Preface
Create index
pd.Index
pd.IntervalIndex
pd.CategoricalIndex
pd.DatetimeIndex
pd.PeriodIndex
pd.TimedeltaIndex
Reading data
set_index
reset_index
set_axis
Operation line index
Operation column index
rename
The dictionary form
Function form
Use cases
Count the total consumption by day
By day 、 Gender statistics mean tips , Total consumption
Stupid method
summary
PrefaceThis article mainly introduces Pandas Row and column indexes in 4 Multiple function operations :
set_index
reset_index
set_axis
rename
Create indexA quick review Pandas Common methods of creating indexes :
pd.IndexIn [1]:
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npIn [2]:
# Specify the type and name s1 = pd.Index([1,2,3,4,5,6,7], dtype="int", name="Peter")s1Out[2]:
Int64Index([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], dtype='int64', name='Peter')pd.IntervalIndexNew interval index IntervalIndex Usually use interval_range() Function to construct , It uses data or numerical intervals , Basic usage :
In [3]:
s2 = pd.interval_range(start=0, end=6, closed="left")s2Out[3]:
IntervalIndex([[0, 1), [1, 2), [2, 3), [3, 4), [4, 5), [5, 6)], closed='left', dtype='interval[int64]')pd.CategoricalIndexIn [4]:
s3 = pd.CategoricalIndex( # Data to be sorted ["S","M","L","XS","M","L","S","M","L","XL"], # Specify the classification order categories=["XS","S","M","L","XL"], # Demand arrangement ordered=True, # Index name name="category")s3Out[4]:
CategoricalIndex(['S', 'M', 'L', 'XS', 'M', 'L', 'S', 'M', 'L', 'XL'], categories=['XS', 'S', 'M', 'L', 'XL'], ordered=True, name='category', dtype='category')pd.DatetimeIndexIndexed by time and date , adopt date_range Function to generate , Specific examples are :
In [5]:
# Date as index ,D On behalf of heaven s4 = pd.date_range("2022-01-01",periods=6, freq="D")s4Out[5]:
DatetimeIndex(['2022-01-01', '2022-01-02', '2022-01-03', '2022-01-04','2022-01-05', '2022-01-06'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')pd.PeriodIndexpd.PeriodIndex It is an index for periodic data , It is convenient to process data with a certain period , The usage is as follows :
In [6]:
s5 = pd.PeriodIndex(['2022-01-01', '2022-01-02', '2022-01-03', '2022-01-04'], freq = '2H')s5Out[6]:
PeriodIndex(['2022-01-01 00:00', '2022-01-02 00:00', '2022-01-03 00:00','2022-01-04 00:00'], dtype='period[2H]', freq='2H')pd.TimedeltaIndexIn [7]:
data = pd.timedelta_range(start='1 day', end='3 days', freq='6H')dataOut[7]:
TimedeltaIndex(['1 days 00:00:00', '1 days 06:00:00', '1 days 12:00:00', '1 days 18:00:00', '2 days 00:00:00', '2 days 06:00:00', '2 days 12:00:00', '2 days 18:00:00', '3 days 00:00:00'], dtype='timedelta64[ns]', freq='6H')In [8]:
s6 = pd.TimedeltaIndex(data)s6Out[8]:
TimedeltaIndex(['1 days 00:00:00', '1 days 06:00:00', '1 days 12:00:00', '1 days 18:00:00', '2 days 00:00:00', '2 days 06:00:00', '2 days 12:00:00', '2 days 18:00:00', '3 days 00:00:00'], dtype='timedelta64[ns]', freq='6H') Reading data Let's pass a Simple data to explain 4 The use of a function . The data are as follows :
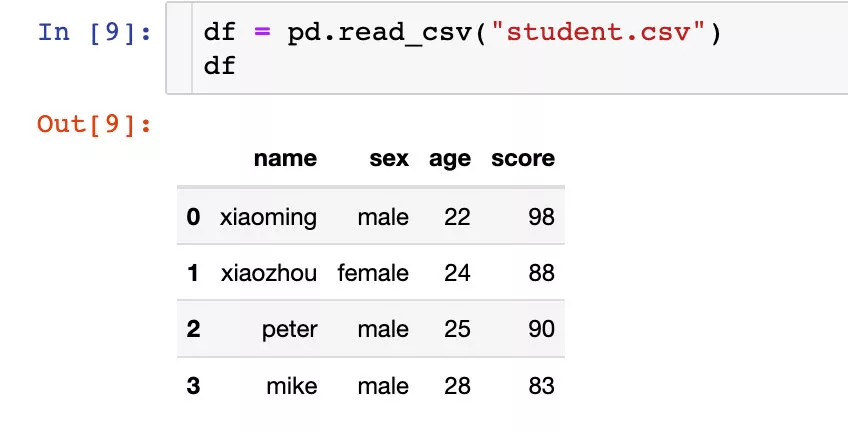
Set single level index
In [10]:
# Set single level index df1 = df.set_index("name")df1
We found that df1 The index of has become name Related values of fields .
