1、Struts2架構圖
這是Struts2官方站點提供的Struts 2 的整體結構。
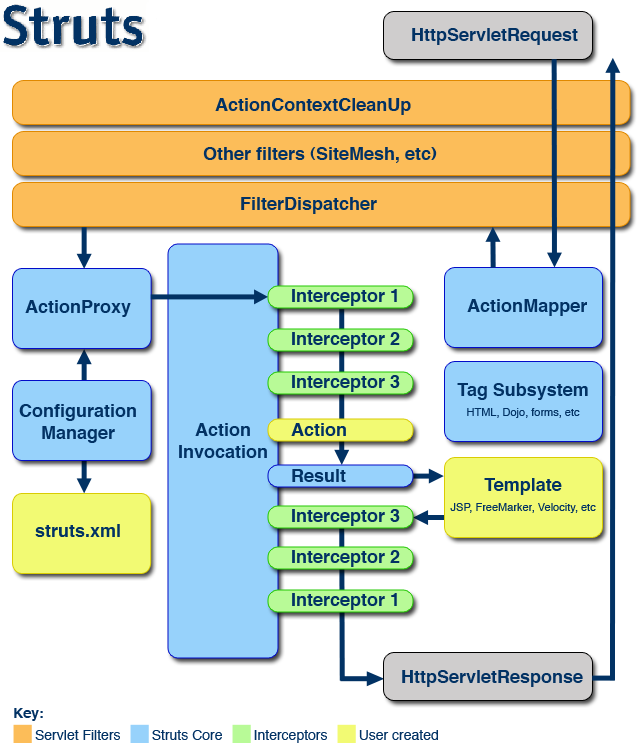
執行流程圖
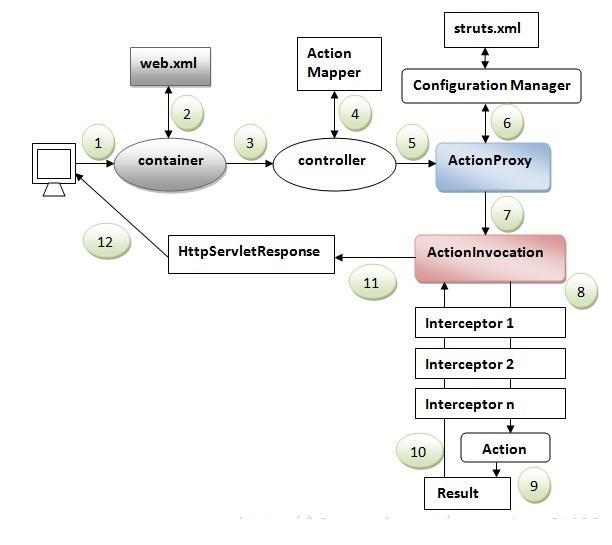
2、Struts2部分類介紹
這部分從Struts2參考文檔中翻譯就可以了。
ActionMapper
ActionMapper其實是HttpServletRequest和Action調用請求的一個映射,它屏蔽了Action對於 Request等 java Servlet類的依賴。Struts2中它的默認實現類是DefaultActionMapper,ActionMapper很 大的用處可以根據自己的需要來設計url格式,它自己也有Restful的實現,具體可以參考文檔的 docs\actionmapper.html。
ActionProxy&ActionInvocation
Action的一個代理,由ActionProxyFactory創建,它本身不包括Action實例,默認實現 DefaultActionProxy是由ActionInvocation持有Action實例。ActionProxy作用是如何取得Action,無論 是本地還是遠程。而 ActionInvocation的作用是如何執行Action,攔截器的功能就是在 ActionInvocation中實現的。
ConfigurationProvider&Configuration
ConfigurationProvider就是Struts2中配置文件的解析器,Struts2中的配置文件主要是尤其實現 類 XmlConfigurationProvider及其子類StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider來解析。
3、Struts2請求流程
1、客戶端發送請求
2、請求先通過ActionContextCleanUp-->FilterDispatcher
3、 FilterDispatcher通過ActionMapper來決定這個Request需要調用哪個Action
4、如果ActionMapper決 定調用某個Action,FilterDispatcher把請求的處理交給ActionProxy,這兒已經轉到它的Delegate-- Dispatcher來執行
5、ActionProxy根據ActionMapping和ConfigurationManager找到需要調用的Action 類
6、ActionProxy創建一個ActionInvocation的實例
7、ActionInvocation調用真正的Action,當 然這涉及到相關攔截器的調用
8、Action執行完畢,ActionInvocation創建Result並返回,當然,如果 要在返回之前做些什麼,可以實現PreResultListener。添加PreResultListener可以在Interceptor中實 現。
另一個版本:大同小異~
一個請求在Struts2框架中的處理大概分為以下幾個步驟:
1.客戶端提起一個(HttpServletRequest)請求,如上文在浏覽器中輸入 ”http://localhost:8080/TestMvc/add.action”就是提起一個(HttpServletRequest)請求 。
2.請求被提交到一系列(主要是三層)的過濾器(Filter),如(ActionContextCleanUp、其他 過濾器(SiteMesh等)、 FilterDispatcher)。注意這裡是有順序的,先ActionContextCleanUp,再其 他過濾器(SiteMesh等)、最後到 FilterDispatcher。
3.FilterDispatcher是控制器的核心,就 是mvc中c控制層的核心。下面粗略的分析下我理解的FilterDispatcher工作流程和原理: FilterDispatcher進行初始化並啟用核心doFilter
其代碼如下:
Java代碼
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws
IOException, ServletException ...{
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
ServletContext servletContext = filterConfig.getServletContext();
// 在這裡處理了HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse。
DispatcherUtils du = DispatcherUtils.getInstance();
du.prepare(request, response);//正如這個方法名字一樣進行locale、encoding以及特殊request parameters設置
try ...{
request = du.wrapRequest(request, servletContext);//對request進行包裝
} catch (IOException e) ...{
String message = "Could not wrap servlet request with MultipartRequestWrapper!";
LOG.error(message, e);
throw new ServletException(message, e);
}
ActionMapperIF mapper = ActionMapperFactory.getMapper();//得到action的mapper
ActionMapping mapping = mapper.getMapping(request);// 得到action 的 mapping
if (mapping == null) ...{
// there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?
