os.getcwd()—— Get the current working directory , That is, the folder where the current program file is located
os.chdir(path)—— Change the current directory , Need to pass a new path
os.listdir(path)—— Returns the list of file names under the specified path
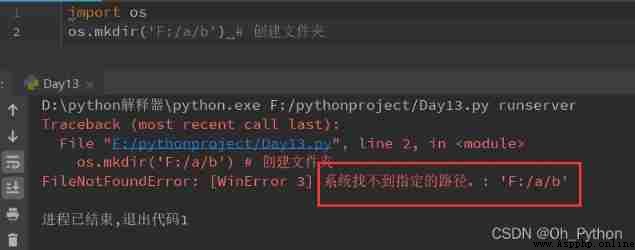
os.mkdir(path)—— Create a folder under a path , If the corresponding path cannot be found, an error will be reported
os.makedirs(path)—— Recursively create folders , Automatically create when path is not found
os.rmdir(path)—— Delete folder
os.remove(path)—— Delete file
os.removedirs(path)—— Recursively delete folders , All must be empty directories , If the folder is not empty, an error will be reported
os.rename( The old name , New name )—— File or folder rename
os.path.split(path)—— Divide the file path into folders and file names , And return it as a binary
os.path.abspath(path)—— return path The absolute path of normalization
os.path.join(path1,path2,……)—— Combine multiple paths and return , For example, the absolute path is obtained by combining the folder and the files inside
os.path.getsize(path)—— Return file size , In bytes
os.path.isfile(path)—— Determine whether the given path is a file , Yes, go back to True, Otherwise return to False
os.path.isdir(path)—— Determine whether the given path is a folder , Yes, go back to True, Otherwise return to False
2.1 os.getcwd()—— Get the current working directory , That is, the folder where the current program file is located
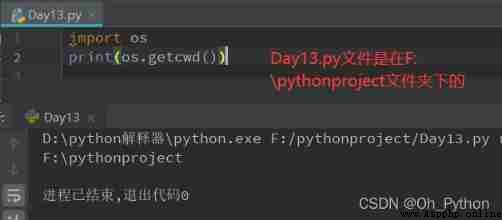
2.2 os.chdir(path)—— Change the current directory , Need to pass a new path
os.listdir(path)—— Returns the list of file names under the specified path
stay F Create one under the disk called “ File operations ” Folder , And create several working files in the folder
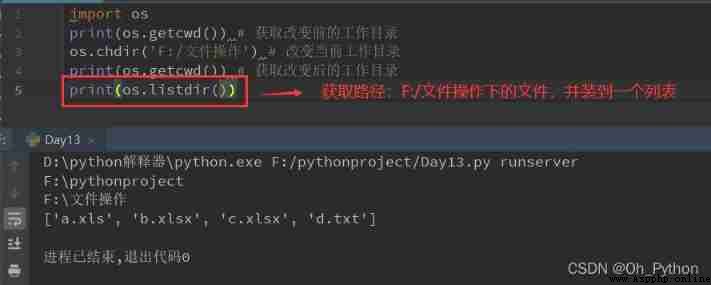
2.3 os.mkdir(path)—— Create a folder under a path , If the corresponding path cannot be found, an error will be reported
os.makedirs(path)—— Recursively create folders , Automatically create when path is not found
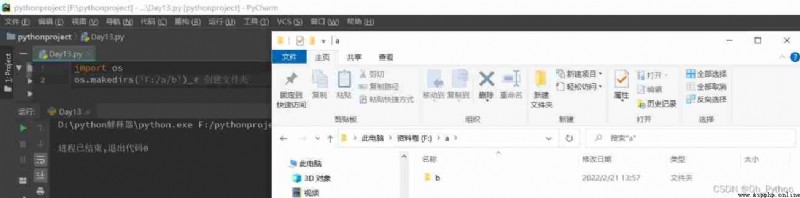
2.4 os.rename( The old name , New name )—— File or folder rename
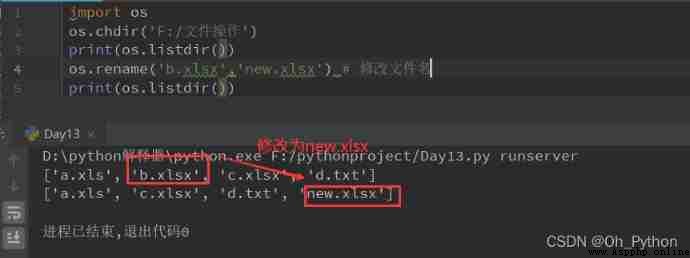
for example : lookup “F:\ File operations " All the files in the folder with xls or xlsx A file with a suffix name
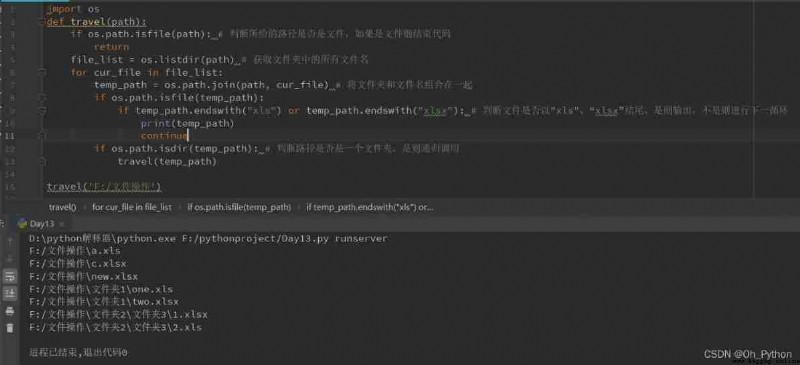
Attach the source code :
import os
def travel(path):
if os.path.isfile(path): # Determine whether the given path is a file , If it is a file, end the code
return
file_list = os.listdir(path) # Gets all the file names in the folder
for cur_file in file_list:
temp_path = os.path.join(path, cur_file) # Combine folder and file names
if os.path.isfile(temp_path):
if temp_path.endswith("xls") or temp_path.endswith("xlsx"): # Judge whether the file is in "xls"、“xlsx” ending , Yes, output , If not, proceed to the next cycle
print(temp_path)
continue
if os.path.isdir(temp_path): # Determine whether the path is a folder , If yes, recursively call
travel(temp_path)
travel('F:/ File operations ')1.1 It can be done by for...in... This kind of statement traverses the object that reads data, which is called an iteratable object
Iteratable object : character string 、 list 、 Tuples 、 Dictionaries 、 aggregate
1.2 An object that satisfies the following conditions can be an iteratable object :
(1) Object implementation __iter__ Method (2)__iter__ Method returns the iterator object
1.3 for How the cycle works :
(1) Call... Internally on an iteratable object __iter__ Method , Get the iterator object
(2) Call again and again through the iterator object __next__ Method to get the iteration result
1.4 Determine whether an object can be iterated
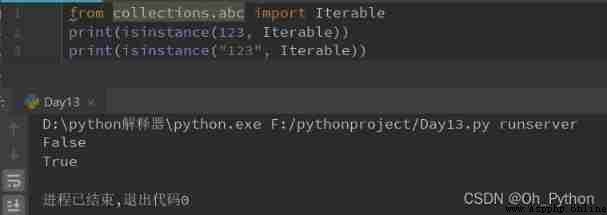
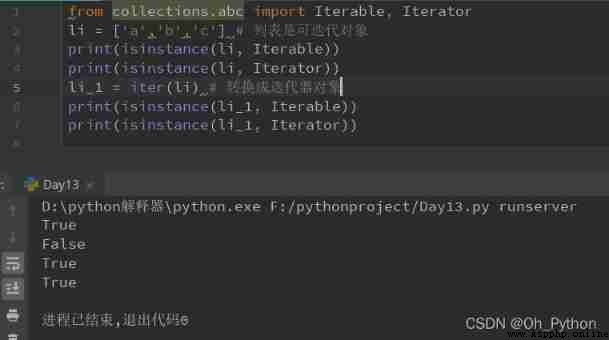
Imported modules :from collections.abc import Iterable
Code :isinstance( object ,Iterable), If the object is iteratable, returns True, Otherwise return to False
An iterator is an object that remembers the traversal location . The iterator object is accessed from the first element of the collection , Until all elements are accessed . Iterators can only move forward and not backward .
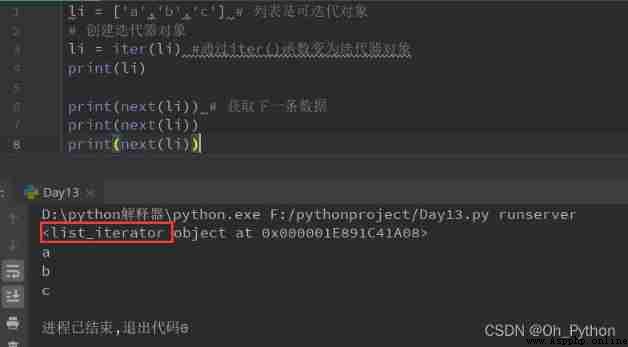
The iterator has two functions :iter() and next()
adopt iter() Function to get iterators of iteratable objects :
The above code can also be written as :
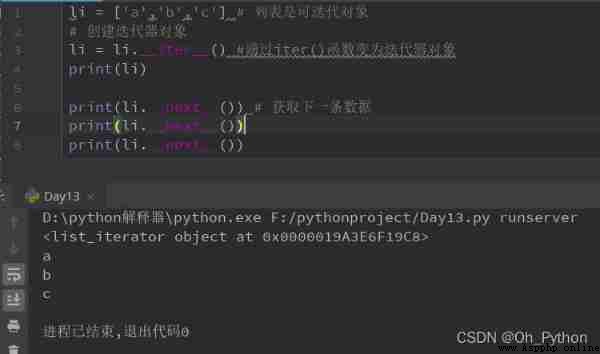
(1)iter() Calling the __iter__ Method , And put __iter__ Method as its own return value
(2) Reuse next() Function to call __next__ Method
When the element is retrieved , Reuse next() When the next piece of data is obtained, a StopIteration abnormal
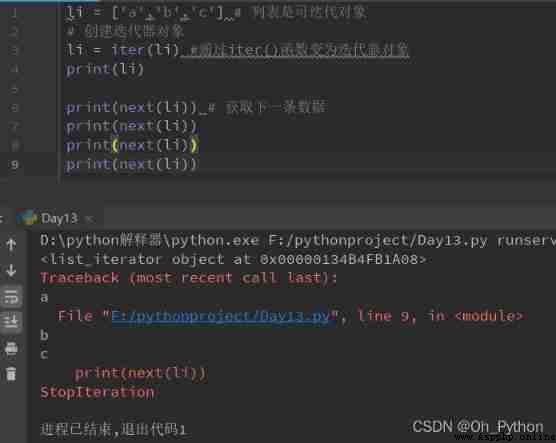
In depth analysis of :
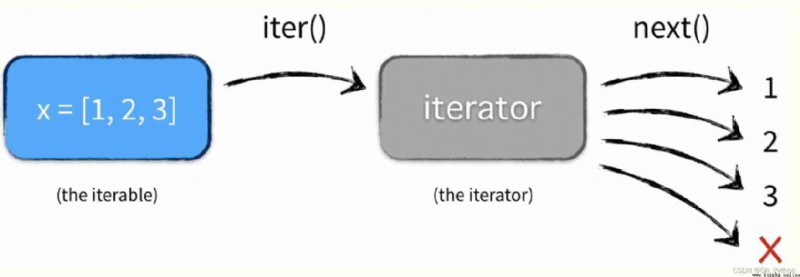
Through the first iter() Function gets an iterable object Iterable The iterator , The obtained iterator is then called again and again next() Method to get the next value and assign it to item, When you meet StopIteration The loop ends after the exception of .
Iteratable object :iterable Iterator object :iterator
(1) Iteratable objects can pass through __iter__() Method becomes an iterator object
(2) If an object has iter() Method , Is an iterable object ; If an object has next() Method , It's an iterator object
(3) Define iteratable objects , Must be realized iter() Method ; Define iterator , Must be realized iter Methods and next Method
Conditions :
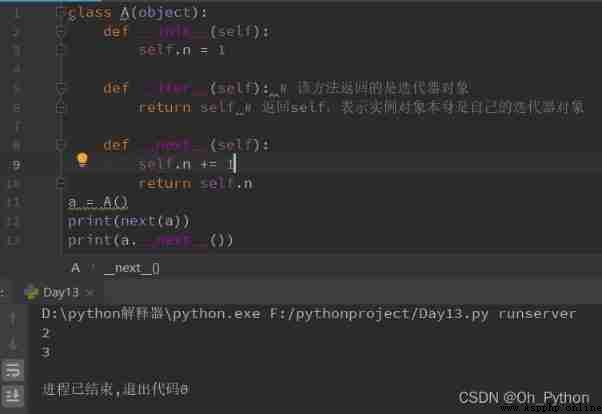
(1) Yes iter Method , Returns the iterator object itself
(2) Yes next Method , Returns the next element of the container or can be thrown StopIteration abnormal
Example 1 :
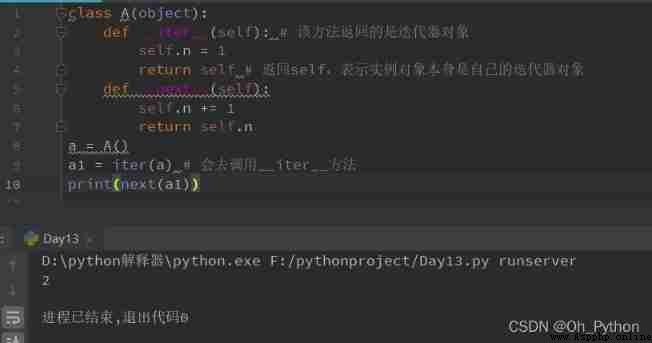
The above code can be rewritten as :
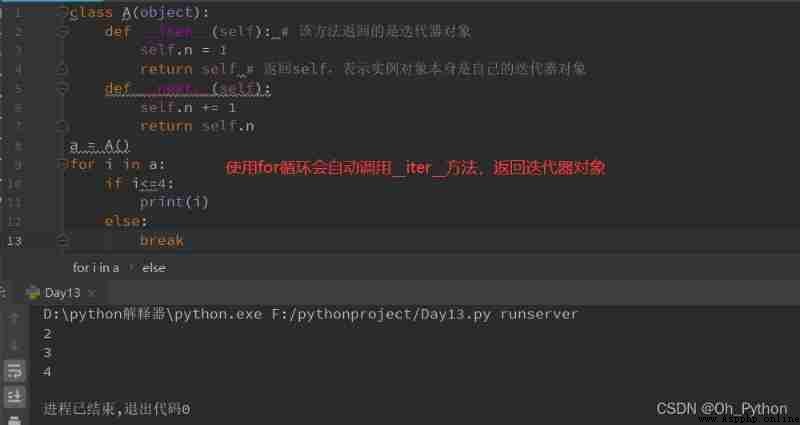
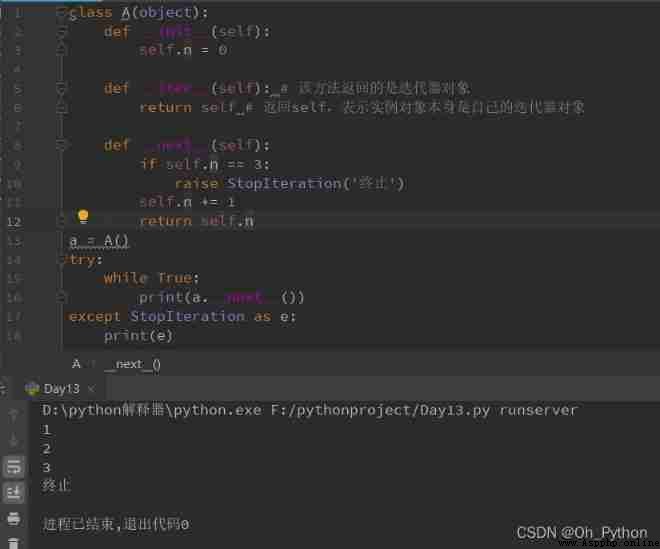
Example 2 :
Example 3 :
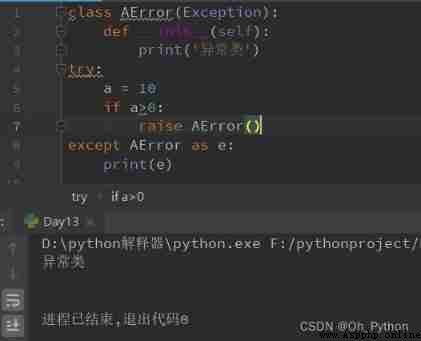
Custom exception classes , Need to inherit Exception class . As long as the defined class inherits from Exception, This class is an exception class .
Example 1 :
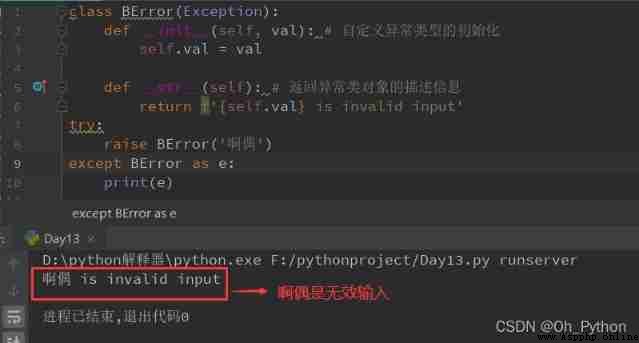
Example 2 :
generator :python Provides a very simple syntax that allows us to write our own iterators
Just... Again def There is yield keyword Is called a generator
Define the way : Similar to the list derivation , Deduce the list [] Change it to ()
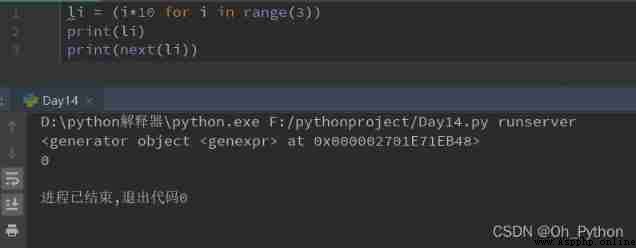
Generator function :python in , Used yield The function becomes a generator (generator)
(1) Ordinary function : Return value with return, Generator functions use yield sentence
(2)yield Statement returns one result at a time , In the middle of each result , Suspend function , So that the next time from where it left to continue
(3)yield The effect interrupts the function . And save the interrupt state
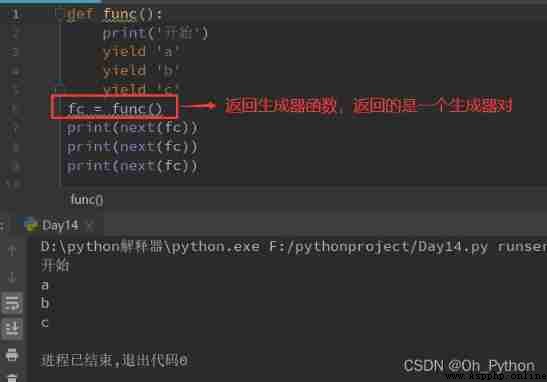
The above code can be rewritten as :
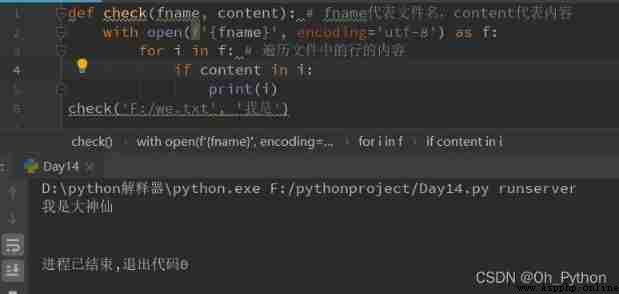
give an example :
Processing documents : The user specifies the file and content to find , Print out every line of the content to be checked in the file .
step :
1、 Write a function , Parameters are files and contents
2、 File operations ——open() function
3、 Find content
4、 Output after finding
Concrete realization :
1、 stay F Create a notepad file on the disk and write the contents
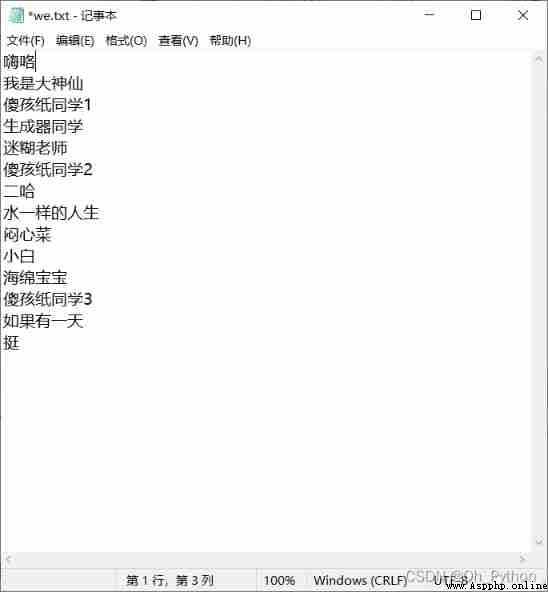
2、 Code implementation