Here's how to set up a multi-level index :
# Set two-tier index df2 = df.set_index(["sex","name"])df2
Reset the index :
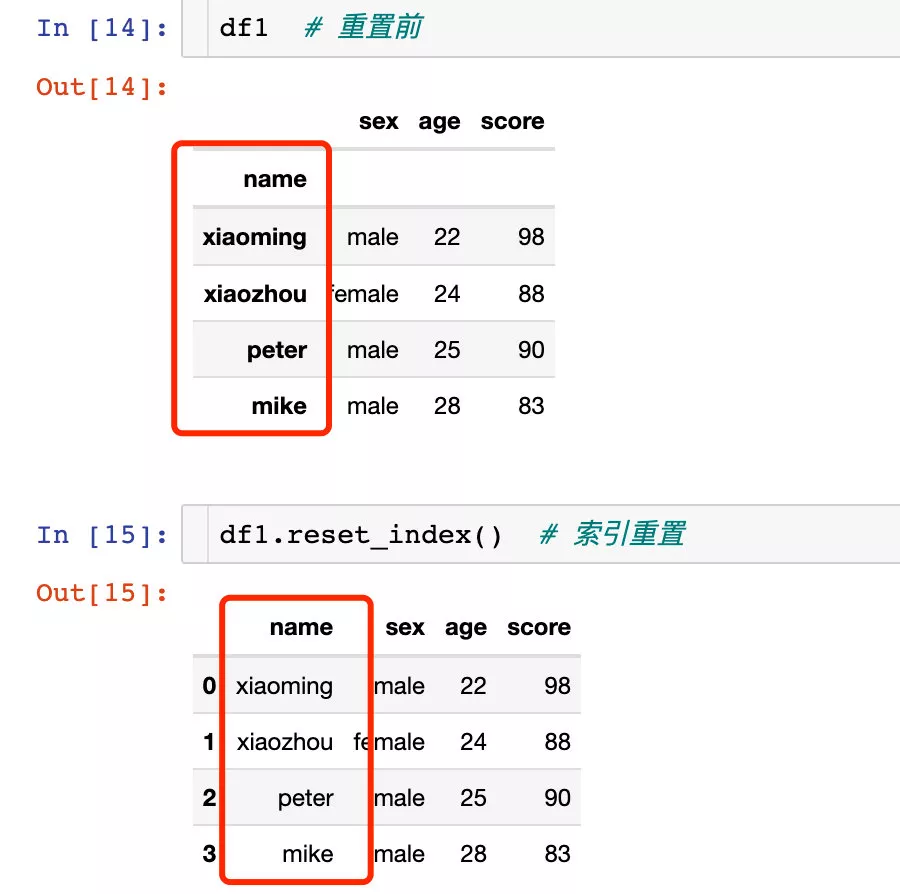
Reset for multi tier indexes :
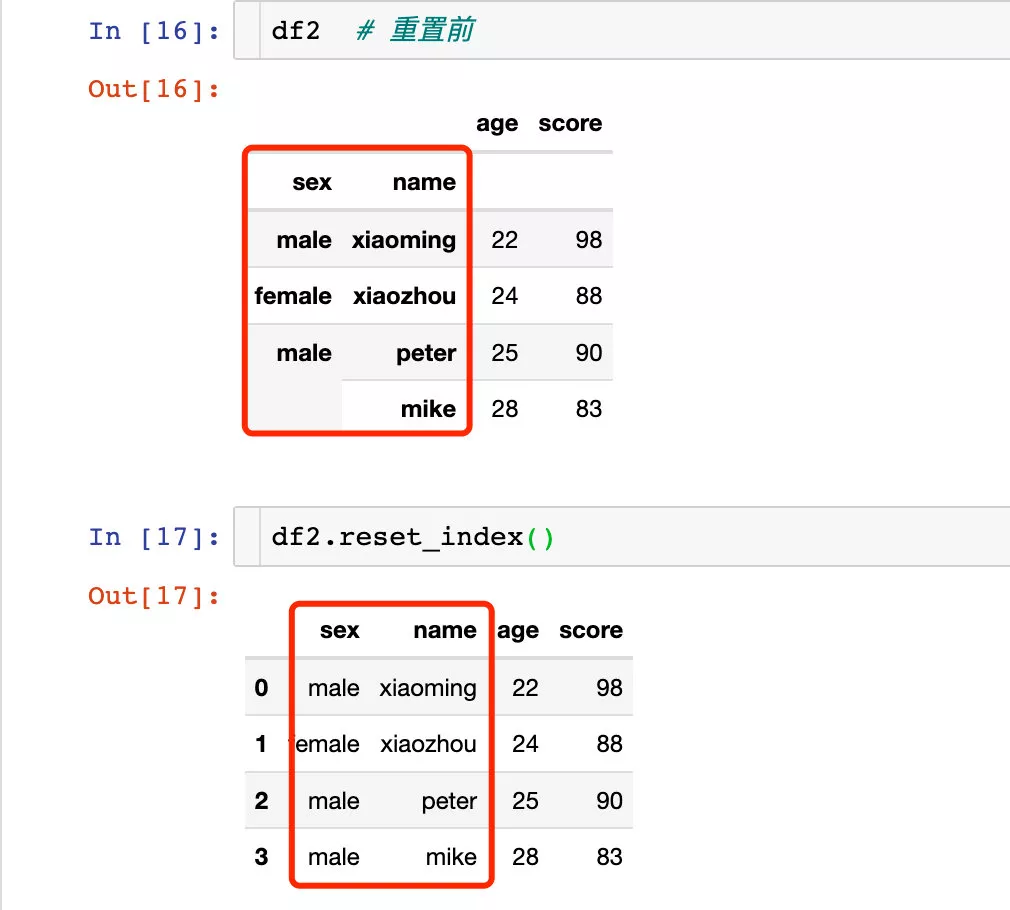
The multi-layer index is directly modified in situ :
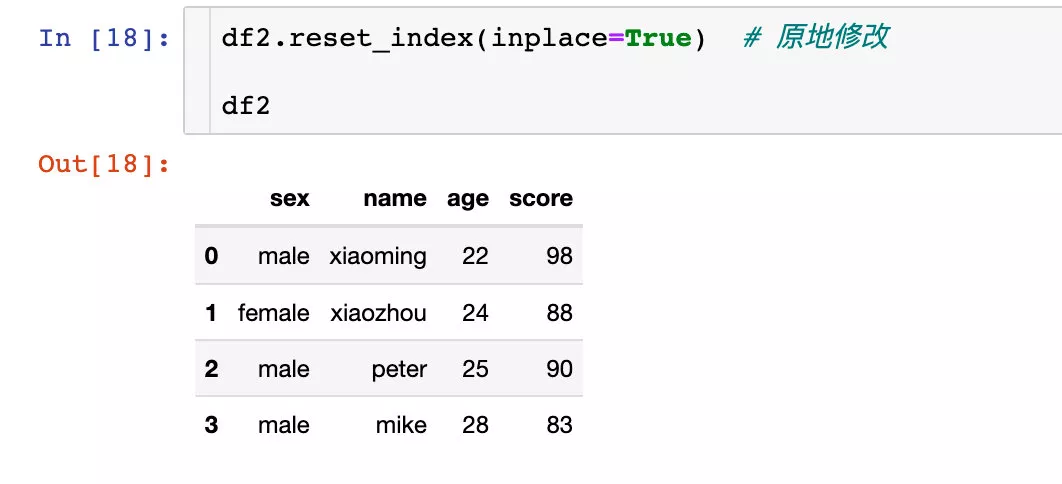
Assign the required data axis axis. among axis=0 Represents the direction of the bank ,axis=1 Represents the direction of the column .
Two different ways of writing :
axis=0 Equivalent to axis="index"axis=1 Equivalent to axis="columns" Operation line index 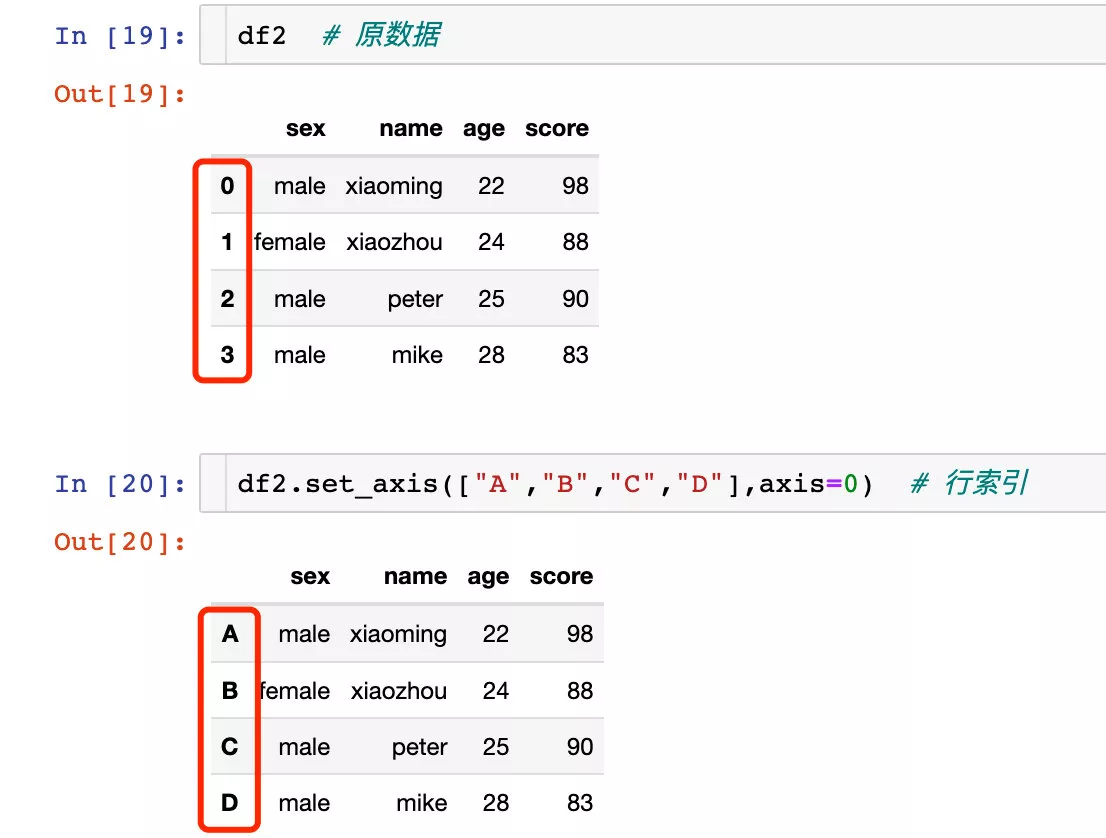
Use index The effect is the same :
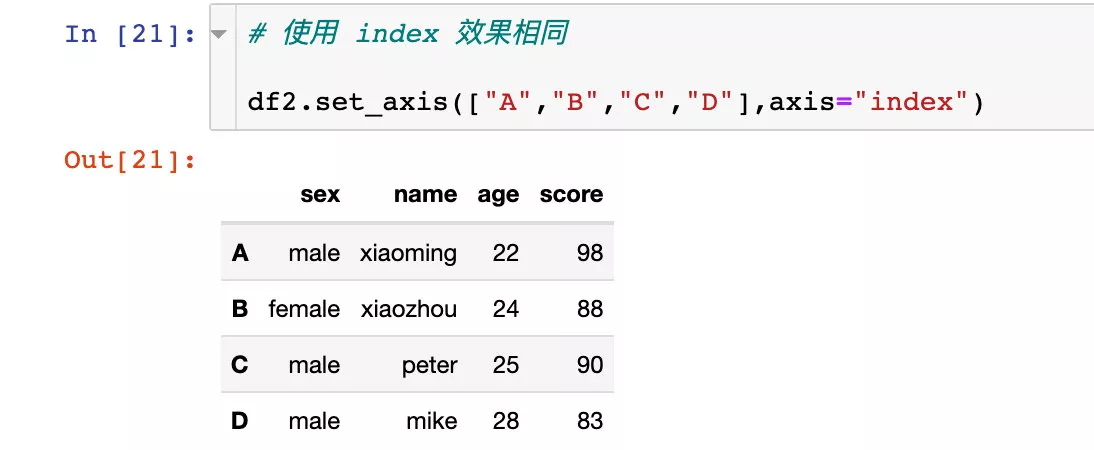
The original df2 There is no change . If we want the change to take effect , It can also be modified directly in situ :
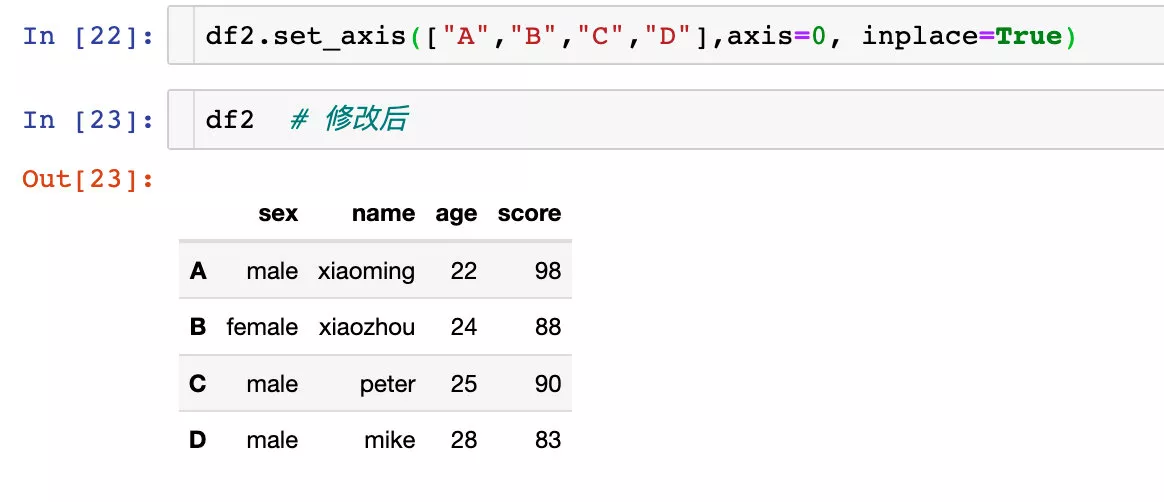
in the light of axis=1 perhaps axis="columns" Operation in direction .
1、 Directly pass in the new name we need to modify :

Use axis="columns" The effect is the same :
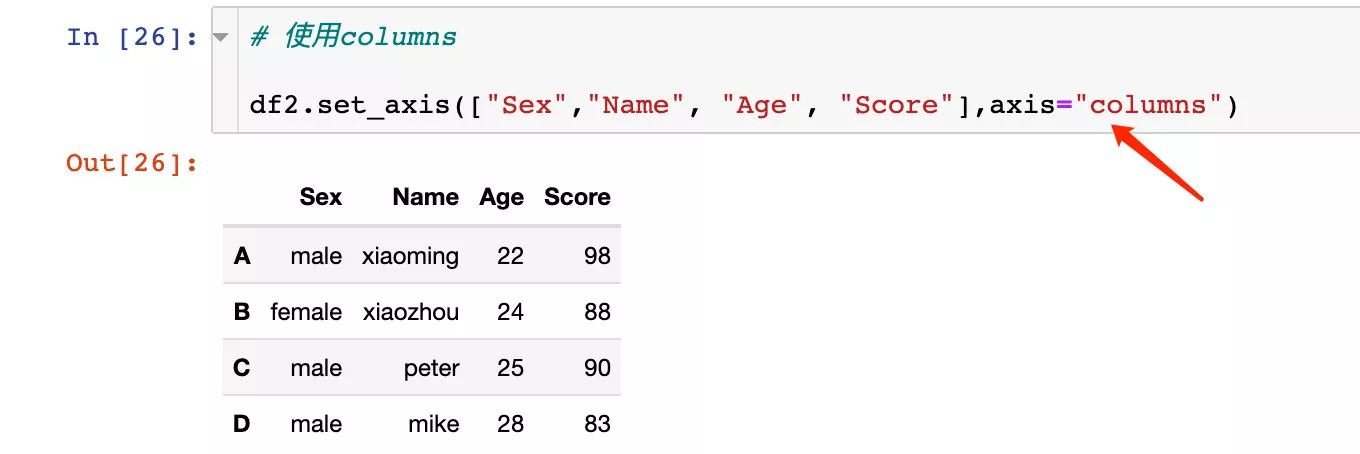
It can also be modified directly in situ :
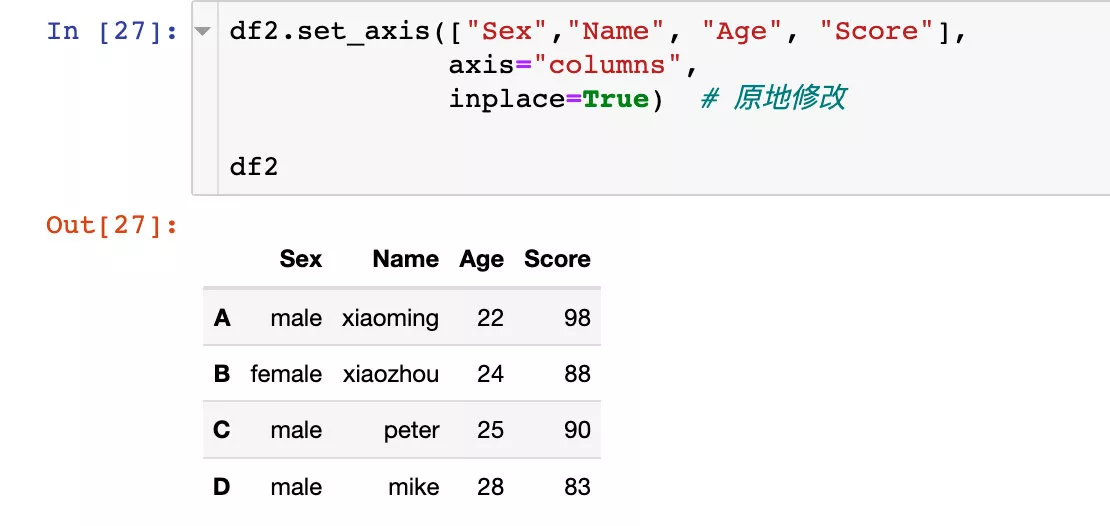
Rename the row index or column index , Suppose our raw data are as follows :

1、 Modify through the dictionary form of one or more attributes passed in :
In [29]:
# Modify the index of a single column ; Non in situ modification df2.rename(columns={"Sex":"sex"})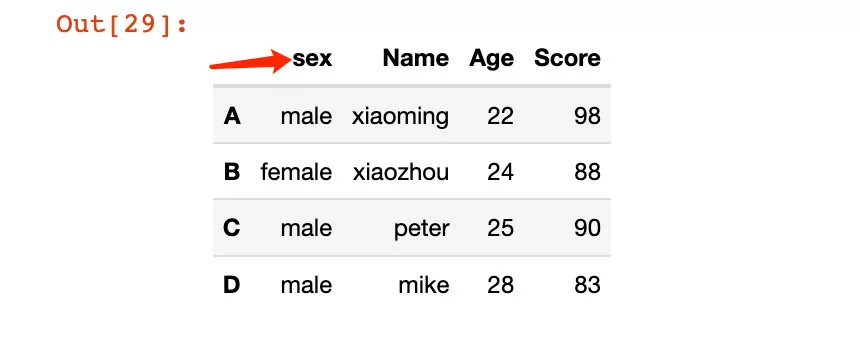
Modify the names of multiple column attributes at the same time :
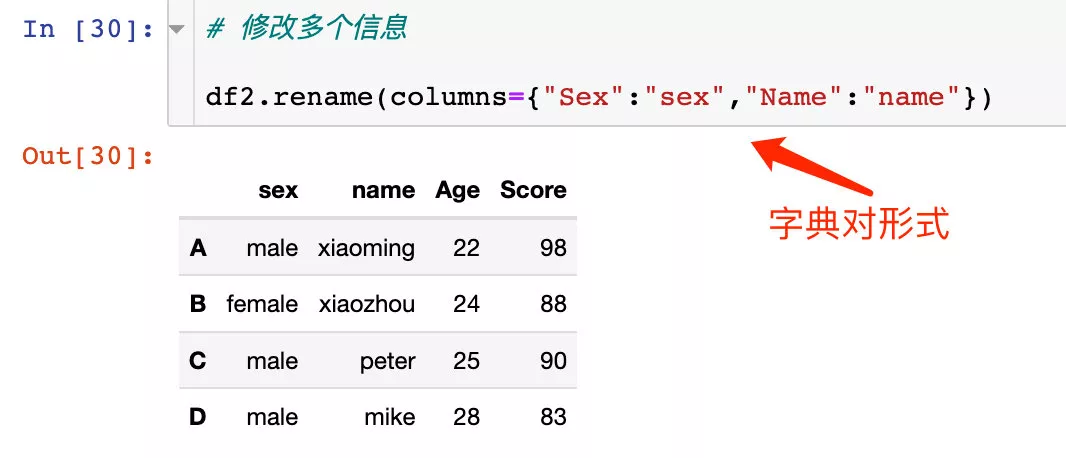
2、 Modify through the passed in function :
In [31]:
# Passing in functions df2.rename(str.upper, axis="columns")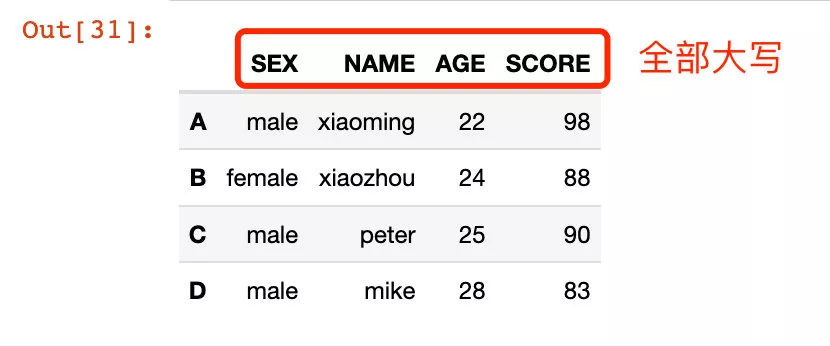
You can also use anonymous functions lambda:
