Statement : Blogger ( Haohong image algorithm ) When writing this blog post , With Python Is the version number 3.9.10.
Dictionaries (dict) The format is as follows :
dict1 = {
key1 : value1, key2 : value2, key3 : value3 }
From the above format we can see :
Each key value of the dictionary key=>value Divide... With a colon , Each pair is separated by commas , The whole dictionary is enclosed in curly brackets {} in .
In addition, the dictionary requires that the key must be unique , But values don't have to be .
# Create a dictionary with content
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
# Method one creates an empty dictionary
dict2 = {
}
# Method 2: create an empty dictionary
dict3 = dict()
The operation results are as follows :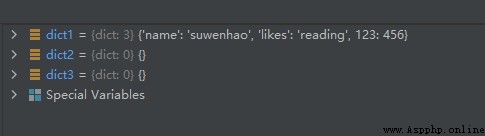
The grammar is as follows :
dict.fromkeys(keys, value)
keys — It's necessary . Specify the iteratable object for the new dictionary key .
value— Optional . Values of all keys . The default value is None.
The first example code is as follows :
x = ('key1', 'key2', 'key3')
y = 0
dict1 = dict.fromkeys(x, y)
The operation results are as follows :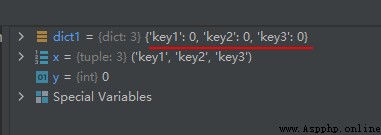
The second example code :
x = ('key1', 'key2', 'key3')
y = (61, 62, 63)
dict1 = dict.fromkeys(x, y)
The operation results are as follows :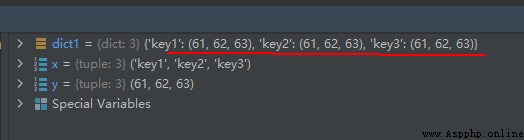
Be careful :key1 The key value of is not 61, It's a tuple (61, 62, 63), this Pay attention to .
The third example code :
x = ('key1', 'key2', 'key3')
dict1 = dict.fromkeys(x)
The operation results are as follows :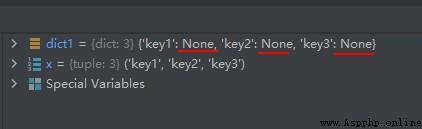
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
str1 = dict1['name']
value1 = dict1[123]
The operation results are as follows :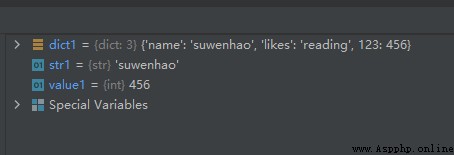
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
k = 1
dict1['name'] = 'wanghong' # Update key name Value
dict1['height'] = 167 # Increase key value
The operation results are as follows :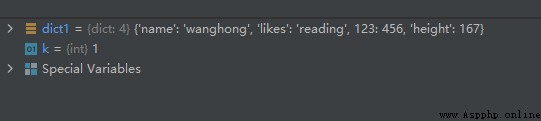
put questions to : Why is there a sentence inserted in the middle "k = 1", See the following blog post for the answers :
https://blog.csdn.net/wenhao_ir/article/details/125416514
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
del dict1['name']
The operation results are as follows :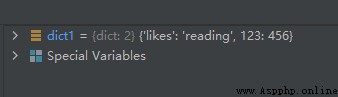
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict2 = {
'name': 'wanghong', 'likes': 'sing', 999: 704}
del dict1
The operation results are as follows :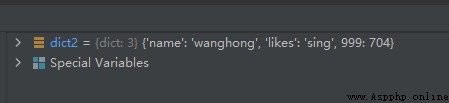
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1.clear()
The operation results are as follows :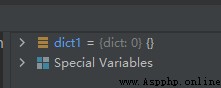
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
len1 = len(dict1)
The operation results are as follows :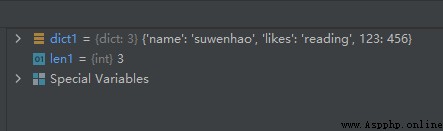
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
str1 = str(dict1)
print(str1)
The operation results are as follows :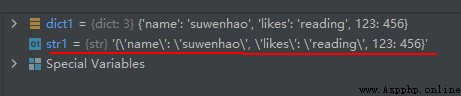
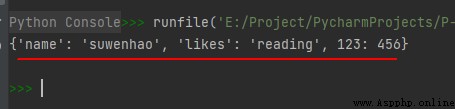
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict2 = dict1.copy()
dict1['name'] = 'zhangsan'
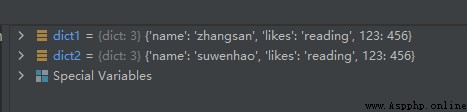
From the running results, we can see that , Method copy() It does realize deep copy , change dict1 The key value of does not affect dict2 Value .
