Today let's walk into python In reptile urllib The world of Library !!
urllib The library contains four commonly used modules :
1. urllib.request
For opening and reading URL
2. urllib.error
contain urllib.request Exception thrown
3. urllib.parse
For parsing URL
4. urllib.robotparser
analysis robot.txt file
urllib.request Defines some open URL Functions and classes of , Include authorization verification 、 Redirect 、 browser cookies etc. .
urllib.request Can simulate a browser request initiation process .
We can use urllib.request Of urlopen Method to open a URL, The syntax is as follows :
urllib.request.urlopen(url, data=None, [timeout, ]*, cafile=None, capath=None)
url:url Address .
data: Other data objects sent to the server , The default is None.
timeout: Set access timeout .
cafile and capath:cafile by CA certificate , capath by CA Path to certificate , Use HTTPS Need to use .
example :
from urllib.request import urlopen
URL = urlopen("https://www.baidu.com/")
print(URL.read())
Running results :
The above code uses urlopen Open Baidu's URL, And then use read() Function to get the HTML Entity code .
read() Function is used to read the contents of a web page , We can specify the read length .
example :print(URL.read(200))
except read() Out of function , It also contains the following two functions to read the contents of the web page :
from urllib.request import urlopen
URL = urlopen("https://www.baidu.com/")
myURL = URL.readlines()
for i in myURL:
print(i)

In addition to that urllib.request Module Reqquest The use of the class , Usually we use this class to simulate the header information of a web page . How to use it is as follows :
class urllib.request.Request(url, data=None, headers={}, origin_req_host=None, unverifiable=False, method=None)
url:url Address .
data: Other data objects sent to the server , The default is None.
headers:HTTP Requested header information , Dictionary format .
origin_req_host: Requested host address ,IP Or domain name .
unverifiable: Rarely use the whole parameter , Used to set whether the web page needs to be verified , The default is False.
method: Request method , Such as GET、POST、DELETE、PUT etc. .
urllib.error The module is urllib.request The exception thrown defines the exception class , The basic exception class is URLError.
urllib.error It contains two methods ,URLError and HTTPError.
URLError yes OSError A subclass of , Used to handle this exception when the program encounters a problem ( Or its derived exception ).
HTTPError yes URLError A subclass of , For handling special HTTP Error, such as when it is an authentication request , Included properties code by HTTP The status code , reason For the cause of the exception ,headers In order to cause HTTPError Specific to HTTP Requested HTTP Response head .
We use getcode() Function to get the web page status code .
Grab and handle exceptions for non-existent web pages .eg: return 200 Indicates that the web page is normal , return 404 It means that the web page does not exist .
Examples are as follows :
from urllib.request import urlopen
import urllib.request
URL1 = urlopen("https://www.baidu.com/")
print(URL1.getcode())
try:
URL2 = urlopen("https://www.baidu.com/1")
except urllib.error.HTTPError as a:
if a.code == 404:
print(404)
Running results :
urllib.parse For parsing URL, The format is as follows :
urllib.parse.urlparse(urlstring, scheme=’’, allow_fragments=True)
Use urllib.parse It can be parsed out URl The content of is a tuple , contain 6 A string : agreement (scheme), Location (netloc), route (path), Parameters (params), Inquire about (query), Judge (fragment).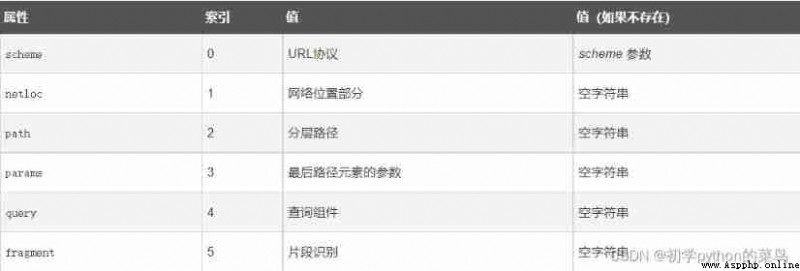
urllib.robotparser For parsing robots.txt file .
robots.txt It is stored in the root directory of the website robots agreement , It is usually used to tell search engines the rules for crawling websites .
There are still many deficiencies and points not mentioned in the article , Here we only have a general understanding , In the follow-up study, we will gradually deepen , Thank you for your support !