# All in lowercase df2.rename(lambda x: x.lower(), axis="columns")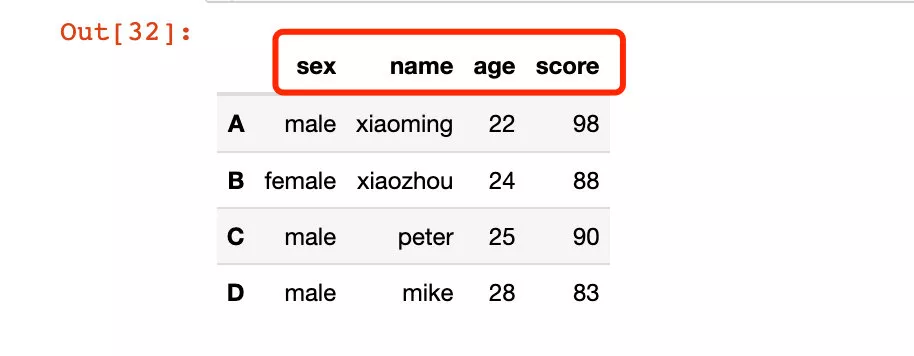
In [33]:
Here we use the visualization Library plotly_express Self contained data sets in the library tips:
import plotly_express as pxtips = px.data.tips() tips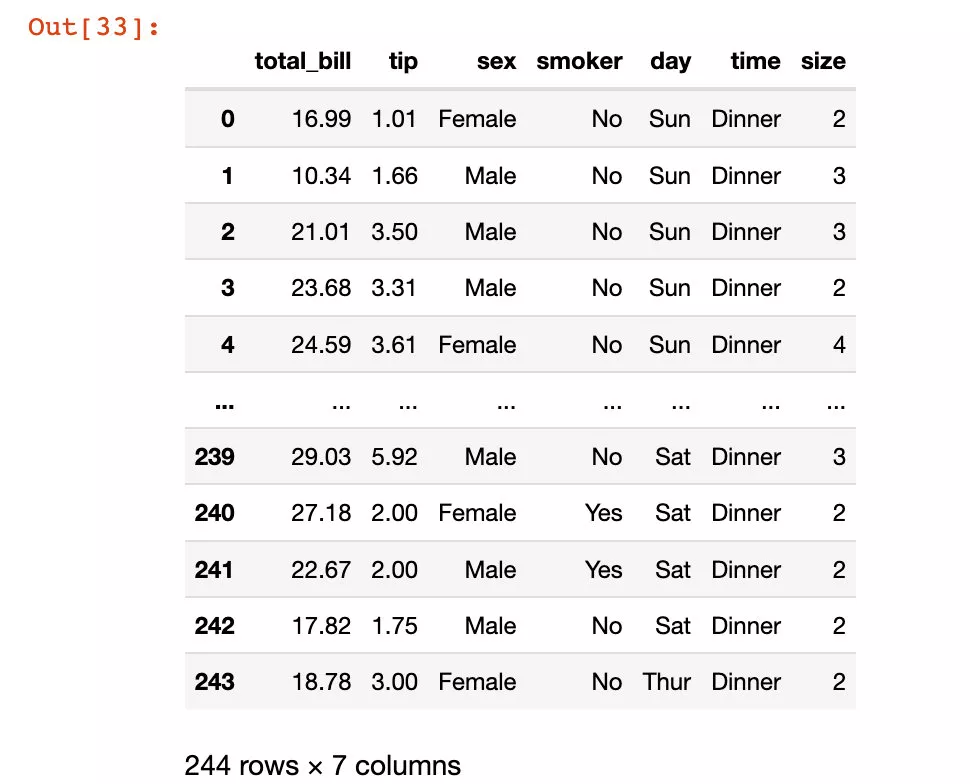
In [34]:
df3 = tips.groupby("day")["total_bill"].sum()df3Out[34]:
dayFri 325.88Sat 1778.40Sun 1627.16Thur 1096.33Name: total_bill, dtype: float64In [35]:
We found that df3 It's actually a Series Data of type :
