
author : Han Xinzi @ShowMeAI
Tutorial address :http://www.showmeai.tech/tuto...
This paper addresses :http://www.showmeai.tech/article-detail/67
Statement : copyright , For reprint, please contact the platform and the author and indicate the source
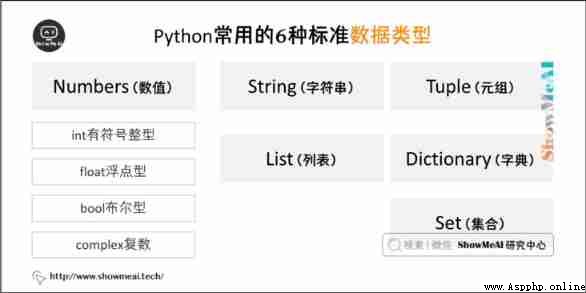
Python Basic data types are generally divided into 6 Kind of : The number (Numbers)、 character string (String)、 list (List)、 Tuples (Tuple)、 Dictionaries (Dictionary)、 aggregate (Set). This article explains in detail Python Variable assignment in 、 Data type and conversion of data type .
The value of a variable stored in memory , This means that when you create variables, you open up a space in memory . Data types based on variables , The interpreter allocates the specified memory , And decide what data can be stored in memory . therefore , Variables can specify different data types , These variables can store integers , Decimal or character .
Equal sign = To the left of the operator is a variable name , Equal sign = To the right of the operator is the value stored in the variable . for example ( The following code can be found in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
num = 100 # Assign an integer variable
weight = 100.0 # floating-point
name = "ShowMeAI" # character string
print(num)
print(weight)
print(name)In the example above ,100,100.0 and "ShowMeAI" Assign to respectively num,weight,name Variable .
Executing the above program will output the following results :
100
100.0
ShowMeAI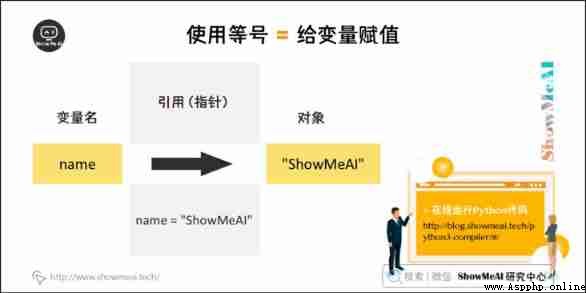
Python Allows you to assign values to multiple variables at the same time . for example :
a = b = c = 1The above instance , Create an integer object , The value is 1, Three variables are allocated to the same memory space .
You can also specify multiple variables for multiple objects . for example :
a, b, c = 1, 2, "ShowMeAI"The above instance , Two integer objects 1 and 2 Assign to variables separately a and b, String object "ShowMeAI" Assign to a variable c.
There can be many types of data stored in memory .
for example , A person's age can be stored in Numbers , His name can be stored in characters .
Python Some standard types are defined , Used to store various types of data .
Python There are the most commonly used 5 Standard data types :
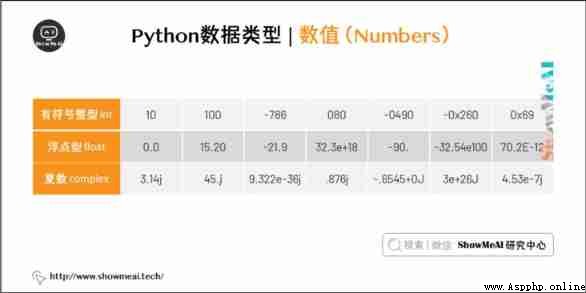
Numeric data types are used to store numeric values .
They are immutable data types , This means that changing the digital data type assigns a new object .
When you specify a value ,Number The object will be created :
num1 = 1
num2 = 10You can also use the del Statement to delete references to some objects .
del The syntax of the sentence is :
del num1[,num2[,num3[....,numN]]]You can use the del Statement to delete references to single or multiple objects . for example :
del num
del num_a, num_bPython Four different types of numbers are supported :
Some examples of numerical types :
String or string (String) It's numbers 、 Letter 、 A string of characters made up of underscores .
