python Provide treatment ( Parse and create )XML Interface of format file :xml.etree.ElementTree( hereinafter referred to as ET) modular .
> notes : since version3.3 after ,xml.etree.cElementTree Module obsolescence .
XML Is a hierarchical data format , Usually it can be used “ Trees ” Express .ET There are two classes in (class) But for XML To said :
The following is an analysis of country_data.xml File as an example :
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank>1</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank>4</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>68</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>(1) Method 1 : from file
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Method 1: from file
tree = ET.parse('XXXX.xml') # File storage path , Get the entire xml
root = tree.getroot() # obtain xml The root node
(2) Method 2 : From file content ( character string )
# Method 2: From string
root = ET.fromstring('XXXX.xml All strings of the file ')explain :ET.fromstring() Function will XML The contents of the document ( String format ) It is directly parsed into a Element object ( node ), This Element It is this that is parsed XML Root node of tree .
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
filePath = 'C:\codes\data\country_data.xml'
##method1: reading from a file
tree = ET.parse(filePath)
root = tree.getroot()
print(root.tag)
##method2: importing from a string
root2 = ET.fromstring('''<?xml version="1.0"?>
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank>1</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
<country name="Singapore">
<rank>4</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>59900</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/>
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>68</rank>
<year>2011</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/>
<neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/>
</country>
</data>''')
print (root2.tag)Output :
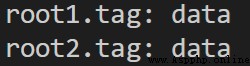
Input :root.tag
Output :data
2Element.attribelement atrribute's name and value DictionariesInput :root[0].attrib
Output :{‘name’:'Liechtenstein'}
3Element.textthe text between the element's start tag and its first child or end tag, or None.( At present element start tag Adjacent to the next tag Text between ) Usually a stringInput :root[0][0].text
Output :1
4Element.tailthe text between the element's end tag and the next tag, or None.( At present element end tag And the next one tag Text between ) Usually a stringInput :root[0][0].tail
Output :None
5Element.keys() Get the current object / Key of node attribute , Returns a list of listInput :root[0].keys()
Output :['name']
6Element.items() Get the current object / Node attribute key value pairs , Returns a list of list[(,)]Input :root[0][3].items()
Output :[('name', 'Austria'), ('direction', 'E')]
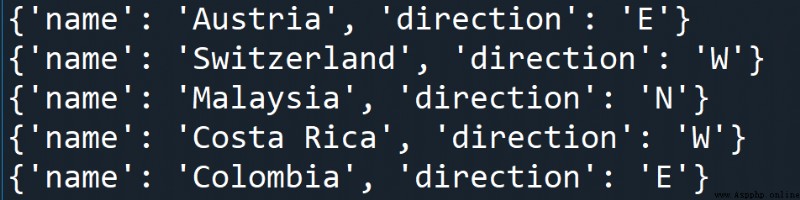
Iterator lookup :Element.iter('tagname')
# Get current element All levels under the object tag by Neighbor The object of
for neighbor in root.iter('neighbor'):
print(neighbor.attrib) Output :
# Find the current element The next level of the object
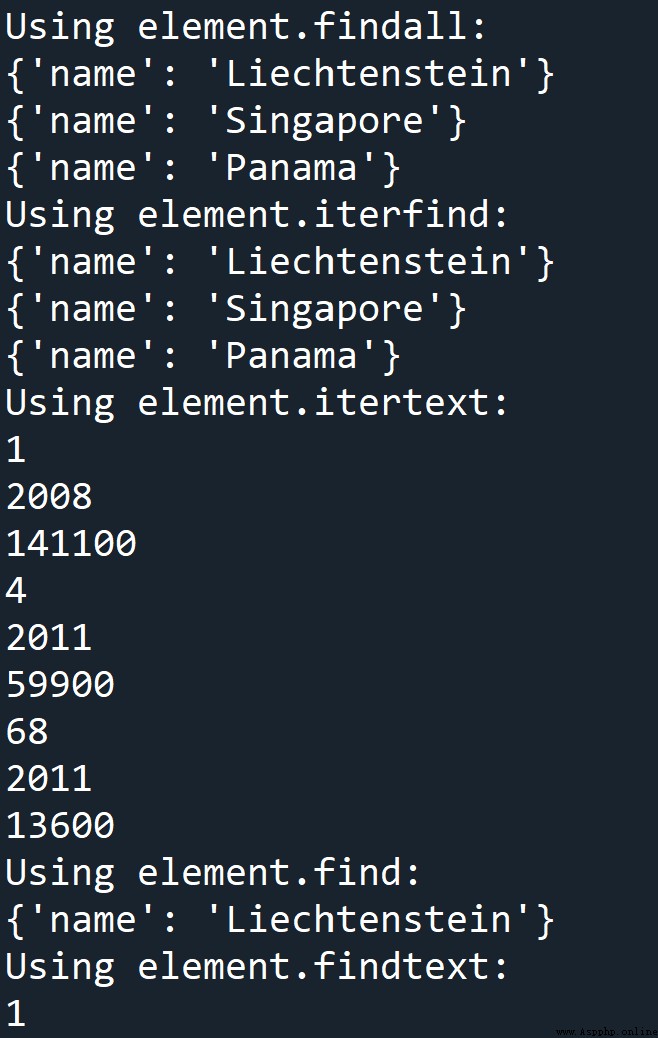
print('Using element.findall:')
ele1 = root.findall('country')
for every in ele1:
print(every.attrib)
print("Using element.iterfind:")
for every in root.iterfind('country'):
print(every.attrib)
print('Using element.itertext:')
for every in root.itertext():
if every.startswith('\n')==False:
print(every)
# Find the current element The first matching object at the next level of the object
print('Using element.find:')
ele = root.find('country')
print(ele.attrib)
print('Using element.findtext:')
ranktext = ele.findtext('rank')
print(ranktext)Output :