
author : Han Xinzi @ShowMeAI
Tutorial address :http://www.showmeai.tech/tuto...
This paper addresses :http://www.showmeai.tech/article-detail/68
Statement : copyright , For reprint, please contact the platform and the author and indicate the source
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values . A simple example 5 +6 = 11 . In the example ,5 and 6 go by the name of Operands ,"+" Called operator .
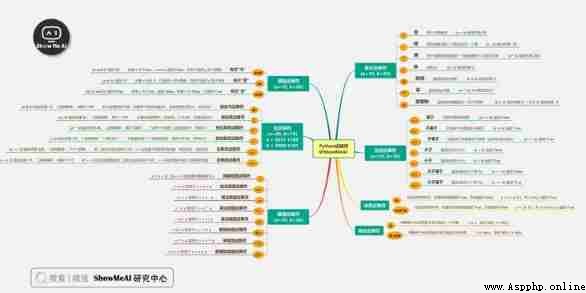
Python The language supports the following types of operators :
The following hypothetical variables : a=10,b=20:
>>> 9//2 4 >>> -9//2 -5The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all arithmetic operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 30
b = 10
c = 0
c = a + b
print(" The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a - b
print(" The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a * b
print(" The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a / b
print(" The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a % b
print(" The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
# Modify variables a 、b 、c
a = 2
b = 3
c = a**b
print(" The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
a = 10
b = 5
c = a//b
print(" The first 7 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)The output of the above code :
The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is : 40 The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is : 20 The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is : 300 The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is : 3.0 The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is : 0 The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is : 8 The first 7 After three operations ,c The value of is : 2
The following hypothetical variables a by 10, Variable b by 20:
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all comparison operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 30
b = 10
c = 0
if a == b :
print("a be equal to b")
else:
print("a It's not equal to b")
if a != b :
print("a It's not equal to b")
else:
print("a be equal to b")
if a < b :
print("a Less than b" )
else:
print("a Greater than or equal to b")
if a > b :
print("a Greater than b")
else:
print("a Less than or equal to b")
# Modify variables a and b Value
a = 5
b = 20
if a <= b :
print("a Less than or equal to b")
else:
print("a Greater than b")
if b >= a :
print("b Greater than or equal to a")
else:
print("b Less than a")The output of the above example :
a It's not equal to b a It's not equal to b a Greater than or equal to b a Greater than b a Less than or equal to b b Greater than or equal to a
The following hypothetical variables a by 10, Variable b by 20:
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all assignment operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 30
b = 10
c = 0
c = a + b
print(" The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c += a
print(" The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c )
c *= a
print(" The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c )
c /= a
print(" The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c )
c = 2
c %= a
print(" The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c **= a
print(" The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c //= a
print(" The first 7 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)The output of the above code :
The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is : 40 The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is : 70 The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is : 2100 The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is : 70.0 The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is : 2 The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is : 1073741824 The first 7 After three operations ,c The value of is : 35791394
Bitwise operators calculate numbers as binary .Python The bitwise algorithm in is as follows :
Variables in the following table a by 60,b by 13, The binary format is as follows :
a = 0011 1100 b = 0000 1101 ----------------- a&b = 0000 1100 a|b = 0011 1101 a^b = 0011 0001 ~a = 1100 0011
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all bit operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 60 # 60 = 0011 1100
b = 13 # 13 = 0000 1101
c = 0
c = a & b; # 12 = 0000 1100
print(" The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a | b; # 61 = 0011 1101
print(" The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a ^ b; # 49 = 0011 0001
print(" The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = ~a; # -61 = 1100 0011
print(" The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a << 2; # 240 = 1111 0000
print(" The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)
c = a >> 2; # 15 = 0000 1111
print(" The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is :", c)The output of the above code :
The first 1 After three operations ,c The value of is : 12 The first 2 After three operations ,c The value of is : 61 The first 3 After three operations ,c The value of is : 49 The first 4 After three operations ,c The value of is : -61 The first 5 After three operations ,c The value of is : 240 The first 6 After three operations ,c The value of is : 15
Python Language supports logical operators , The following hypothetical variables a by 10, b by 20:
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all logical operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 10
b = 20
if a and b :
print("1. Variable a and b All for true")
else:
print("1. Variable a and b One didn't do it true")
if a or b :
print("2. Variable a and b All for true, Or one of the variables is true")
else:
print("2. Variable a and b Not for true")
# Modify variables a Value
a = 0
if a and b :
print("3. Variable a and b All for true")
else:
print("3. Variable a and b One didn't do it true")
if a or b :
print("4. Variable a and b All for true, Or one of the variables is true")
else:
print("4. Variable a and b Not for true")
if not( a and b ):
print("5. Variable a and b All for false, Or one of the variables is false")
else:
print("5. Variable a and b All for true")The output of the above code :
1. Variable a and b All for true 2. Variable a and b All for true, Or one of the variables is true 3. Variable a and b One didn't do it true 4. Variable a and b All for true, Or one of the variables is true 5. Variable a and b All for false, Or one of the variables is false
In addition to some of the above operators ,Python Member operators are also supported , The test case contains a series of members , Including strings , List or tuple .
