適配器模式是一種結構型設計模式, 它能使接口不兼容的對象能夠相互合作。通過組合對象的方式來創建新功能。
適配器幫助我們使兩個不兼容的接口兼容。這到底是什麼意思呢?如果我們有一個舊的組件,我們想在一個新的系統中使用它,或者我們想在一個舊的系統中使用一個新的組件。兩者很少能在不需要修改代碼的情況下進行交流。
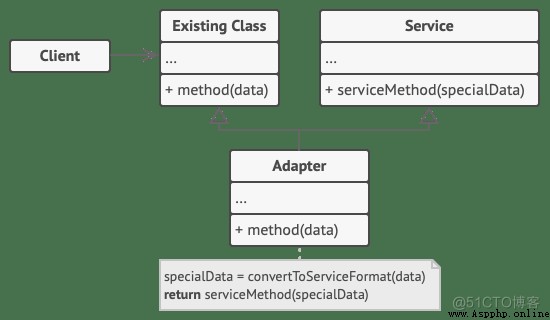
但是,改變代碼並不總是可能的,要麼是因為我們無法訪問它,要麼是因為它不切實際。在這種情況下,我們可以寫一個額外的層,對兩個接口之間的通信進行一些必要的修改,在兩個接口之間實現通信。
這個層被稱為適配器。
適配器不僅可以轉換不同格式的數據, 其還有助於采用不同接口的對象之間的合作。 它的運作方式如下:
有時你甚至可以創建一個雙向適配器來實現雙向轉換調用。
當我們的 client 想要打開風扇,而風扇提供了 turnOn 方法,直接調用 turnOn 即可享受涼爽的風,比如下圖:
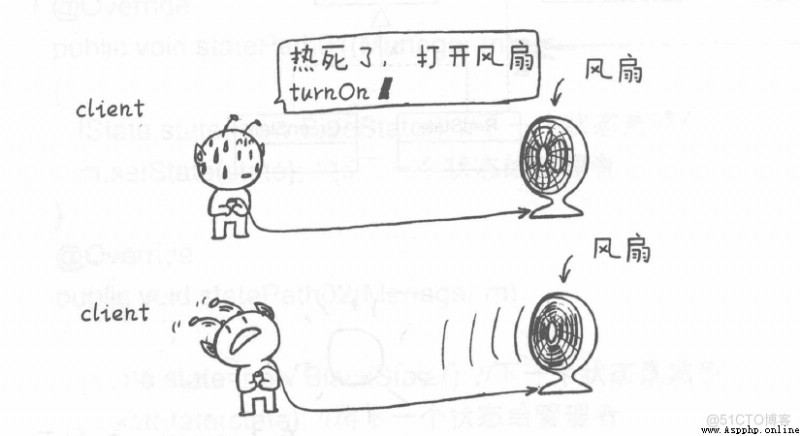
然後同樣是打開的操作,client 想通過 turnOn 調用打開電視機,而電視機沒有這個方法,電視機提供的 open 方法。
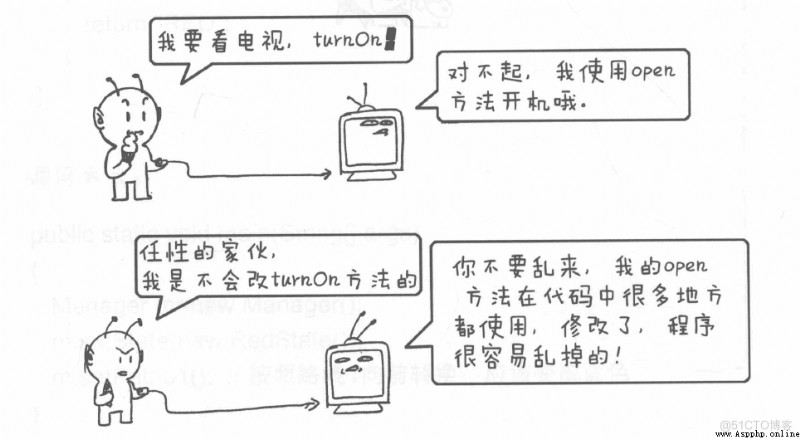
如果我們直接把 open 方法改為 turnOn 的方法,可能會引發系統的一系列其他問題,這個時候就需要我們的適配器模式了。
客戶端可以會使用各種各樣的適配器,為了方便保存,可以為適配器抽象出一個接口,UML 圖如下:
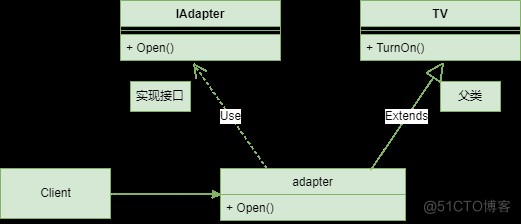
適配器 (Adapter) 是一個可以同時與客戶端和服務交互的類: 它在實現客戶端接口的同時封裝了服務對象。 適配器接受客戶端通過適配器接口發起的調用, 並將其轉換為適用於被封裝服務對象的調用。
客戶端代碼只需通過接口與適配器交互即可, 無需與具體的適配器類耦合。 因此, 你可以向程序中添加新類型的適配器而無需修改已有代碼。 這在服務類的接口被更改或替換時很有用: 你無需修改客戶端代碼就可以創建新的適配器類。
代碼如下:
public interface IAdapter {
public void turnOn(); // 通用開機函數
}
public class Tv {
public void open() {
System.out.println("電視機 TV 開機,只能使用 open 函數");
}
}
public class TvAdapter extends Tv implements IAdapter {
public void turnOn() {
super.open(); // 適配器模式
}
}
調用方式:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IAdapter adapter = new TvAdapter();
adapter.turnOn();
}
}
這一實現使用了繼承機制: 適配器同時繼承兩個對象的接口。 請注意, 這種方式僅能在支持多重繼承的編程語言中實現, 例如 C++。
class Target:
"""
The Target defines the domain-specific interface used by the client code.
"""
def request(self) -> str:
return "Target: The default target's behavior."
class Adaptee:
"""
The Adaptee contains some useful behavior, but its interface is incompatible
with the existing client code. The Adaptee needs some adaptation before the
client code can use it.
"""
def specific_request(self) -> str:
return ".eetpadA eht fo roivaheb laicepS"
class Adapter(Target, Adaptee):
"""
The Adapter makes the Adaptee's interface compatible with the Target's
interface via multiple inheritance.
"""
def request(self) -> str:
return f"Adapter: (TRANSLATED) {self.specific_request()[::-1]}"
def client_code(target: "Target") -> None:
"""
The client code supports all classes that follow the Target interface.
"""
print(target.request(), end="")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Client: I can work just fine with the Target objects:")
target = Target()
client_code(target)
print("\n")
adaptee = Adaptee()
print("Client: The Adaptee class has a weird interface. "
"See, I don't understand it:")
print(f"Adaptee: {adaptee.specific_request()}", end="\n\n")
print("Client: But I can work with it via the Adapter:")
adapter = Adapter()
client_code(adapter)
運行該程序:
Client: I can work just fine with the Target objects:
Target: The default target's behavior.
Client: The Adaptee class has a weird interface. See, I don't understand it:
Adaptee: .eetpadA eht fo roivaheb laicepS
Client: But I can work with it via the Adapter:
Adapter: (TRANSLATED) Special behavior of the Adaptee.
優點:
缺點:
參考鏈接: