')) 查看身份,如果沒有則返還默認值
#結果
dict_keys(['name', 'age', 'city'])
dict_values(['westos', 18, '西安'])
dict_items([('name', 'westos'), ('age', 18), ('city', '西安')])
westos
陝西
2、增加和修改
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
print(d)
d['privince']='陝西' 如果沒有則增加
print(d)
d['privince']='山東' 如果有則修改
print(d)
#結果
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安'}
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安', 'privince': '陝西'}
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安', 'privince': '山東'}
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18}
d.setdefault('city','西安') 如果沒有則添加
print(d)
d.setdefault('city','北京') 如果有key值,則不做操作
print(d)
#結果
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安'}
{
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18, 'city': '西安'}
3、刪除
d = {
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18}
del d['name']
print(d)
#結果
{
'age': 18}
d = {
'name': 'westos', 'age': 18}
d.pop('name')
print(d)
#結果
{
'age': 18}
4、遍歷
一般的遍歷只會遍歷出key值
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
for items in d:
print(items)
#結果
name
age
city
遍歷出所有
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
for item in d.items():
print(item)
#結果
('name', 'westos')
('age', 18)
('city', '西安')
分別遍歷出key和value(很重要)
d = {
"name":"westos","age":18,"city":"西安"}
for key,value in d.items():
print(f'key={
key},value={
value}')
#結果
key=name,value=westos
key=age,value=18
key=city,value=西安
5、默認字典
(1)、int整型
設置默認的value值,這裡定義int整型
from collections import defaultdict
d = defaultdict(int)
print(d)
print(d['views'])
#結果
defaultdict(<class 'int'>, {
})
0
采用這種方式可以直接進行補充
from collections import defaultdict
d = defaultdict(int)
d['view'] +=1
d['transfer'] +=1
print(d)
#結果
defaultdict(<class 'int'>, {
'view': 1, 'transfer': 1})
(2)、list類型
這裡設置為列表類型,可以用列表的append進行追加
d = defaultdict(list)
d['allow_users'].append('westos')
d['deny_users'].extend('ck1,ck2')
print(d)
#結果
defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {
'allow_users': ['westos'], 'deny_users': ['ck1', 'ck2']})
(3)、set集合類型
defaultdict(<class ‘set’>, {‘love_movies’: {‘前任3’, ‘電影xxx’, ‘黑客帝國’}})
有序序列擁有的特性:索引,切片,鏈接操作符,重復操作符以及成員操作符的部分特性。
1、可變和不可變(a賦值b,a改變值後,b地址是否能改變)
可變數據類型:list,set,dict
不可變數據類型:數值,元組
2、序列
見ppt