Recently, I found that many friends around me are not happy to use pandas, Switch to other data operation Libraries , As a data worker , Basically open your mouth pandas, Closed mouth pandas 了 , So I wrote this series to make more friends fall in love with pandas.
Series article description :
Series name ( Serial number of series articles )—— This series of articles specifically address the needs
platform :
Recently I was reading a book about using pandas A book for data processing , On 2020 Published in , There is a section on the statistical data processing of online retail goods , Each order and each item is recorded separately , Therefore, when you only care about orders, you will find that there are multiple same order numbers , This article discusses how to count the monthly order quantity . The data is read as follows :
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('Online_Retail.csv.zip', parse_dates=['InvoiceDate'])
df_new = df.dropna().copy()
# Lending month
df_new['YearMonth'] = df_new['InvoiceDate'].map(lambda x: 100 * x.year + x.month)
ps: Data acquisition method :
github:
https://github.com/lk-itween/FunnyCodeRepository/raw/main/PandasSaved/data/Online_Retail.csv.zip
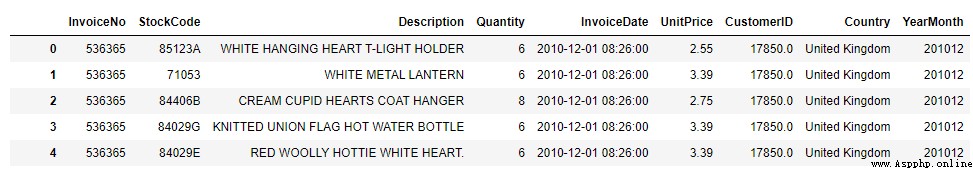
(406829, 9)
Because only the order number is concerned , Repeated order numbers will make the data statistics inaccurate , The order number needs to be de duplicated before statistics .
df_new.groupby('InvoiceNo')['YearMonth'].unique().value_counts().sort_index()
pandas from 2020 It has been updated many times since its development in , The methods in the previous book may not be implemented , In this case, the following error reports will be generated , The reason is unique() After execution, each row of data is of list type ,value_counts Can't handle .

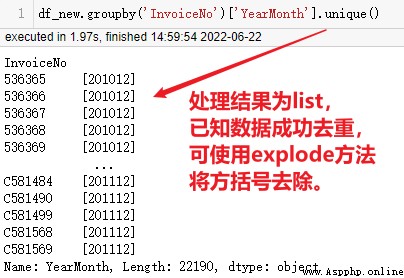
Change the code as follows to complete the requirements .
df_new.groupby('InvoiceNo')['YearMonth'].unique().explode().value_counts().sort_index()
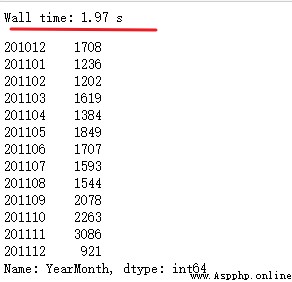
( Manual watermark : original CSDN The fate of the sleepers ,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46281427?spm=1011.2124.3001.5343 , official account A11Dot send )
df_new.groupby('InvoiceNo')['YearMonth'].value_counts().reset_index(name='count')['YearMonth'].value_counts().sort_index()
first value_counts The function of is to YearMonth duplicate removal , The required column name is already used as an index , adopt reset_index Reset index to column data , Right again YearMonth Conduct value_counts Count the monthly order volume .
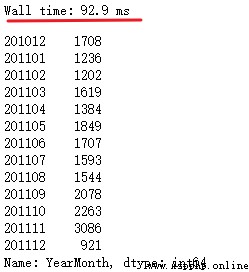
On the same computer , This method is faster than the method mentioned in the book , Probably unique It takes some time to process , However, this treatment complicates the thinking ,pandas De reprocessing can be used directly drop_duplicates.
df_new[['InvoiceNo', 'YearMonth']].drop_duplicates()['YearMonth'].value_counts().sort_index()
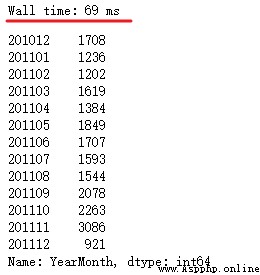
Compare the first two methods , The code is a lot shorter , Processing time is also reduced .
This article introduces the examples in the book , Reproduce the code in the book , Combined with existing data processing methods , Step by step optimize the way your code is handled , Explain the similarities and differences of each method , Complete data requirements . The source data can be obtained at the beginning of the article .
Watch the sky , Listen to the wind and rain at dawn .
Made on June 22, 2002