Tuple creation
Deletion of tuples
The output of some elements of tuples
Nesting of tuples
Calculation of the number of tuple elements :len()
Solving the maximum and minimum values of elements in tuples :max(),min()
The number of occurrences of an element in a tuple :count function
The index of an element in a tuple :index(), Returned is a subscript value
Modification of tuple element value : Element values of tuples cannot be modified .
Tuple creationtuple=() # Create an empty tuple print(tuple)print(type(tuple))Output :
()
<class 'tuple'>
Define tuples that contain only one element : The element must be followed by a comma , Otherwise the compiler will recognize it as an integer .
give an example :
tuple2 = (1,)print(tuple2)print(type(tuple2))tuple2 = (1)print(tuple2)print(type(tuple2))Output :
Deletion of tuples(1,)
<class 'tuple'>
1
<class 'int'>
del Tuple name to be deleted
tuple2 = (1,2,3,4,5,6)print(tuple2)del tuple2print(tuple2)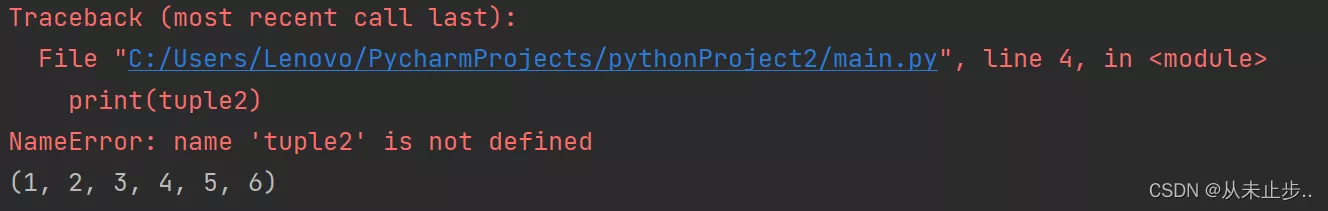
Because we are in the third line of code for tuple2 Deleted , So the compiler will report an error ,tuple2 Not defined .
Determine whether an element is in a tuple :in/ not in sentence
give an example :
tuple2 = (1,2,3,4,5,6)if 4 in tuple2: print("YES")else: print("NO")if 10 in tuple2: print("YES")else: print("NO")Output :
The output of some elements of tuplesYES
NO
Similar to slicing a list .
give an example :
tuple2 = (1,2,3,4,5,6)print(tuple2[0:3])Output :
Nesting of tuples(1, 2, 3)
Similar to the nesting of lists , Just replace the list with tuples
give an example :
tuple1=((1,2,3),(4,5,6),(7,8,9))for tuple1s in tuple1: print(tuple1s) for tuple1_s in tuple1s: print(tuple1_s)Output :
Calculation of the number of tuple elements :len()(1, 2, 3)
1
2
3
(4, 5, 6)
4
5
6
(7, 8, 9)
7
8
9
give an example :
tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)print(len(tuple1))Output :
Solving the maximum and minimum values of elements in tuples :max(),min()9
give an example :
tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)print(max(tuple1))print(min(tuple1))Output :
The number of occurrences of an element in a tuple :count function9
1
give an example :
tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,3,3,2,2)print(tuple1.count(3))Output :
The index of an element in a tuple :index(), Returned is a subscript value3
give an example :
tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,3,3,2,2)print(tuple1.index(2))Output :
Modification of tuple element value : Element values of tuples cannot be modified .1
give an example :
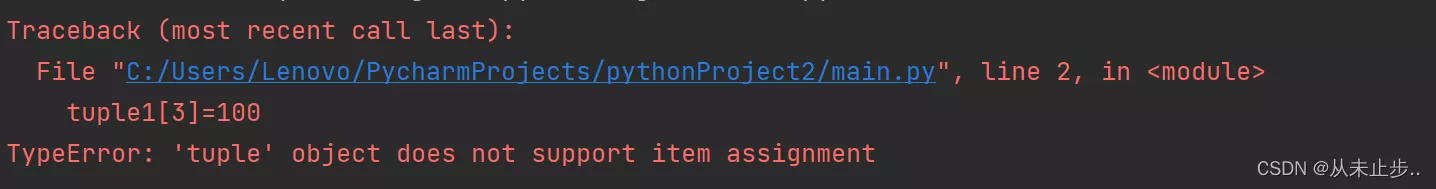
tuple1=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,3,3,2,2)tuple1[3]=100print(tuple1)Output :
This is about Python This is the end of the article on the use of tuples of learning , More about Python Tuple content please search the previous articles of the software development network or continue to browse the following related articles. I hope you will support the software development network in the future !