argparse Module makes it easy to write user-friendly command-line interface . The program defines the parameters it needs , then argparse Will find out how to start from sys.argv Parse out those parameters . argparse The module also automatically generates help and user manuals , And report an error message when the user passes in invalid parameters to the program .
Use argparse Three steps to pass in parameters from the command line :
1, The first step is to create a ArgumentParser object :
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='process some integers')
2, The second step calls add_argument() Method to add parameters
parser.add_argument('-f', 'binfile', default='', help='input bin file')
3, The third step calls parse_args() Method to parse parameters , Then we can use args.binfile Call the parameter
args = parser.parse_args()
One ,ArgumentParser() Parameters that can be added in parentheses
class argparse.ArgumentParser(prog=None, usage=None, description=None, epilog=None, parents=[], formatter_class=argparse.HelpFormatter, prefix_chars='-', fromfile_prefix_chars=None, argument_default=None, conflict_handler='error', add_help=True, allow_abbrev=True)
Create a new ArgumentParser object . All parameters should be passed in as keyword parameters . Each parameter is described in more detail below , But in short , They are :
prog - Program name ( The default value is :sys.argv[0])
usage - A string describing the purpose of the program ( The default value is : Generate... From parameters added to the parser )
description - The text displayed before the parameter help document ( The default value is : nothing )
epilog - The text displayed after the parameter help document ( The default value is : nothing )
parents - One ArgumentParser List of objects , Their parameters should also be included
formatter_class - A class for customizing the output format of help documents
prefix_chars - Prefix character set of optional parameters ( The default value is : ‘-‘)
fromfile_prefix_chars - When other parameters need to be read from the file , Prefix character set used to identify file names ( The default value is : None)
argument_default - Global default values for parameters ( The default value is : None)
conflict_handler - Policies for resolving conflict options ( Usually not necessary )
add_help - Add a... To the parser -h/--help Options ( The default value is : True)
allow_abbrev - If the abbreviation is unambiguous , The abbreviated long option is allowed ( The default value is :True)
stay 3.5 Version change : Added allow_abbrev Parameters .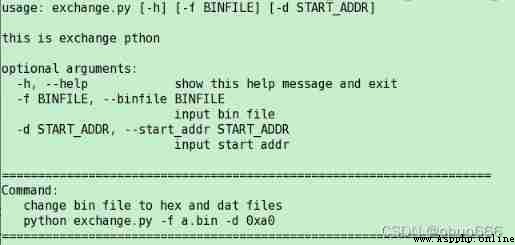

Two ,add_argument
The regular usage is as follows :
import argparse
demo_doc="change bin file to hex"
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class.RawTextHelpFormatter,epilog=demo_doc)
parser.add_argument('-f' ,'--binfile' ,default='' ,help='input bin file')
parser.add_argument('-d' ,'--start_addr' ,default='' ,help='input bin file')
args = parser.parse_argsArgumentParser.add_argument(name or flags...[, action][, nargs][, const][, default][, type][, choices][, required][, help][, metavar][, dest]), A brief description of parameter usage is as follows :
name or flags - A list of named or option strings , for example foo or -f, --foo.
action - The basic type of action used when parameters appear on the command line .
nargs - The number of command line arguments that should be consumed .
const - By some action and nargs Select the required constant .
default - The value used when the parameter does not appear on the command line .
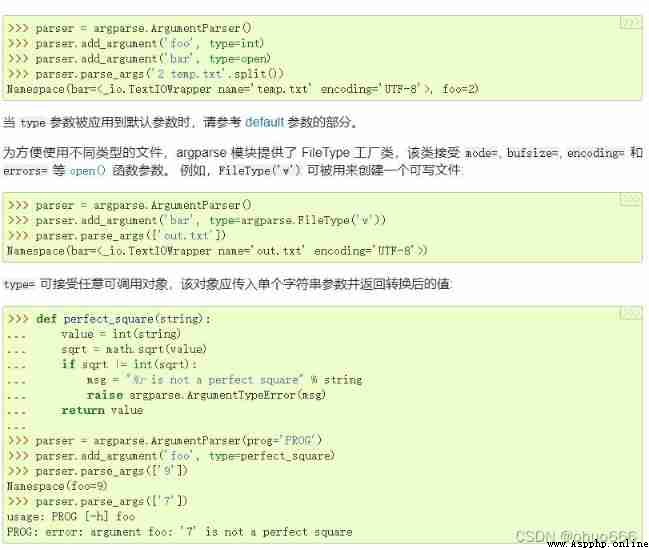
type - The type to which command line arguments should be converted .
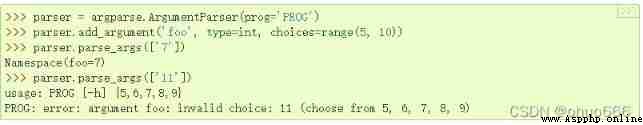
choices - Container of available parameters .
required - Whether this command line option can be omitted ( Only options are available ).
help - A brief description of the effect of this option .
metavar - Example of parameter values used in usage method messages .
dest - Be added to parse_args() The property name on the returned object .add_argument Option parameters are passed - Prefix identification , No addition - It will be recognized as a position parameter :
Creation of option parameters :parser.add_argument('-f', '--foo')
Creation of position parameters :parser.add_argument('bar')
‘store’ Store the value of the parameter , This is a action The default value of .
‘store_const’ Storage is const The value specified by the named parameter .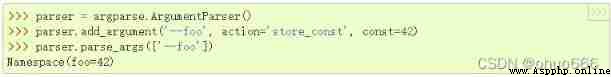
‘store_true' and 'store_false', yes ’store_const‘ Separately used for storage True and False Worth special use cases , The default values are True and False.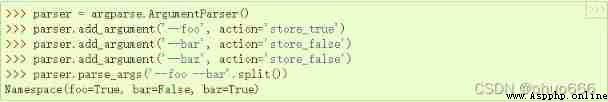
’append' Store a list , And append each parameter value to the list . 
‘version’ Add a version information parameter 
For more parameter information, please see 16.4. argparse — Command line options 、 Parameter and subcommand parsers — Python 3.5.10 file
N An integer , On the command line N Parameters will be saved in a list ,N by 1 when , What is stored is a list with only one data 
'?' If there are parameters, a number is stored ( It's not a list ), Save without parameters default value , If you enter a flag entry on the command line , But if it is not followed by a parameter, it will be saved const The number that follows 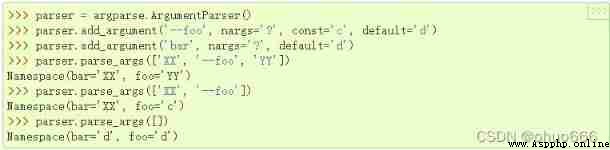
‘*’ All input parameters in the command line are saved in a list .
‘+’, and ‘*’ similar , All current command line parameters are aggregated into a list , If there is no parameter, an error will be reported .
argparse.REMAINDER, All remaining command line parameters are aggregated into a list .



This article is a summary of my own use , The following articles are cited at large in the parameter interpretation section , Please move to the following link to support the original version . 16.4. argparse — Command line options 、 Parameter and subcommand parsers — Python 3.5.10 file  https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.5/library/argparse.html#argparse.Action
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.5/library/argparse.html#argparse.Action