type(df3) # Series Data of type Out[35]:
pandas.core.series.SeriesIn [36]:
So let's go through reset_index The function turns it into DataFrame data :
df4 = df3.reset_index()df4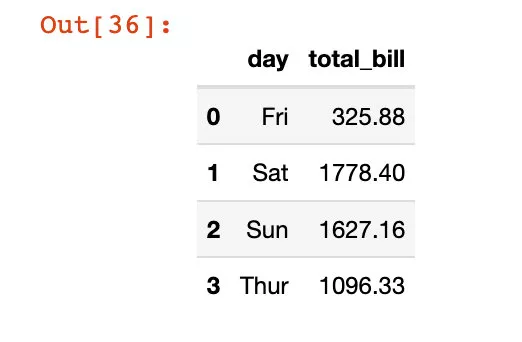
Let's rename the index in the column direction :
In [37]:
# Directly modify in situ df4.rename(columns={"day":"Day", "total_bill":"Amount"}, inplace=True)df4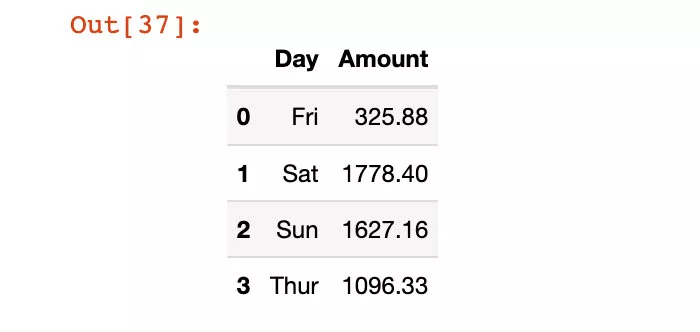
In [38]:
df5 = tips.groupby(["day","sex"]).agg({"tip":"mean", "total_bill":"sum"})df5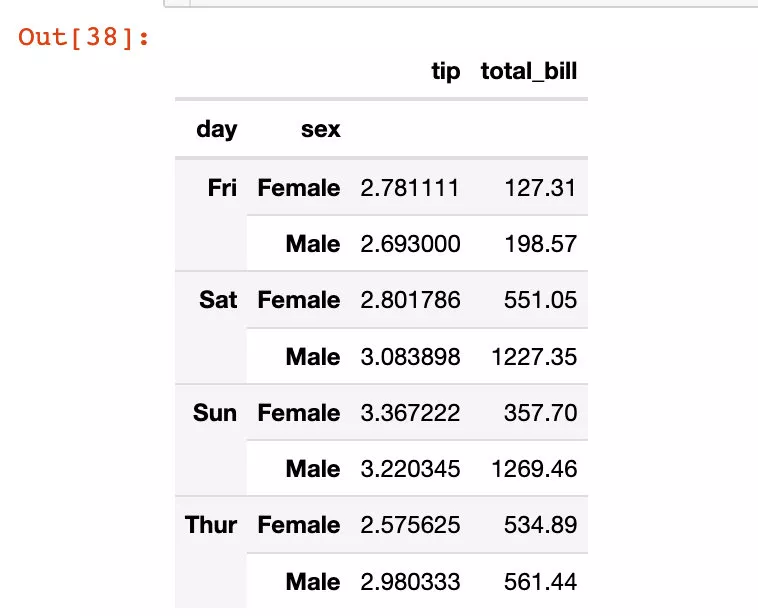
We found that df5 yes df5 Is a data frame with multiple indexes :
