establish TCP Socket
import socket
# establish tcp Socket socket.SOCK_STREAM TCP socket.SOCK_DGRAM UDP
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Close socket
s.close()
establish UDP Socket
import socket
# establish tcp Socket socket.SOCK_STREAM TCP socket.SOCK_DGRAM UDP
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Close socket
s.close()
UDP send data
Servers End
import socket
# establish tcp Socket
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Prepare recipient address
dest_addr =('192.168.199.101',8080)
# Bind local information ip Generally do not write , Represents any address of this computer
local_addr = ('', 8888)
s.bind(local_addr)
send_date = input(" Please input data ")
s.sendto(send_date.encode('utf-8'),dest_addr)
# Close socket
s.close()
Cllient
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from socket import *
def main():
# Create socket
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM)
# Bind local information ip Generally do not write , Represents any address of this computer
local_addr = ('', 8888)
s.bind(local_addr)
# Waiting for the receiver to send data recvfrom When there is no data, it will block
recv_data = s.recvfrom(1024) # 1024 Indicates the maximum number of bytes received this time
# Display received data
print(recv_data) # (b' data ', ('127.0.0.1 The sender IP', 8080 port ))
# windows Receive data using gbk decode Linu Next Decode using the sender format
print(recv_data[0].decode("gbk"))
# Close socket
s.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Tcp socket
Clinet
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from socket import *
def main():
# Create socket
tcp_cli_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Bind local information
server_ip = ('127.0.0.1', 8888)
# Connect to server
tcp_cli_socket.connect(server_ip)
# send data
send_data = input(" Please input the data to be sent :")
tcp_cli_socket.send(send_data.encode("gbk"))
# receive data
rescv_data = tcp_cli_socket.recv(1024)
print(rescv_data.decode('gbk'))
tcp_cli_socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Tcp service
# _*_encoding:utf-8 _*_
from socket import *
# tcp The server technological process 1. establish socket 2.bind binding ip And port 3. listen Make socket a passive link
# 4.accept Waiting for client access 5.recv/send Receive and send data
def main():
# Create socket
tcp_ser_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Local information
local_addr = ("", 8808)
# binding
tcp_ser_socket.bind(local_addr)
# Use socket The default property of the socket is active , Use listen Turn it into a passive , In this way, you can receive other people's connections
tcp_ser_socket.listen(1024)
# If a new client comes to link to the server , Then a new socket is generated , Specifically for this user
# client_socket A client service
client_socket, clientAddr = tcp_ser_socket.accept()
print("---------------")
print("client_socket:{} \n clientAddr:{}".format(client_socket, clientAddr))
print("***************")
# Receive the data sent by the other party
recv_data = client_socket.recv(1024)
print(" Data received :", recv_data.decode('gbk'))
# Send data to client
client_socket.send("test from server".encode('gbk'))
# Close the socket assigned to this client
client_socket.close()
tcp_ser_socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
loop Serving clients
# _*_encoding:utf-8 _*_
from socket import *
# tcp The server technological process 1. establish socket 2.bind binding ip And port 3. listen Make socket a passive link
# 4.accept Waiting for client access 5.recv/send Receive and send data
def main():
# Create socket
tcp_ser_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Local information
local_addr = ("", 8808)
# binding
tcp_ser_socket.bind(local_addr)
# Use socket The default property of the socket is active , Use listen Turn it into a passive , In this way, you can receive other people's connections
tcp_ser_socket.listen(1024)
while True:
# If a new client comes to link to the server , Then a new socket is generated , Specifically for this user
# client_socket A client service
client_socket, clientAddr = tcp_ser_socket.accept()
print("---------------")
print("client_socket:{} \n clientAddr:{}".format(client_socket, clientAddr))
print("***************")
while True: # Serve the same client multiple times
# Receive the data sent by the other party
recv_data = client_socket.recv(1024)
print(" Data received :", recv_data.decode('gbk'))
if recv_data:
# Send data to client
client_socket.send("test from server".encode('gbk'))
else:
# Close the socket assigned to this client
break
client_socket.close()
print("---over---")
tcp_ser_socket.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
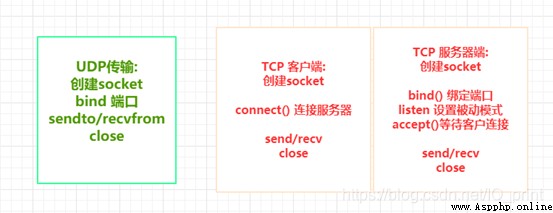
Join multithreading socket
import socket
import threading
def recv_data(udp_socket):
while True:
data = udp_socket.recvfrom(1024)[0].decode('gbk')
print("\n receive data :" + data)
def send_data(udp_socket):
while True:
s_data = input(" Please input the data to be sent ")
udp_socket.sendto(s_data.encode('gbk'),("127.0.0.1",7890))
def main():
udp_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
udp_socket.bind(("", 7788))
resv_thread = threading.Thread(target=recv_data, args=(udp_socket,))
send_thread = threading.Thread(target=send_data, args=(udp_socket,))
send_thread.start()
resv_thread.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()