String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
if ("".equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo())
...{
resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
}
if ("true".equals(Configuration.get(WebWorkConstants.WEBWORK_SERVE_STATIC_CONTENT))
&& resourcePath.startsWith("/webwork")) ...{
String name = resourcePath.substring("/webwork".length());
findStaticResource(name, response);
} else ...{
// this is a normal request, let it pass through
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// WW did its job here
return;
}
Object o = null;
try ...{
//setupContainer(request);
o = beforeActionInvocation(request, servletContext);
//整個框架最最核心的方法,下面分析
du.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
} finally ...{
afterActionInvocation(request, servletContext, o);
ActionContext.setContext(null);
}
}
du.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
//這個方法詢問ActionMapper是否需要調用某個Action來處理這個(request)請求,如果ActionMapper
決定需要調用某個Action,FilterDispatcher把請求的處理交給ActionProxy
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String
namespace, String actionName, Map requestMap, Map parameterMap, Map sessionMap, Map
applicationMap) ...{
HashMap extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, parameterMap, sessionMap,
applicationMap, request, response, getServletConfig()); //實例化Map請求 ,詢問ActionMapper
是否需要調用某個Action來處理這個(request)請求
extraContext.put(SERVLET_DISPATCHER, this);
OgnlValueStack stack = (OgnlValueStack) request.getAttribute
(ServletActionContext.WEBWORK_VALUESTACK_KEY);
if (stack != null) ...{
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK,new OgnlValueStack(stack));
}
try ...{
ActionProxy proxy = ActionProxyFactory.getFactory().createActionProxy(namespace,
actionName, extraContext);
//這裡actionName是通過兩道getActionName解析出來的, FilterDispatcher把請求的處理交給
ActionProxy,下面是ServletDispatcher的 TODO:
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.WEBWORK_VALUESTACK_KEY,
proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
proxy.execute();
//通過代理模式執行ActionProxy
if (stack != null)...{
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.WEBWORK_VALUESTACK_KEY,stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) ...{
log.error("Could not find action", e);
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) ...{
log.error("Could not execute action", e);
sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
}
}
4.FilterDispatcher詢問ActionMapper是否需要調用某個Action來處理這個(request)請求,如果 ActionMapper決定需要調用某個Action,FilterDispatcher把請求的處理交給ActionProxy。
5.ActionProxy通過Configuration Manager(struts.xml)詢問框架的配置文件,找到需要調用的Action 類.
