Think aloud : Let's set a small goal first ,2 After hours, it is abnormal
Text begins
When an error is detected , The interpreter can't continue , On the contrary, there are some wrong hints , That's what's called “ abnormal ”.
for example :
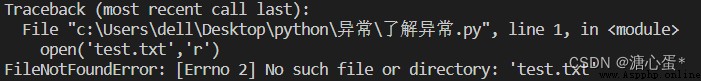
r Open a nonexistent file in open('test.txt','r')
try:
The code that could have an error
except:
If there is an exception to the execution of the code
demand : Try to r Mode open file , If the file doesn't exist , with w Mode on .
try:
open('test.txt','r')
except:
open('test.txt','w')
try:
The code that could have an error
except Exception types :
If the code executed by this exception type is caught
print(num) # NameError: name 'num' is not defined.
''' : The preceding is the error type ,: The following is the exception information .'''
try:
print(num)
except NameError:
print(' Erroneous ')
# Running results : Erroneous
When more than one exception is caught , The name of the exception type to be caught , Put it in except after , And use tuples to write .
try:
print(1/0)
except (NameError,ZeroDivisionError):
print(' Erroneous ')
# Running results : Erroneous
try:
print(1/0)
except (NameError,ZeroDivisionError) as error:
print(error) # division by zero
Exception Is the parent of all program exceptions .
try:
print(1/0)
except Exception as error:
print(error) # division by zero
else Represents the code to execute if there are no exceptions
try:
print(1) # 1
except Exception as error:
print(error)
else:
print(' There is no exception else') # There is no exception else
finally Represents the code to be executed regardless of whether it is abnormal or not , For example, closing a file .
try:
f = open('test.txt','r')
except Exception as error:
f = open('test.txt','w')
else:
print(' No abnormal ') # Don't execute
finally:
f.close()
demand : Call other py File and run .

demand :
except Catch exceptions and prompt the user .Code :
import time
try:
f = open('test.txt') # The default open mode is ‘r’
# Try looping through the content
try:
while True:
con = f.readline()
# The read value has no content , Description has been read , The cycle should be rolled out
if len(con) == 0:
break
print(con)
# Force to stop 1s The clock
time.sleep(1)
except:
# ctrl + c To terminate the program , It's too fast , No time to press , Import time modular
print(' The program was terminated unexpectedly ')
except:
print(' The file does not exist ')
finally:
f.close()
print(' The file is closed ')
effect :
Be careful : If you are pycharm Open in ,ctrl+c Maybe not , Refer to the expanded content above to open .
stay Python in , The syntax for throwing a custom exception is raise Exception class object .
effect : It is used to feed back the situation that does not meet the program logic to the user . Used to report errors .
demand : Insufficient password length , Abnormal Report ( User enters password , If the input length is insufficient 3 position , False report , That is, a custom exception is thrown , And catch the exception )
# 1. Custom exception classes
class ShortInputError(Exception):
def __init__(self, length,min_len) -> None:
# The length of the password entered by the user
self.length = length
# Minimum length required by the system
self.min_len = min_len
# Set the description of the exception thrown
def __str__(self) -> str:
return f' The length you entered is {
self.length}, No less than {
self.min_len}'
# 2. Throw custom exception
def main():
try:
con = input(' Please input a password :')
if len(con) < 3:
raise ShortInputError(len(con),3)
# 3. Capture exception
except Exception as result:
print(result)
else:
print(' The password has been entered ')
t = 0
t = 1
while t:
main()