1.Series
1.1 Create... From a list Series
1.2 Create... From a dictionary Series
2.DataFrame
3. Index object
4. see DataFrame Common properties of
Preface :
Pandas There are three data structures :Series、DataFrame and Panel.Series It's like an array ;DataFrame It's like a table ;Panel Can be regarded as Excel Multiple forms for Sheet
1.SeriesSeries Is a one-dimensional array object , Contains a sequence of values , And contains data labels , Known as the index (index), Access the data in the array through the index .
1.1 Create... From a list Seriesexample 1. Create... From a list
import pandas as pdobj = pd.Series([1,-2,3,4]) # It consists of only one array print(obj)Output :
0 1
1 -2
2 3
3 4
dtype: int64
The first column of the output is index, The second column is the data value. If you create Series Is not specified index,Pandas Integer data will be used as the Series Of index. You can also use Python The index in index And slicing slice technology
example 2. establish Series Specify the index when
import pandas as pdi = ["a","c","d","a"]v = [2,4,5,7]t = pd.Series(v,index=i,name="col")print(t)out:
a 2
c 4
d 5
a 7
Name: col, dtype: int64
Just create Series It specifies index, actually Pandas There are still hidden index Location information . therefore Series There are two ways to describe a piece of data : Location and label
example 3.Series Location and use of labels
import pandas as pdval = [2,4,5,6]idx1 = range(10,14)idx2 = "hello the cruel world".split()s0 = pd.Series(val)s1 = pd.Series(val,index=idx1)t = pd.Series(val,index=idx2)print(s0.index)print(s1.index)print(t.index)print(s0[0])print(s1[10])print('default:',t[0],'label:',t["hello"])1.2 Create... From a dictionary SeriesIf the data is stored in a Python In the dictionary , You can also create... Directly from this dictionary Series
example 4. Create... From a dictionary Series
import pandas as pdsdata = {'Ohio':35000,'Texass':71000,'Oregon':16000,'Utah':5000}obj = pd.Series(sdata)print(obj)Ohio 35000
Texass 71000
Oregon 16000
Utah 5000
dtype: int64
If only one dictionary is passed in , Then the result Series The index in is the key of the original dictionary ( Arrange in order )
example 5. Create... From a dictionary Series Index of time
import pandas as pdsdata = {"a":100,"b":200,"e":300}obj = pd.Series(sdata)print(obj)a 100
b 200
e 300
dtype: int64
If the key value in the dictionary does not match the specified index , Then the corresponding value is NaN
example 6. The key value does not match the specified index
import pandas as pdsdata = {"a":100,"b":200,"e":300}letter = ["a","b","c","e"]obj = pd.Series(sdata,index=letter)print(obj)a 100.0
b 200.0
c NaN
e 300.0
dtype: float64
For many applications ,Series An important function is : It will automatically align the data of different indexes in arithmetic operation
example 7. Automatic alignment of different index data
import pandas as pdsdata = {'Ohio':35000,'Texas':71000,'Oregon':16000,'Utah':5000}obj1 = pd.Series(sdata)states = ['California','Ohio','Oregon','Texas']obj2 = pd.Series(sdata,index=states)print(obj1+obj2)California NaN
Ohio 70000.0
Oregon 32000.0
Texas 142000.0
Utah NaN
dtype: float64
Series The index of can be modified locally by assignment
example 8.Series Modification of the index
import pandas as pdobj = pd.Series([4,7,-3,2])obj.index = ['Bob','Steve','Jeff','Ryan']print(obj)2.DataFrameBob 4
Steve 7
Jeff -3
Ryan 2
dtype: int64
DataFrame It's a tabular data structure , It has an ordered set of columns , Each column can be a different type of value ( The number 、 character string 、 Boolean value, etc ).DataFrame There are both row and column indexes , It can be seen by Series A dictionary made up of ( Share the same index ). Compared with other types of data structures ,DataFrame Row oriented and column oriented operations in are basically balanced
structure DataFrame There are many ways , The most common is to pass in a list of equal length or NumPy An array of dictionaries to form DataFrame
example 9.DataFrame The creation of
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data)print(df)name sex year city
0 Zhang San female 2001 Beijing
1 Li Si female 2001 Shanghai
2 Wang Wu male 2003 Guangzhou
3 Xiao Ming male 2002 Beijing
DataFrame It will be indexed automatically ( Follow Series equally ), And all columns will be arranged in order . If a column name sequence is specified , be DataFrame The columns will be arranged in the specified order
example 10.DataFrame The index of
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city'])print(df)name year sex city
0 Zhang San 2001 female Beijing
1 Li Si 2001 female Shanghai
2 Wang Wu 2003 male Guangzhou
3 Xiao Ming 2002 male Beijing
Follow Series equally , If the incoming column cannot be found in the data , It will produce NaN value .