如上文的struts.xml配置
查看本欄目
Java代碼
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration
2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<include file="struts-default.xml"/>
<package name="struts2" extends="struts-default">
<action name="add"
class="edisundong.AddAction" >
<result>add.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
如果提交請求的是add.action,那麼找到的Action類就是edisundong.AddAction。
6.ActionProxy 創建一個ActionInvocation的實例,同時ActionInvocation通過代理模式調用Action。但 在調用之前 ActionInvocation會根據配置加載Action相關的所有Interceptor。(Interceptor是struts2 另一個核心級的概念)
下面我們來看看ActionInvocation是如何工作的:
ActionInvocation 是 Xworks 中Action 調度的核心。而對Interceptor 的調度,也正是由ActionInvocation負責。 ActionInvocation 是一個接口,而DefaultActionInvocation 則是Webwork 對ActionInvocation的默認 實現。
Interceptor 的調度流程大致如下:
1. ActionInvocation初始化時,根據配置,加載 Action相關的所有Interceptor。
2. 通過ActionInvocation.invoke方法調用Action實現時,執行 Interceptor。
Interceptor將很多功能從我們的Action中獨立出來,大量減少了我們Action的代碼, 獨立出來的行為具有很好的重用性。XWork、 WebWork的許多功能都是有Interceptor實現,可以在配置文 件中組裝Action用到的Interceptor,它會按照你指定的順序,在 Action執行前後運行。
那麼什麼是 攔截器。
攔截器就是AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)的一種實現。(AOP是指用於在某個方法或 字段被訪問之前,進行攔截然後在之前或之後加入某些操作。)
攔截器的例子這裡就不展開了。
struts-default.xml文件摘取的內容:
Java代碼
< interceptor name ="alias" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.AliasInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="autowiring" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.spring.interceptor.ActionAutowiringInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="chain" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ChainingInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="conversionError" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.StrutsConversionErrorInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="createSession" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.CreateSessionInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="debugging" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.debugging.DebuggingInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="external-ref" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExternalReferencesInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="execAndWait" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ExecuteAndWaitInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="exception" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ExceptionMappingInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="fileUpload" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.FileUploadInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="i18n" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.I18nInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="logger" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.LoggingInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="model-driven" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ModelDrivenInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="scoped-model-driven" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ScopedModelDrivenInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="params" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ParametersInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="prepare" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.PrepareInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="static-params" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.StaticParametersInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="scope" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ScopeInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="servlet-config" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletConfigInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="sessionAutowiring" class ="org.apache.struts2.spring.interceptor.SessionContextAutowiringInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="timer" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.TimerInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="token" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.TokenInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="token-session" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.TokenSessionStoreInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="validation" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.ValidationInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="workflow" class ="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.DefaultWorkflowInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="store" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.MessageStoreInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="checkbox" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.CheckboxInterceptor" /> < interceptor name ="profiling" class ="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ProfilingActivationInterceptor" />
7.一旦Action執行完畢,ActionInvocation負責根據struts.xml中的配置找到對應的返回結果。如上 文中將結構返回“add.jsp”,但大部分時候都是返回另外一個action,那麼流程又得走一遍