This article summarizes a few of my studies python In the process , Several super easy-to-use operations , Here to share , I'm sure you will like it very much , Directory as follows . Here you can ask for it in advance , Remember to watch it a little bit . These are just some of the techniques , I will share with you slowly in the future .
stay python You can use continuous assignment in , To assign values to multiple variables at once , There are mainly the following two ways .
# Multiple variables are assigned the same value
a = b = c = 8
print(a,b,c)
# Multiple variables are assigned different values
a, b, c = 1, 2, 3
print(a,b,c)
give the result as follows :
But there is a fallible point , I need your attention .
# What do you think the following results will be .
a = 6
a, b = 8, a
print(a,b)
give the result as follows :

Some people may think the result should be 8 and 8, But it's not . Because in continuous assignment statements, the right side of the equation is actually a local variable , Instead of the actual variable value itself . For example, in the above example , Dexter a, stay python When parsing , It's just a variable a Variable pointed to 6 Assign to b, instead of a=8 after a Result , This point is just beginning to learn python People may easily misunderstand . I really don't understand , At least you have to remember !
a, b = 6, 8
print(" Replace the previous a and b Value ", a, b, "\n")
a, b = b, a
print(" After replacement a and b Value ", a, b)
give the result as follows :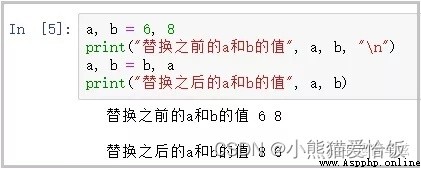
3. Merge dictionaries
This operation can merge the same keys in the dictionary , But the final value is not an additive operation , Instead, use the value in the key of this variable later .
x = {"a":1 ,"b":3}
y = {"b":2 ,"d":4}
z = {**x, **y}
print(z)
give the result as follows :
List derivation is used in daily programming , Play a very important role ( Especially with python When doing data cleaning ), It can simplify our code , It's very useful , Here I will summarize its usage for you .
① General form
x = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
y = [i**2 for i in x]
print(y)
give the result as follows :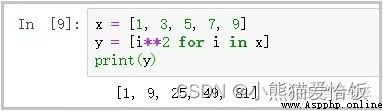
② belt if The list parsing formula of
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
y = [i for i in x if i % 2 == 0]
print(y)
give the result as follows :
③ belt if…else… The list parsing formula of
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
y = [" I'm even " if i % 2 == 0 else " I'm odd " for i in x]
print(y)
give the result as follows :
The following is an operation of string formatting , I believe you must have learned % and format String formatting for , But this f String formatting is also super easy to use , The performance is also higher than the former .
x = {"a":1, "b":2, "c":3, "d":4}
for key, value in x.items():
print(f"{key}:{value}")
give the result as follows :
6. Iterate over a list or array , Return element value and index
This operation is absolutely super easy to use , After we get the index value of the element , have access to if Conditions , Filter the elements .
x = [" Zhang San ", " Li Si ", " Wang Wu ", " Zhao Liu ", " Wang Wu "]
for index, value in enumerate(x):
if x[index] == " Wang Wu ":
print("\n"," Guess who I am , I am a :",x[index])
else:
print("\n"," I am not Wang Wu , I am a :",x[index])
give the result as follows :
① Segmentation of string
x = "my name is huang wei"
y = x.split(" ")
print(y)
x1 = "2020-02-02"
y1 = x1.split("-")
print(y1)
give the result as follows :
② String merging
x2 = ['my', 'name', 'is', 'huang', 'wei']
y2 = " ".join(x2)
print(y2)
x3 = ['2020', '02', '02']
y3 = "-".join(x3)
print(y3)
give the result as follows :
