choice() Method to return a list , Random items of tuples or strings .
Here are choice() The grammar of the method :
import random
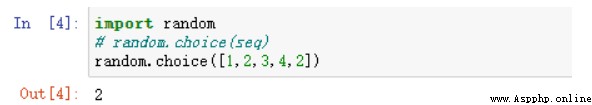
random.choice( seq )
Be careful :choice() It's not directly accessible , Import required random modular , And then through random Static objects call the method .
seq -- It could be a list , Tuples or strings .
Return random item .
Here's how to use choice() Examples of methods :
#!/usr/bin/python
import random
print "choice([1, 2, 3, 5, 9]) : ", random.choice([1, 2, 3, 5, 9])
print "choice('A String') : ", random.choice('A String')
The output of the above example is :
choice([1, 2, 3, 5, 9]) : 2
choice('A String') : n
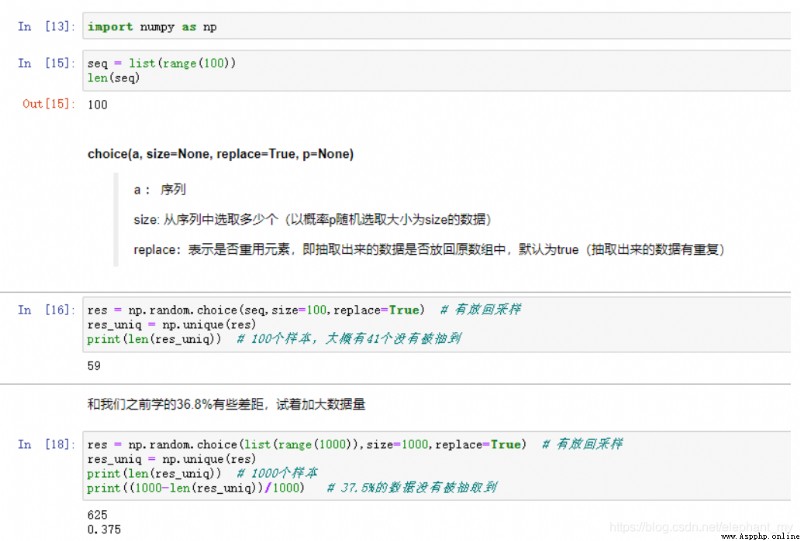
random.choice() function : From the given 1 Random sampling function in dimension group .
numpy.random.choice(a, size=None, replace=True, p=None)
a : If it's a one-dimensional array , It means random sampling from this one-dimensional array ; If it is int type , It means the from 0 To a-1 Random sampling in this sequence .
size : Number of sampling results , The default is 1. It can be an integer , Indicates the quantity to be sampled ; It can also be for tuple, Such as (m, n, k), Then the quantity to be sampled is m *n *k, size by (m, n, k).
replace : boolean type , Whether the sampled sample should be replaced ? I don't quite understand this place , We measured it and found that replace Designated as True when , The sampled elements will repeat ; When replace Designated as False when , Sampling does not repeat .
p : A one-dimensional array , Formulated the a The probability of sampling each element in , If default None, be a Each element in the has the same probability of being sampled .
Be careful :
replaceThe representative means whether to put it back after sampling , If it is False Words , Then the three numbers are different , If it is True Words , There may be repeated , Because the front one was put back .pThe number of median values must be equal to a The number of data in is consistent .
Return value :samples : single item or ndarray(The generated random samples)
ValueError:
If a is an int and less than zero, if a or p are not 1-dimensional, if a is an array-like of size 0, if p is not a vector of probabilities, if a and p have different lengths, or if replace=False and the sample size is greater than the population size
From size to 3 Of np.arange(5) Generate a uniform (p=None) A random sample of :
>>> np.random.choice(5, 3)
array([0, 3, 4])
>>> #This is equivalent to np.random.randint(0,5,3)
From size to 3 Of np.arange(5) Generate a Nonuniformity (p Valuable ) A random sample of :
>>> np.random.choice(5, 3, p=[0.1, 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0])
array([3, 3, 0])
From size to 3 Of np.arange(5) Generate a uniform A random sample of , There is no replacement ( repeat ):
>>> np.random.choice(5, 3, replace=False)
array([3,1,0])
>>> #This is equivalent to np.random.permutation(np.arange(5))[:3]
From size to 3 Of np.arange(5) Generate a Nonuniformity A random sample of , There is no replacement ( repeat ):
>>> np.random.choice(5, 3, replace=False, p=[0.1, 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0])
array([2, 3, 0])
The first parameter in the above example can be replaced by an arbitrary array , Not just integers . for example :
>>> aa_milne_arr = ['pooh', 'rabbit', 'piglet', 'Christopher']
>>> np.random.choice(aa_milne_arr, 5, p=[0.5, 0.1, 0.1, 0.3])
array(['pooh', 'pooh', 'pooh', 'Christopher', 'piglet'],
dtype='|S11')
In practice , First create a mask Variable , And then through mask To sample the data to be sampled :
mask = np.random.choice(split_size, batch_size)
captions = data['%s_captions' % split][mask]
image_idxs = data['%s_image_idxs' % split][mask]
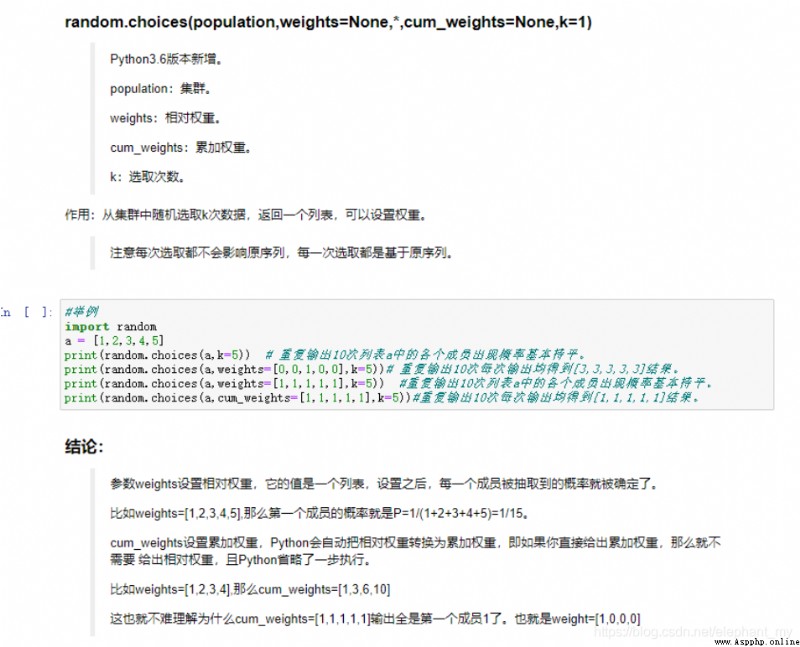
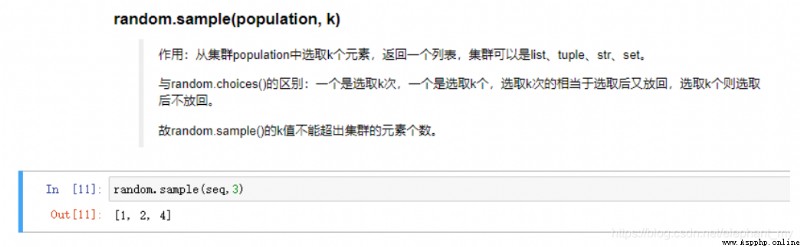
python in choice contrast ( stay numpy and random There have been ) Plus sample() Function comparison