example 11.DataFrame The empty value when created
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'])print(df)name year sex city address
0 Zhang San 2001 female Beijing NaN
1 Li Si 2001 female Shanghai NaN
2 Wang Wu 2003 male Guangzhou NaN
3 Xiao Ming 2002 male Beijing NaN
DataFrame Constructor's columns The function gives the name of the column ,index give label label
example 12.DataFrame Specify the column name at build time
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'],index = ['a','b','c','d'])print(df)3. Index objectname year sex city address
a Zhang San 2001 female Beijing NaN
b Li Si 2001 female Shanghai NaN
c Wang Wu 2003 male Guangzhou NaN
d Xiao Ming 2002 male Beijing NaN
Pandas The index object of is responsible for the management of axis labels and other metadata ( For example, shaft name, etc ). structure Series or DataFrame when , Any array or other sequence tags used will be converted to a Index
example 13. Show DataFrame Indexes and columns for
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'],index = ['a','b','c','d'])print(df)print(df.index)print(df.columns)name year sex city address
a Zhang San 2001 female Beijing NaN
b Li Si 2001 female Shanghai NaN
c Wang Wu 2003 male Guangzhou NaN
d Xiao Ming 2002 male Beijing NaN
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')
Index(['name', 'year', 'sex', 'city', 'address'], dtype='object')
The index object cannot be modified , Otherwise, an error will be reported . Immutability is very important , Because this can make Index Objects are safely shared among multiple data structures
Except that it looks like an array ,Index The function of is also similar to a fixed size collection
example 14.DataFrame Of Index
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'],index = ['a','b','c','d'])print('name'in df.columns)print('a'in df.index)True
True
Each index has some methods and properties , They can be used to set up logic and answer common questions about the data contained in the index .
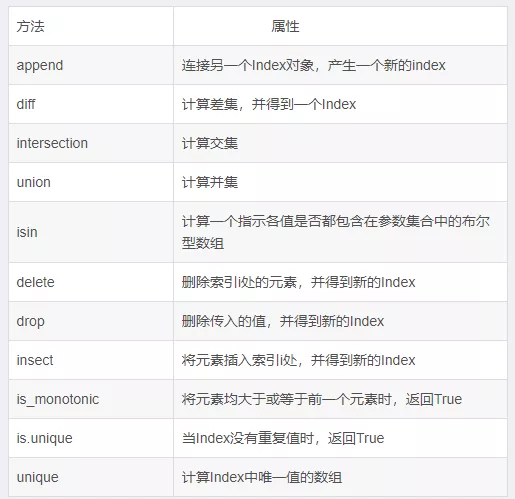
example 15. Insert index value
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'],index = ['a','b','c','d'])df.index.insert(1,'w')Index(['a', 'w', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')4. see DataFrame Common properties of DataFrame The basic properties of are value、index、columns、dtypes、ndim and shape, You can get DataFrame The elements of 、 Indexes 、 Name 、 type 、 Dimensions and shapes .
example 16. Show DataFrame Properties of
import pandas as pddata = { 'name':[' Zhang San ',' Li Si ',' Wang Wu ',' Xiao Ming '], 'sex':['female','female','male','male'], 'year':[2001,2001,2003,2002], 'city':[' Beijing ',' Shanghai ',' Guangzhou ',' Beijing ']}df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns = ['name','year','sex','city','address'],index = ['a','b','c','d'])print(df)print(' All values in the information table are :\n',df.values)print(' All columns in the information table are :\n',df.columns)print(' Number of elements in the information table :\n',df.size)print(' Dimension of information table :\n',df.ndim)print(' The shape of the information table :\n',df.shape) #// Output name year sex city addressa Zhang San 2001 female Beijing NaNb Li Si 2001 female Shanghai NaNc Wang Wu 2003 male Guangzhou NaNd Xiao Ming 2002 male Beijing NaN All values in the information table are : [[' Zhang San ' 2001 'female' ' Beijing ' nan] [' Li Si ' 2001 'female' ' Shanghai ' nan] [' Wang Wu ' 2003 'male' ' Guangzhou ' nan] [' Xiao Ming ' 2002 'male' ' Beijing ' nan]] All columns in the information table are : Index(['name', 'year', 'sex', 'city', 'address'], dtype='object') Number of elements in the information table : 20 Dimension of information table : 2 The shape of the information table : (4, 5)This is about Python Pandas This is the end of the article on detailed explanation of data structure in , More about Python Pandas Please search the previous articles of software development network or continue to browse the relevant articles below. I hope you will support software development network more in the future !