目錄
一、列表
1)列表的概念
2)列表的創建
3)列表的訪問
4)列表添加元素
5)列表刪除元素
6)列表修改元素
7)列表的 * 和 + 操作
二、元組
1)元組的概念
2)元組的創建
3)元組的訪問
4)元組的增刪改
5)元組的 * 和 + 操作
三、字典
1)字典的概念
2)字典的創建
3)字典的訪問
4)字典添加鍵
5)字典刪除鍵
6)字典修改鍵
列表是Python中內置有序可變序列,列表的所有元素放在一對中括號“[ ]”中,並使用逗號分隔開。
當列表元素增加或刪除時,列表對象自動進行擴展或收縮內存,保證元素之間沒有縫隙。
一個列表中的數據類型可以各不相同,可以同時分別為整數、實數、字符串等基本類型,甚至是列表、元組、字典、集合以及其他自定義類型的對象。
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
List2 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"]
List3 = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5]
List4 = [1, "a", 1.1]例1.1
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for i in range(len(List1)): print(List1[i], end='\t')輸出
例1.2
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出

例1.3
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] List1.append(6) List1.append(7) for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
例1.4
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] List1.insert(0, "a") # 索引位置為 0 的地方添加 "a" List1.insert(len(List1) - 1, "b") # 索引位置為 6 - 1 = 5 的位置添加 "b" for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
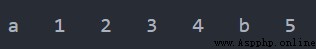
例1.5
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] List1.pop(0) # 刪除第一個元素 List1.pop(len(List1) - 1) # 刪除最後一個元素 for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
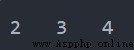
例1.6
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] List1.remove(2) # 刪除元素 2 List1.remove(4) # 刪除元素 4 for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
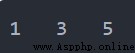
例1.7
List1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] List1[0] = "a" # 第一個元素改為 a List1[len(List1) - 1] = "b" # 最後一個元素改為 b for item in List1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
例1.8
List1 = [1] List2 = [2, 3, 4, 5] List1 = List1 * 5 for item in List1: print(item, end='\t') print() List3 = List1 + List2 for item in List3: print(item, end='\t')輸出
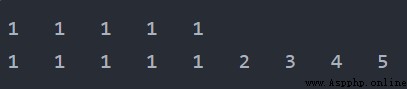
元組和列表類似,但屬於不可變序列,元組一旦創建,用任何方法都不可以修改其元素。
元組的定義方式和列表相同,但定義時所有元素是放在一對圓括號“()”中,而不是方括號。
tuple1 = (1,)
tuple2 = ("a", "b", "c", "d", "e")
tuple3 = (1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5)
tuple4 = (1, "a", 1.1)例2.1
tuple1 = (1) tuple2 = ("a") tuple3 = (1,) print(type(tuple1), type(tuple2), type(tuple3), sep=" . ") # 以 . 為分割 打印輸出輸出

例2.2
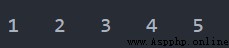
tuple1 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) for i in range(len(tuple1)): print(tuple1[i], end='\t')輸出
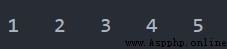
例2.3
tuple1 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) for item in tuple1: print(item, end='\t')輸出
元組屬於不可變序列,不能做修改!!!
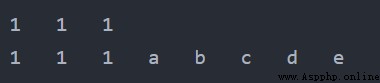
例2.4
tuple1 = (1,) tuple2 = ("a", "b", "c", "d", "e") tuple1 = tuple1 * 3 for item in tuple1: print(item, end='\t') print() tuple3 = tuple1 + tuple2 for item in tuple3: print(item, end='\t')輸出
字典是無序可變序列,由鍵、值組成,鍵必須是唯一的,但值則不必。
定義字典時,每個元素的鍵和值用冒號分隔,元素之間用逗號分隔,所有的元素放在一對大括號“{}”中。
字典中的鍵可以為任意不可變數據,比如整數、實數、復數、字符串、元組等等。
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"}
dict2 = {1: "a", 2: "b"}
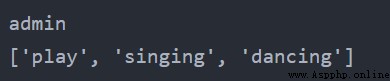
dict3 = {1.1: 1, 1.2: 2}例3.1
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456", "hobby": ["play", "singing", "dancing"]} print(dict1["name"]) print(dict1["hobby"]) 輸出
例3.2
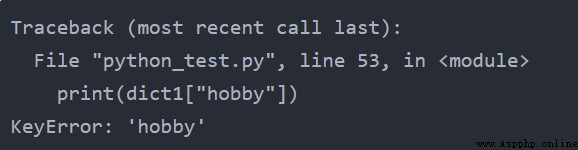
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"} print(dict1["hobby"])輸出
例3.3
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"} res = dict1.get("name", "沒有該鍵") print(res) # 有該鍵,正常打印對應的值 res = dict1.get("hobby", "沒有該鍵") print(res) # 沒有該鍵,打印 沒有該鍵輸出
例3.4
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"} print(dict1) dict1["hobby"] = ["play", "singing"] print(dict1)輸出
例3.5
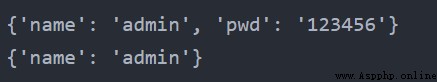
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"} print(dict1) del dict1["pwd"] print(dict1)輸出
例3.6
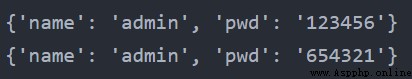
dict1 = {"name": "admin", "pwd": "123456"} print(dict1) dict1["pwd"] = "654321" print(dict1)輸出
The end ……
原創不易,轉載請標明出處。
對您有幫助的話可以一鍵三連,會持續更新的(嘻嘻)。