It is generally recorded as :
s = "a1a2···an" # n>=0It's the data type that represents text in programming languages .
python The list of strings for has 2 The order of values is :

If you want to get a substring from a string , have access to [ Header subscript : Tail subscript ] To intercept the corresponding string , The subscript is from 0 From the beginning , It can be positive or negative , The subscript can be empty to indicate that the head or tail is taken .
[ Header subscript : Tail subscript ] The substring obtained contains the character of the header and subscript , But characters that don't contain trailing subscripts .
such as :
>>> s = 'ShowMeAI'
>>> s[6:8]
'AI'When using colon delimited strings ,python Return a new object , The result contains consecutive content identified by this pair of offsets , The start on the left contains the lower boundary .
The above results include s[1] Value b, But not the maximum range Tail subscript , Namely s[5] Value f.
have access to __ plus (+)__ Connect strings , Use asterisk (*) Repeat the operation on the string . as follows ( The following code can be found in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
str = 'Hello ShowMeAI!'
print(str) # Output full string
print(str[0]) # The first character in the output string
print(str[2:5]) # A string between the third and sixth in the output string
print(str[2:]) # Output a string starting with the third character
print(str * 2) # Output string twice
print(str + " Awesome") # Output the string of the connection The output of the above example :
Hello ShowMeAI!
H
llo
llo ShowMeAI!
Hello ShowMeAI!Hello ShowMeAI!
Hello ShowMeAI! AwesomePython List interception can receive the third parameter , The parameter function is the step size of interception , The following examples are in the index 1 To the index 4 And set the step size to 2( One place apart ) To intercept a string :

more python For the detailed explanation of string, please refer to python String and operation
List( list ) yes Python The most frequently used data type in .
List can complete the data structure implementation of most collection classes . It supports characters , Numbers , Strings can even contain lists ( That is, nesting ).
List with [ ] identification , yes python The most common composite data type .
The cutting of the values in the list can also use variables [ Header subscript : Tail subscript ] , You can intercept the corresponding list , Left to right index default 0 Start , Right to left index default -1 Start , The subscript can be empty to indicate that the head or tail is taken .
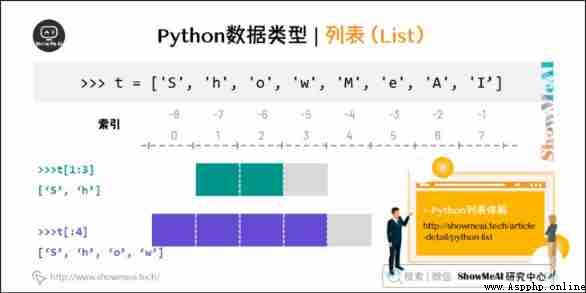
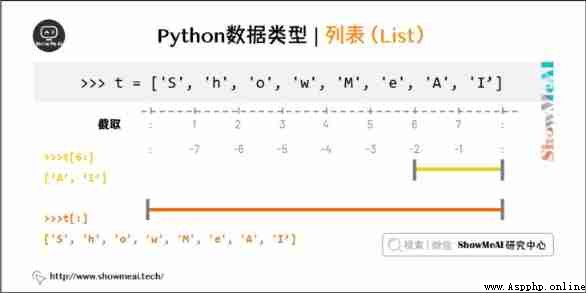
plus + Is the list join operator , asterisk * Is a repeat operation . as follows ( The following code can be found in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
list = [ 'ShowMeAI', 786 , 2.23, 'show', 70.2 ]
tinylist = [123, 'show']
print(list) # Output complete list
print(list[0]) # The first element of the output list
print(list[1:3]) # Output the second to third elements
print(list[2:]) # Output all elements from the third to the end of the list
print(tinylist * 2) # Output the list twice
print(list + tinylist) # Print a list of combinations The output of the above example :
['ShowMeAI', 786, 2.23, 'show', 70.2]
ShowMeAI
[786, 2.23]
[2.23, 'show', 70.2]
[123, 'show', 123, 'show']
['ShowMeAI', 786, 2.23, 'show', 70.2, 123, 'show']more python For the detailed explanation of the list, please refer to python list
Tuples are another data type , Be similar to List( list ).
