1. Time stamp
1.1 time.time()
1.2 Time stamp turn character string
2. Structured time
2.1 Local time
2.2 Greenwich mean time ( Time zone )
2.3 Structured time turn character string
2.4 character string turn Structured time
2.5 Properties of structured data
2.6 Structured time turn Time stamp
Import related libraries
import time1. Time stamp 1.1 time.time()time.time() What you can get is Time stamp . namely 1970 year 1 month 1 Japan 0 when 0 branch 0 The offset from seconds to the present time s
t1 = time.time()print('t1:', t1)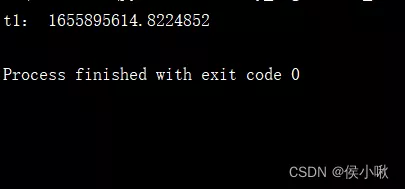
Convert timestamps to A fixed format String , have access to time.ctime() Method .( But not very often )
t = time.ctime(time.time())print(t)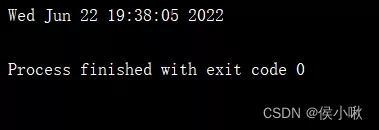
It is easier for us to use structured time
2.1 Local timeLocal time is related to time zone .
t2 = time.localtime(time.time()) print("t2:", t2)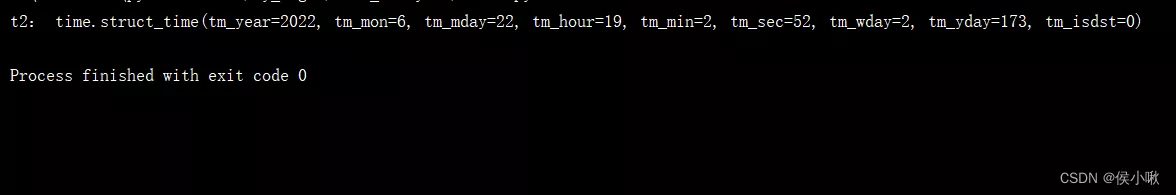
Greenwich mean time (0 The time zone ) Later than Beijing time 8 Hour only ( Global benchmarks , Using this time can eliminate the impact of writing code in different places )
t3 = time.gmtime(time.time())print("t3:", t3)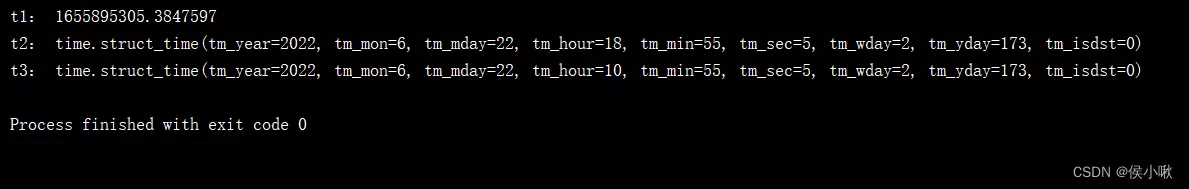
String form is generally accepted by human beings
t4 = time.strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S", t2)print(t4)print(type(t4))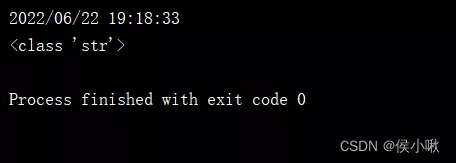
Reverse operation of the above operation
t5 = time.strptime('2022/06/22 20:30:35', "%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")print(t5)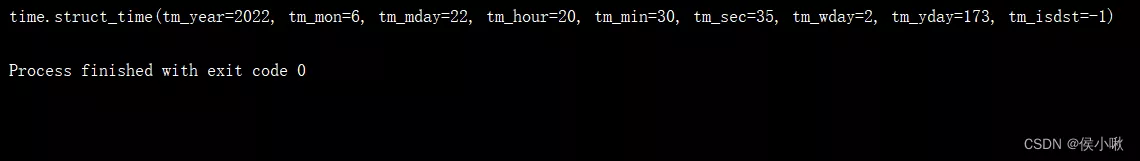
print(" year :", t2.tm_year)print(" month :", t2.tm_mon)print(" Japan :", t2.tm_mday)print(" when ", t2.tm_hour)print(" branch ", t2.tm_min)print(" second ", t2.tm_sec)print(" Days of the week have passed :", t2.tm_wday)print(" This year has passed :", t2.tm_yday)print(" Is it daylight saving time ", t2.tm_isdst)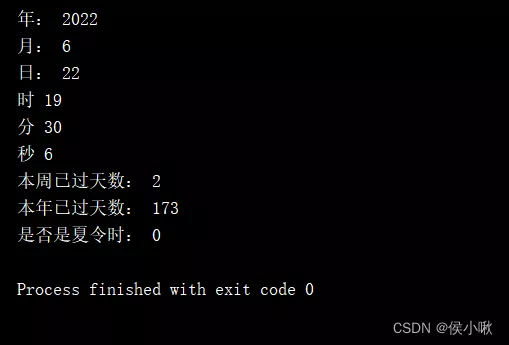
t7 = time.mktime(t2)print(t7)
This is about Python time This is the end of the article on the use of module timestamp and structured time , More about Python time Please search the previous articles of SDN or continue to browse the relevant articles below. I hope you can support SDN in the future !