目錄
字符串的格式化
常見的格式字符
例子:
format()方法
【 例1】
【例2】
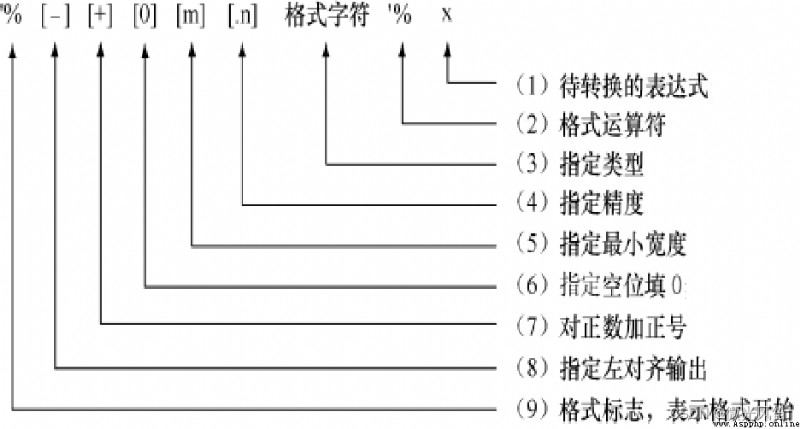
格式字符
說明
%s
字符串 (采用str()的顯示)
%r
字符串 (采用repr()的顯示)
%c
單個字符
%b
二進制整數
%d
十進制整數
%i
十進制整數
%o
八進制整數
%x
十六進制整數
%e
指數 (基底寫為e)
%E
指數 (基底寫為E)
%f、%F、%F
浮點數
%g
指數(e)或浮點數 (根據顯示長度)
%G
指數(E)或浮點數 (根據顯示長度)
%%
字符"%""%"
>>> x = 1235
>>> so="%o" % x
>>> so
"2323"
>>> sh = "%x" % x
>>> sh
"4d3"
>>> se = "%e" % x
>>> se
"1.235000e+03"
>>> chr(ord("3")+1)
"4"
>>> "%s"%65
"65"
>>> "%s"%65333
"65333"
>>> "%d"%"555" #試圖將字符串轉換為整數進行輸出,拋出異常
TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str
>>> int('555') #可以使用int()函數將合法的數字字符串轉換為整數
555
>>> '%s'%[1, 2, 3]
'[1, 2, 3]'
>>> str((1,2,3)) #可以使用str()函數將任意類型數據轉換為字符串
'(1, 2, 3)'
>>> str([1,2,3])
'[1, 2, 3]'
更加靈活,不僅可以使用位置進行格式化,還支持使用與位置無關的參數名字來進行格式化,並且支持序列解包格式化字符串
print("The number {0:,} in hex is: {0:#x}, the number {1} in oct is {1:#o}".format(5555,55))
輸出:
The number 5,555 in hex is:0x15b3, the number 55 in oct is 0o67
解析:
{0:}或者{0}代表format(a0,a1,a2)中的a0,{0:#格式字符}即對a0進行格式化
print("my name is {name}, my age is {age}, and my QQ is {qq}".format(name = "Dong Fuguo",age = 37,qq = "306467355"))
輸出:
my name is Dong Fuguo, my age is 37, and my QQ is 306467355
 [Excel report summary of interesting projects] Python+pandas+xlwings realizes batch extraction of table information, summarizes it into a table and sends it to the mailbox
[Excel report summary of interesting projects] Python+pandas+xlwings realizes batch extraction of table information, summarizes it into a table and sends it to the mailbox
文章目錄前言一、Sub-function details1.