Python Provides if、elif、else To make logical judgments
The format is as follows :
if Judge the condition 1:
Execute statement 1...
elif Judge the condition 2:
Execute statement 2...
elif Judge the condition 3:
Execute statement 3...
else:
Execute statement 4...
for A loop can traverse any sequence
str = 'Python'
for s in str:
print(s)
Output results :
P
y
t
h
o
n
Examples are as follows :
m=0
while m<=5:
print(m)
m=m+1
print(m+1)
Output results :
0
1
2
3
4
5
7
Use in for Circulation and while Loop statement , End cycle .
Examples are as follows :
str = 'Python'
for s in str:
if s == 'o':
break
print(s)
Output results :
P
y
t
h
be used for for loop while Loop statement , Terminate the loop , Into the next loop
Examples are as follows :
str = 'Python'
for s in str:
if s == 'o':
continue
print(s)
Output results :
P
y
t
h
n
pass It's an empty statement , Generally used for occupying , Make the program complete
Introduce mathematical module math
import math
Examples are as follows :
import math
math.sqrt(1024)
math Functions in modules
random modular
random(x) function
Randomly generate one 0 To 1 A real number in a range
uniform(x,y) function
Randomly generate one x Real numbers in the range to
Examples are as follows :
s = 'Python'
print(s[0]) # Access the first character
s = 'Python'
print(s[1:3]) # visit yt
print(s[:3]) # visit Pyt
print(s[3:]) # visit hon
Output results :
P
yt
Pyt
hon
ord() Function returns the encoding of the character ,chr Function to convert the encoding to characters
Examples are as follows :
s1 = 'Hello'
s2 = 'Python'
print('s1 + s2 -->', s1 + s2)
print('s1 * 2 -->', s1 * 2)
print('s1[0] -->', s1[0])
print('s1[0:2] -->',s1[0:2])
print('"H" in s1 -->','H' in s1)
print('"H" not in s1 -->','H' not in s1)
print('\\r -->', R'\r')
Output results :
s1 + s2 --> HelloPython
s1 * 2 --> HelloHello
s1[0] --> H
s1[0:2] --> He
"H" in s1 --> True
"H" not in s1 --> False
\r --> \r
Python Use % Formatted string
Examples are as follows :
print('Hello %s' % 'Python')
print('{0} {1}'.format('Hello', 'Python'))
Output results :
Hello Python
Hello Python
A string of format() Method to format , This way is to replace the placeholders in the string with the passed in parameters {0}、{1}…
Sequential indexes support non negative and negative numbers , The index is nonnegative , from 0 Start , As shown below
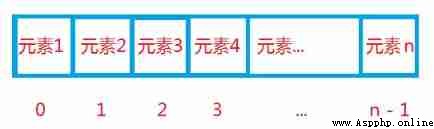
The index is negative, counting from right to left , from -1 Start , As shown in the figure

Examples are as follows :
str = 'Python'
print('str[0] str[-6] =', str[0], str[-6])
print('str[5] str[-1] =', str[5], str[-1])
Output results :
str[0] str[-6] = P P
str[5] str[-1] = n n
Slicing can access a range of elements , The syntax is shown below :
sname[start : end : step]
Examples are as follows :
str = 'Python'
print(str[:3])
print(str[3:])
print(str[:])
Output results :
Pyt
hon
Python
Pto
establish
All the elements in the list are placed in one [] in , Use... Between adjacent elements , Separate , for example :
A=[111,0.5,'python']
visit
Access the values in the list by index , It can be used : Intercept the elements in the range , for example :
A=[666,0.5,'python']
print(A[0],A[1],A[2])
print(A[:])
print(A[1::2])
Output results :
666 0.5 python
[666, 0.5, 'python']
[0.5]
to update
You can modify the elements in the list directly , It can also be used. append() Add a new element to the list , for example :
A=[666,0.5,'python']
A[0]=111 # modify
print(A)
A.append(222) # increase
print(A[:])
print(A[1::2])
Output results :
[111, 0.5, 'python']
[111, 0.5, 'python', 222]
[0.5, 222]
Delete
Use del Delete the elements in the list , for example :
A=[666,0.5,'python']
del A[1]
print(A)
Output results :
[666, 'python']
Common functions
count()
Count the number of times an element appears in the list ( It can also be used to count the occurrence of an element in a string Number of times and the number of times an element appears in a tuple ) for example :
A=['a','a','a']
B='dfsagad'
C=(1,1,2,3,3,1)
print(A.count("a"))
print(B.count("a"))
print(C.count(1))
Output results :
3
2
3
index()
Find an element in the list ( character string , Tuples ) The place where they all appear ( Index ), for example :
A=['a','b','c']
print(A.index('b'))
Output results :
1
remove()
Remove the first occurrence of an element in the list , for example :
A=['a','b','c','b']
A.remove('b')
print(A)
Output results :
['a', 'c', 'b']
sort()
Sort the elements in the list , for example :
A=['a','f','g','b','c','b']
B=[4,2,3,1,1]
A.sort()
B.sort()
print(A)
print(B)
Output results :
['a', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'f', 'g']
[1, 1, 2, 3, 4]
copy()
Copy list , for example :
A=['a','b',1,2]
B=A.copy()
print(B)
Output results :
['a', 'b', 1, 2]
establish
All elements in a tuple are placed in parentheses (), in , Two adjacent elements are represented by , separate
visit
Access to the same list
modify
Elements in tuples cannot be modified , We can only operate on it by reassigning it
Delete
Elements in tuples cannot be deleted , We can only delete the entire tuple
Common functions
len()
Compute tuple ( Length of string , The number of elements in the list ) The number of elements in , for example :
A=['a','b',1,2]
B=A.copy()
print(B)
print(len(A))
C='hjkvvj'
print(len(C))
E=(1,2,'d')
print(len(E))
Output results :
['a', 'b', 1, 2]
4
6
3
max() and min()
Return a tuple ( list , character string ) Maximum element in , minimum value , for example :
A=['a','b','g','f']
B='12345'
C=('a','b','g','f')
print(min(A),max(B),min(C))
Output results :
a 5 a
tuple()
Convert list to tuple , for example :
C=['a','b','g','f']
A=tuple(C)
print(A)
Output results :
('a', 'b', 'g', 'f')