In [39]:
type(df5) Out[39]:
pandas.core.frame.DataFrameWe can choose to reset one of the indexes :
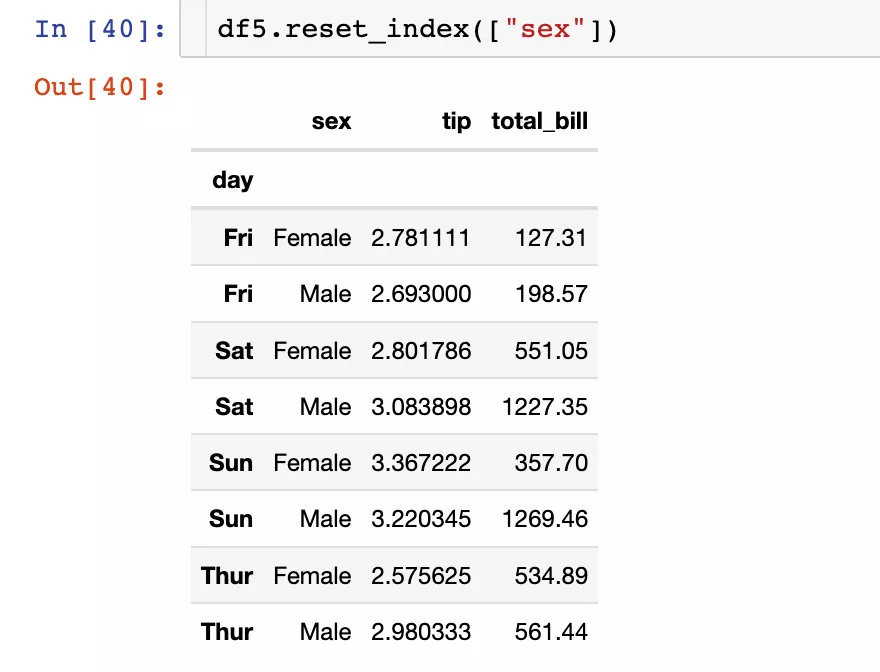
While resetting the index , Directly discard the original field information : Below sex The message was deleted
In [41]:
df5.reset_index(["sex"],drop=True) # Non in situ modification 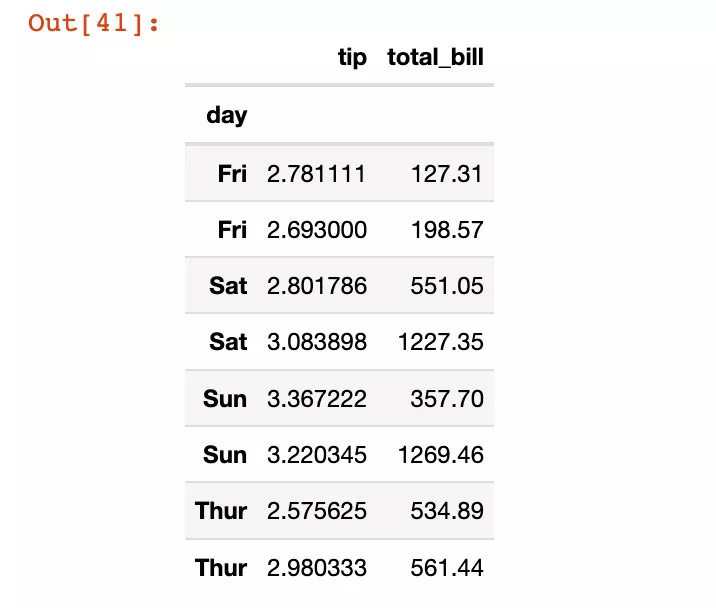
The index in the column direction is directly modified in place :
df5.reset_index(inplace=True) # Modify in place df5 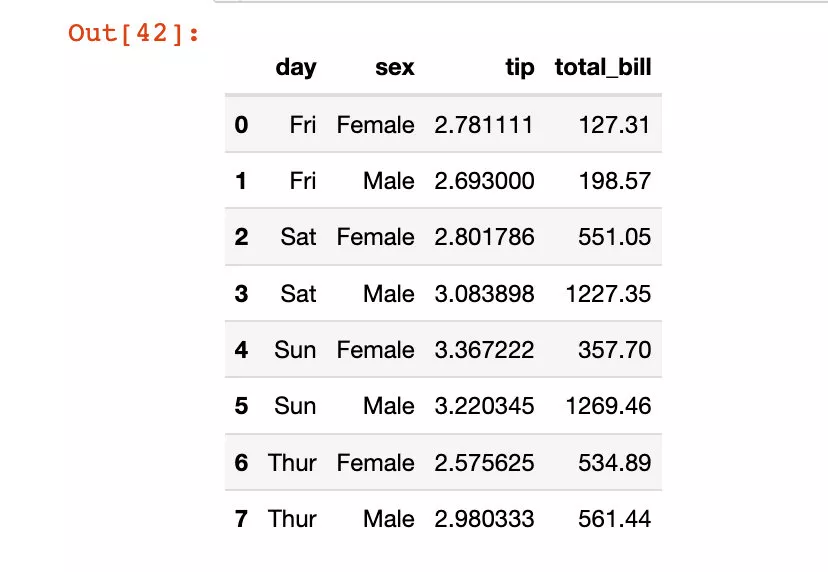
