Java The essential function of constructors is to initialize objects , That is, initialize the instance variable , Assign initial value to ;
Instead of creating objects , Create objects by new Keyword , When using new Keyword will open up a block of memory in the heap memory for the object , Just wait for the constructor to initialize this memory , Assign initial values to instance variables . It is the default value before the initial value is assigned . The constructor in the code is different from the constructor after compilation , The compiled constructor contains more .
Constructors can be used to initialize member variables when initializing objects .
public class mystudent {
Integer age;
String name;
public static String addr = "beijing";
mystudent(Integer age,String name){
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
Constructors , Is used to initialize member variables age and name Of .
there age, And name Is instance variable , Class cannot be called directly , Can only be called through an object .
however addr yes Static variables , Class can be called directly
mystudent.addrThe difference between static variables and instance variables is :
python There is no constructor , But there are __new__ And __init__
__new__ Create objects
__init__ Initialize object
Python Class variables 、 example ( member ) Variables and local variables
Original address :
Python Class variables 、 example ( member ) Variables and local variables _ Green fruit HA The blog of -CSDN Blog
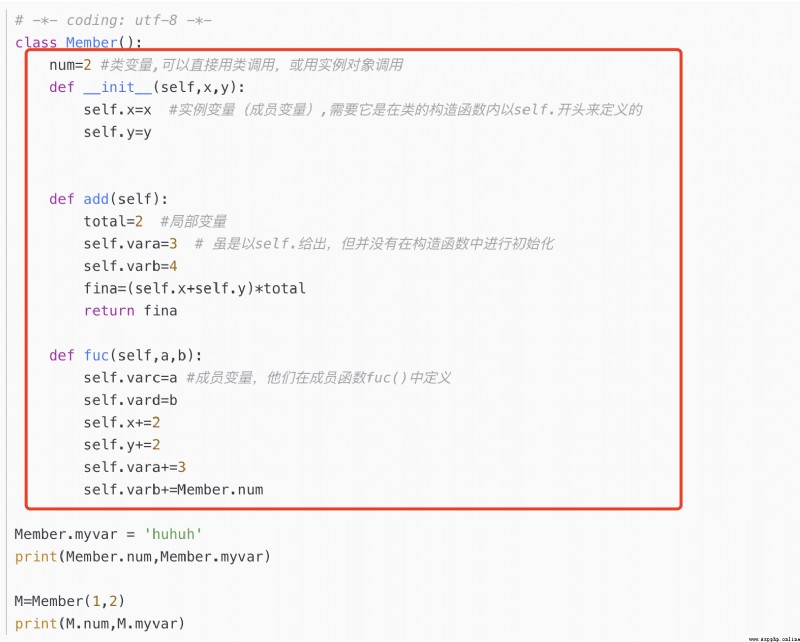
Here are two ways to define class variables 、 Two ways to read 、 The calling method in the class
Definition
1. Defined in class , And Constructors 、 A normal function is a level indented function .( In the following example num)
2. Defined outside the class , Direct use Class name . Variable name New class variable .( In the following example myvar)
Read
1. Directly use the attribute of the class name obtain : Class name . Class variables ( In the following example Member.num and Member.myvar)
2. Instantiate the class first , Instantiate the properties of the object obtain : Instance object . Class variables ( In the following example M.num and M.myvar)
call
1. Call in class : Class name . Class variables , You cannot use class variables directly , Shall be Member.num instead of num
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
class Member():
num=2 # Class variables , You can call... Directly with a class , Or call... With an instance object
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x # Instance variables ( Member variables ), It needs to be in the constructor of the class self. It's defined at the beginning
self.y=y
def add(self):
total=2 # local variable
self.vara=3 # Although self. give , But it is not initialized in the constructor
self.varb=4
fina=(self.x+self.y)*total
return fina
def fuc(self,a,b):
self.varc=a # Member variables , They are in member functions fuc() In the definition of
self.vard=b
self.x+=2
self.y+=2
self.vara+=3
self.varb+=Member.num
Member.myvar = 'huhuh'
print(Member.num,Member.myvar)
M=Member(1,2)
print(M.num,M.myvar)
(1) Member variables in the constructor :
Definition : stay __init__(self, Member variables )
Read : Only instance objects . Member variables , Cannot class name . Member variables , That is only M.x You can't Member.x
call : Constructor member variables , seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function : When instantiating a class , You need to assign a value to this variable . Ordinary functions in the class can directly call this variable , The way is :self. Member variables ,
Scope of action : Class , Its value can be modified by other functions
(2) Member variables in ordinary functions
Definition : Ordinary functions in classes def xxx(self, Member variables )
Read : Only instance objects . Member variables , Cannot class name . Member variables , That is only M.vara You can't Member.vara
call : The way is self. Member variables , The normal function is called only after the class is instantiated , here , This member variable will generate , See the following example : Must call first add After the function ,fuc Function self.vara and self.varb Will be executed normally , Don't complain .
Scope of action : Class , Its value can be modified by other functions
Local variables are relatively simple , Follow those who are not in the class def The local variables of a function are the same .
Scope of action : Inside the function
summary : Member functions
1. Difference
(1) Member variables in the constructor , After class instantiation , You can use
(2) In a class, in a normal function Member variables , This function can only be called first , To use this member variable .
2. The same thing :
(1) In class , It's all global