Set creation
Disorder
Operands in collection
Add elements to the collection
Delete the first element in the collection
Delete the specified element in the collection
Determine whether the element is in the collection
Traversal of the set
Calculation of the number of set elements
Collections and dictionaries , list , Nesting of tuples
Sets and tuples
Sets and lists
Set creationUse built-in functions set() To transform or use {} Including , The elements in the collection : Disorder , The opposite sex , deterministic .
give an example :
numbers=set(range(0,7))// Use built-in functions to convert print(numbers)print(type(numbers))Output :
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
<class 'set'>
The opposite sex
fruit={'apple','orange','banana',"apple",'apple','orange','banana',"apple"}print(fruit)print(type(fruit))Output :
Disorder{'apple', 'banana', 'orange'}
<class 'set'>
Elements in a collection cannot be accessed by subscript .
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12})print(fruit[2])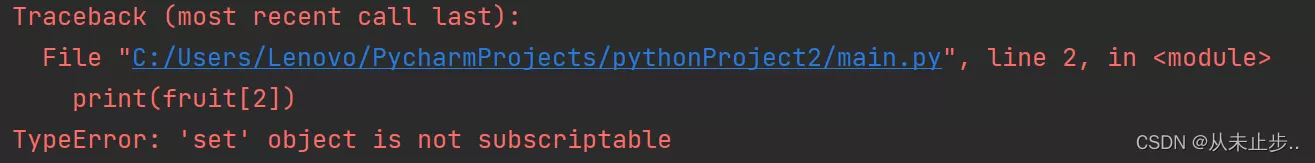
add() function
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12})fruit.add("bc")print(fruit)Output :
Delete the first element in the collection{'bc', 'apple', 9, 12, 'dbu', 'axn'}
pop() function
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12})fruit.pop()print(fruit)Output :
Delete the specified element in the collection{'apple', 9, 12, 'axn'}
1:remove() function , If the element does not exist, an error will be reported
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12})fruit.remove("banana")print(fruit)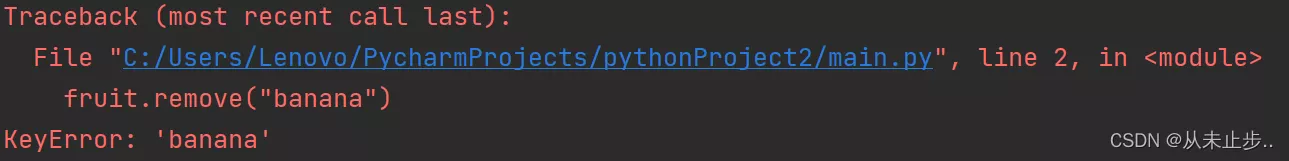
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})fruit.remove("apple")print(fruit)Output :
{'dbu', 'axn', 9, 12}
2:discard() function , If the specified element does not exist, no error will be reported
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})fruit.discard("banana")print(fruit)Output :
{'dbu', 'apple', 9, 'axn', 12}
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})fruit.discard("apple")print(fruit)Output :
Determine whether the element is in the collection{'dbu', 'axn', 9, 12}
if in/not in sentence
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})if "apple" in fruit: print("yes")else: print("NO")if "banana" not in fruit: print("YES")else: print("NO")Output :
Traversal of the setyes
YES
for loop
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})for i in fruit: print(i,end=' ')Output :
Calculation of the number of set elementsaxn 9 apple 12 dbu
len() function
give an example :
fruit =set({'apple',9,"axn","dbu",12,"apple"})print(len(fruit))Output :
Collections and dictionaries , list , Nesting of tuples5// Note the uniqueness of the set elements
Collections and dictionaries :
s1=set({"name":"jason","age":19," Address ":" The Beijing municipal "})print(s1)print(type(s1))Output :
Sets and tuples{' Address ', 'name', 'age'}// Output key names only
<class 'set'>
give an example :
s1={("name","jason","age",19," Address "," The Beijing municipal "),12,34,0}print(s1)print(type(s1))Output :
{0, 34, ('name', 'jason', 'age', 19, ' Address ', ' The Beijing municipal '), 12}
<class 'set'>
Use built-in functions to convert :
s1=set({"name","jason","age",19," Address "," The Beijing municipal "})print(s1)print(type(s1))Output :
Sets and lists{'age', 'jason', 19, ' Address ', ' The Beijing municipal ', 'name'}
<class 'set'>
give an example :
s2=set(["name","jason","age",19," Address "," The Beijing municipal "])print(s2)print(type(s2))Output :
{' The Beijing municipal ', 'age', 'jason', 19, 'name', ' Address '}
<class 'set'>
This is about Python This is the end of the article on the creation of sets and the use of common functions in , More about Python Please search the previous articles of SDN or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope you will support SDN more in the future !