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict2 = dict1
dict1['name'] = 'zhangsan'
The operation results are as follows :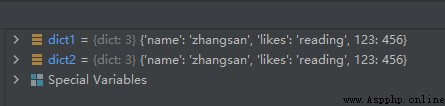
From the above running results, we can see that ,dict1 The modification of key values affects dict2 Key value of , Both of them share memory space .
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
bool1 = 'name' in dict1
bool2 = 'weight' in dict1
The operation results are as follows :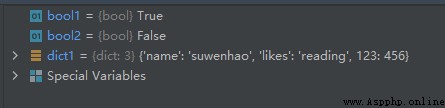
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1_items = dict1.items()
print(dict1_items)
The operation results are as follows :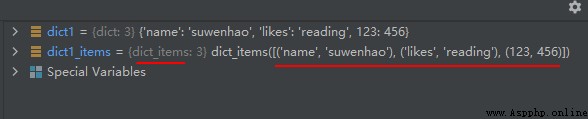
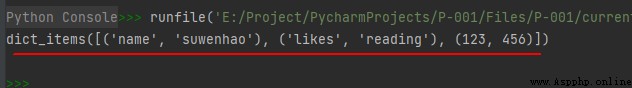
so , This view object is to replace the dictionary object with a formal representation .
For example, the original key value form is :
'name': 'suwenhao'
Convert to view object (dict_items) The following is the form :
('name', 'suwenhao')
It is worth noting that , The original key value must be changed , The corresponding view object will also change , Take an example :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1_items = dict1.items()
dict1['name'] = 'zhangsan'
print(dict1_items)
The results are shown in the following figure :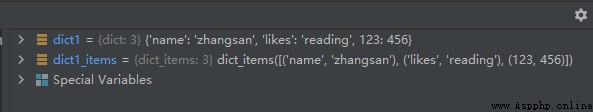
View objects can use functions list() Convert to list type , Like the following example :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1_items = dict1.items()
list1 = list(dict1_items)
The operation results are as follows :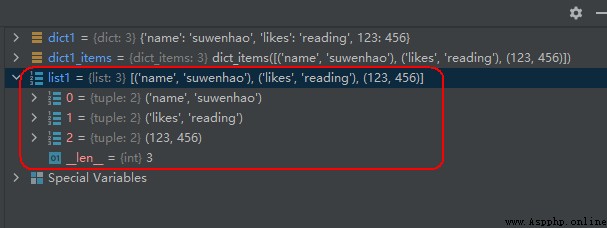
As can be seen from the above results , After converting to a list object , Each key value is a tuple (tuple).
About view objects , Be careful , We can't make any changes to the view object , Because the view objects of the dictionary are read-only .
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1_keys = dict1.keys()
list1 = list(dict1_keys)
The operation results are as follows :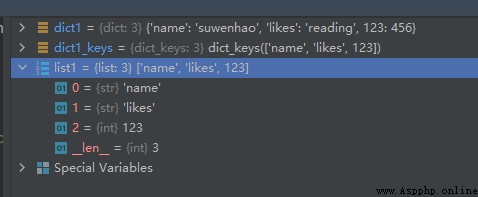
For relevant knowledge and instructions, please refer to “10- Usage method items() View object that gets dictionary keys and values ”
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict1_values = dict1.values()
list1 = list(dict1_values)
The operation results are as follows :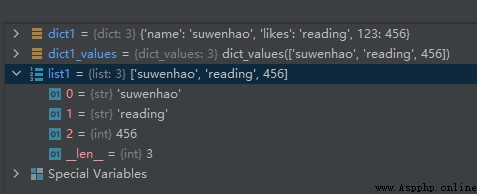
For relevant knowledge and instructions, please refer to “10- Usage method items() View object that gets dictionary keys and values ”
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
str1 = dict1.get('name')
The operation results are as follows :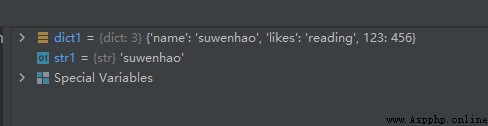
Method setdefault() The grammar is as follows :
dict.setdefault(key, default=None)
Parameters :
key – Find the key value .
default – When the key doesn't exist , Set the default key value .
Return value :
If key stay In the dictionary , Return the corresponding value . If it's not in the dictionary , The insert key And set the default value default, And back to default ,default The default value is None.
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
str1 = dict1.setdefault('name', 'zhangsan')
str2 = dict1.setdefault('likes', None)
temp1 = dict1.setdefault('weight', None)
The operation results are as follows :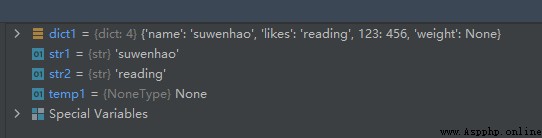
Result analysis :
Because of the key ’name’ Is there , So the sentence :
str1 = dict1.setdefault('name', 'zhangsan')
Does not change its key value , And returned its key value ‘suwenhao’
Because of the key ’weight’ It doesn't exist , So in the dictionary dict1 New key in ’weight’, Its value is set to None.
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
dict2 = {
'weight': 30}
dict1.update(dict2)
The operation results are as follows :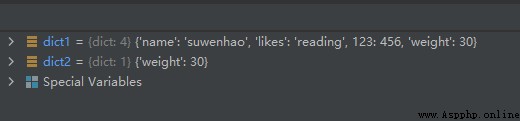
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
temp1 = dict1.pop('name')
The operation results are as follows :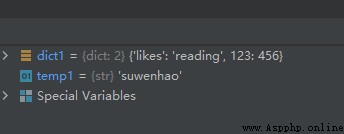
The last key value inserted is usually the last key value .
The sample code is as follows :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
temp1 = dict1.popitem()
The operation results are as follows :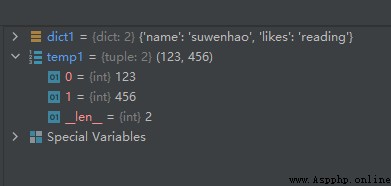
1、 The same key is not allowed to appear twice . When creating, if the same key is assigned twice , The latter value will be remembered , The following example :
dict1 = {
'name': 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456, 'name': 'zhangsan'}
str1 = dict1['name']
The operation results are as follows :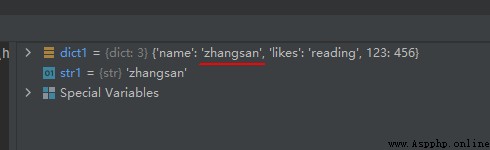
2、 The key must be immutable , So you can use numbers , A string or tuple acts as , Not with lists , As the following statement :
dict1 = {
['name']: 'suwenhao', 'likes': 'reading', 123: 456}
When running, the error is as follows :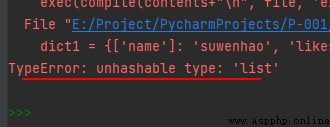
Reference material :
https://blog.csdn.net/wenhao_ir/article/details/125100220