Catalog
One 、 Definition of tuple
Two 、 Tuples are commonly used
3、 ... and 、 Loop traversal
Four 、 Application scenarios
Tuple( Tuples ) Like a list , The difference is that the elements of a tuple cannot be modified
Tuples represent a sequence of elements , Tuples are in python In development , There are specific application scenarios , Used to store a string of information , Use... Between data , Separate
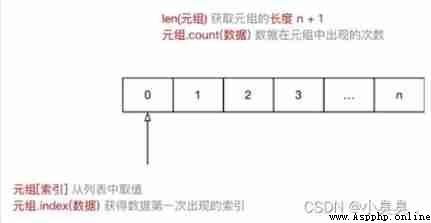
Tuple use () Definition , The index of the tuple is from 0 Start , Index is the position number of data in tuple
info_tuple = ("zhangsan",18,1.75)Create an empty tuple
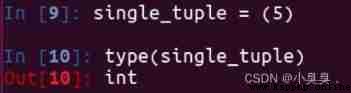
tuple = ()When a tuple contains only one element , Comma needs to be added after element
info_tuple = (50,)The wrong sample :
stay ipython3 Define a tuple in , for example :info = ()
Input info. Press down TAB key ,ipython The following functions can be used by tuples :

info_tuple = ("zhangsan",18,1.75)
# 1. Value and index
print(info_tuple[0])
# Already know the content of data retrieval , Want to know the index of the data in the tuple
print(info_tuple.index("zhangsan"))
# 2. Statistics count
print(info_tuple.count("zhangsan"))
# Count the number of elements contained in the tuple
print(len(info_tuple))Value is to get the data stored in the specified location from the tuple
Traversal is to get data from tuples from beginning to end
info_tuple = ("zhangsan",18,1.75)
# Iterate through tuples
for my_info in info_tuple:
# Use format string splicing my_info This variable is inconvenient !
# Because the data types usually stored in tuples are different !
print(my_info)stay python in , have access to for Loop through all variables of non numeric type : list 、 Tuples 、 Dictionaries and strings
Tips : In actual development , Unless you can confirm the data type in the tuple , Otherwise, there are not many loop traversal requirements for tuples
Although you can use for in Traversal tuples , But in development , More application scenarios are :
Parameters and return values of functions , A function can take any number of parameters , Or return more than one data at a time
Format string , Format the... After the string () It's essentially a tuple
Make the list non modifiable , To protect data security
# Format string , Format the... After the string () It's essentially a tuple
# info = (" Xiao Ming ",18)
# print("%s The age of %d" % info)
print("%s The age of %d Height is %.2f" % (" Xiao Ming ",18,1.75))info_str = "%s The age of %d Height is %.2f" % (" Xiao Ming ",18,1.75)
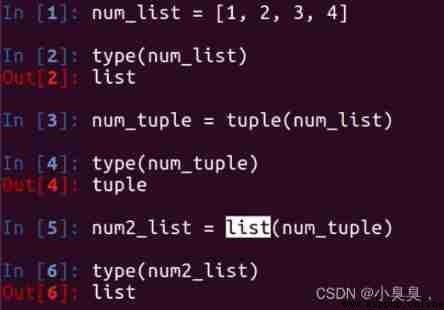
print(info_str)Conversion between tuples and lists
Use list Function to convert tuples into lists
list( Tuples )Use tuple Function to convert a list to a tuple
tuple( list )