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all member operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 10
b = 20
list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
if ( a in list ):
print("1. Variable a In the given list list in ")
else:
print("1. Variable a Not in the given list list in ")
if ( b not in list ):
print("2. Variable b Not in the given list list in ")
else:
print("2. Variable b In the given list list in ")
# Modify variables a Value
a = 2
if ( a in list ):
print("3. Variable a In the given list list in ")
else:
print("3. Variable a Not in the given list list in ")The output of the above code :
1. Variable a Not in the given list list in 2. Variable b Not in the given list list in 3. Variable a In the given list list in
Identity operators are used to compare the storage units of two objects
notes : id() Function to get the memory address of an object .
The following code demonstrates Python Operation of all identity operators ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 20
b = 20
if ( a is b ):
print("1.a and b Have the same logo ")
else:
print("1.a and b There is no identical logo ")
if ( a is not b ):
print("2.a and b There is no identical logo ")
else:
print("2.a and b Have the same logo ")
# Modify variables b Value
b = 30
if ( a is b ):
print("3.a and b Have the same logo ")
else:
print("3.a and b There is no identical logo ")
if ( a is not b ):
print("4.a and b There is no identical logo ")
else:
print("4.a and b Have the same logo ")The output of the above example :
1.a and b Have the same logo 2.a and b Have the same logo 3.a and b There is no identical logo 4.a and b There is no identical logo
is And == difference :
is Used to determine whether two variable reference objects are the same ( The same memory space ), == Used to determine whether the values of reference variables are equal .
>>> a = [1, 2, 3] >>> b = a >>> b is a True >>> b == a True >>> b = a[:] >>> b is a False >>> b == a True
The following table lists all operators from the highest to the lowest priority :

The following code demonstrates Python All operator priority operations ( The code can be in On-line python3 Environmental Science Run in ):
a = 20
b = 10
c = 15
d = 5
e = 0
e = (a + b) * c / d #( 30 * 15 ) / 5
print("(a + b) * c / d The result of operation is :", e)
e = ((a + b) * c) / d # (30 * 15 ) / 5
print("((a + b) * c) / d The result of operation is :", e)
e = (a + b) * (c / d); # (30) * (15/5)
print("(a + b) * (c / d) The result of operation is :", e)
e = a + (b * c) / d; # 20 + (150/5)
print("a + (b * c) / d The result of operation is :", e)The output of the above example :
(a + b) * c / d The result of operation is : 90.0 ((a + b) * c) / d The result of operation is : 90.0 (a + b) * (c / d) The result of operation is : 90.0 a + (b * c) / d The result of operation is : 50.0
The code for this tutorial series can be found in ShowMeAI Corresponding github Download , Can be local python Environment is running , Babies who can surf the Internet scientifically can also use google colab One click operation and interactive operation learning Oh !
This tutorial series covers Python The quick look-up table can be downloaded and obtained at the following address :