Finally, a stupid method is introduced to modify the name of the column index : Is to assign all the new names to the data frame in the form of a list columns attribute
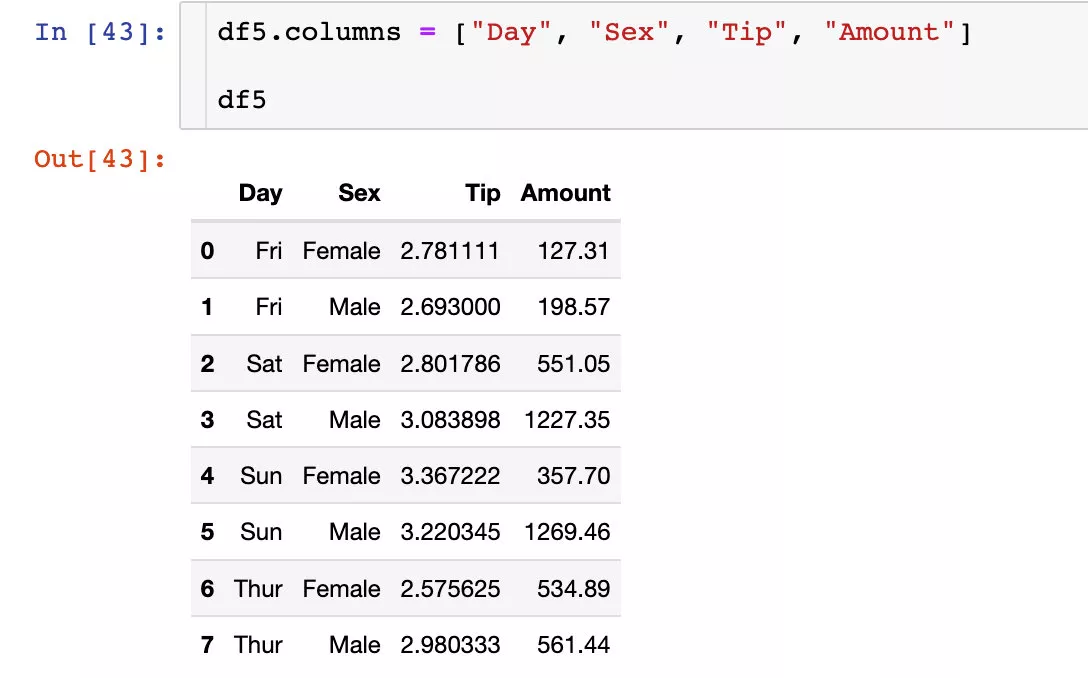
It is very convenient to use when the number of column indexes is small , If there are too many, it is not recommended to use .
summaryThis is about Python pandas This is the end of the article on index setting and modification , More about pandas Please search the previous articles of SDN or continue to browse the related articles below. I hope you can support SDN more in the future !