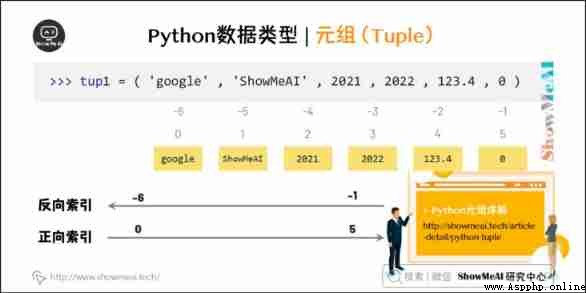
Tuple use () identification . The inner elements are separated by commas . But tuples cannot be assigned twice , Equivalent to read-only list .( The following code can be found in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in )
tuple = ( 'ShowMeAI', 786 , 2.23, 'show', 70.2 )
tinytuple = (123, 'show')
print(tuple) # Output full tuples
print(tuple[0]) # The first element of the output tuple
print(tuple[1:3]) # Output the second to fourth ( It doesn't contain ) The elements of
print(tuple[2:]) # Output all elements from the third to the end of the list
print(tinytuple * 2) # Output tuples twice
print(tuple + tinytuple) # Print combined tuples The output of the above example :
('ShowMeAI', 786, 2.23, 'show', 70.2)
ShowMeAI
(786, 2.23)
(2.23, 'show', 70.2)
(123, 'show', 123, 'show')
('ShowMeAI', 786, 2.23, 'show', 70.2, 123, 'show')The following is a tuple invalid , Because tuples are not allowed to be updated . The list is allowed to be updated :
tuple = ( 'ShowMeAI', 345 , 2.23, 'show', 456.2 )
list = [ 'ShowMeAI', 345 , 2.23, 'show', 456.2 ]
tuple[2] = 100 # Illegal application in tuple
list[2] = 100 # In the list are legitimate applications more python For detailed explanation of tuples, please refer to python Tuples
Dictionaries (dictionary) Except for the list python The most flexible type of built-in data structure . A list is an ordered collection of objects , A dictionary is an unordered collection of objects .
The difference between the two is : The elements in the dictionary are accessed by keys , Instead of accessing by offset .
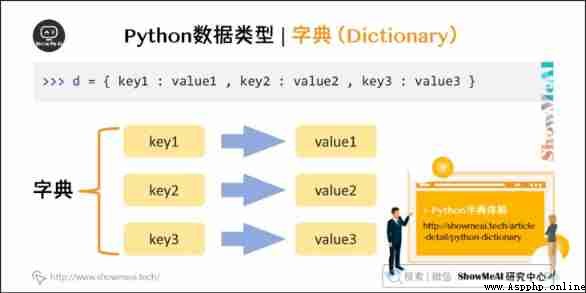
Dictionary use "{ }" identification . The dictionary is indexed by (key) The value corresponding to it value form .( The following code can be found in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in )
dict = {}
dict['one'] = "This is one"
dict[2] = "This is two"
tinydict = {'name': 'ShowMeAI','code':3456, 'dept': 'AI'}
print(dict['one']) # The output key is 'one' Value
print(dict[2]) # The output key is 2 Value
print(tinydict) # Output complete dictionary
print(tinydict.keys()) # Output all keys
print(tinydict.values()) # Output all values The output is :
This is one
This is two
{'name': 'ShowMeAI', 'code': 3456, 'dept': 'AI'}
dict_keys(['name', 'code', 'dept'])
dict_values(['ShowMeAI', 3456, 'AI'])more python For the detailed explanation of the dictionary, you can refer to python Dictionaries
occasionally , We need to transform the built-in types of data , Conversion of data types , You just need to use the data type as the function name .
The following built-in functions can perform conversion between data types . These functions return a new object , Represents the value of the transformation .
Please click to B I'm looking at it from the website 【 Bilingual subtitles 】 edition
https://www.bilibili.com/vide...
The code for this tutorial series can be found in ShowMeAI Corresponding github Download , Can be local python Environment is running , Babies who can surf the Internet scientifically can also use google colab One click operation and interactive operation learning Oh !
This tutorial series covers Python The quick look-up table can be downloaded and obtained at the following address :
