實體Bean的連接策略(JOINED Strategy)
在上一篇文章中,使用單表策略將一個表從邏輯上分成了多個表。但這樣可能會造成空巢字段,也就 是說,一個邏輯表只由部分字段組成,而物理的表的很多字段的值就會為null。為了解決這個問題,可以 將t_accounts表物理地分成多個表。為了與t_accounts表進行對比,新建一個t_myaccounts表,結構如圖 1所示。
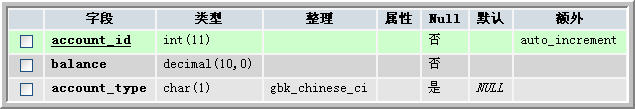
圖1 t_myaccounts表
從t_myaccounts的結構可以看出,在該表中只包含了t_accounts表的前三個字段,而後兩個在邏輯上 分到了不同的表,因此,首先要建立兩個物理表:t_checkingaccount和t_savingsaccount。這兩個表的 結構如下:
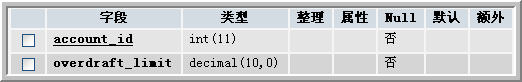
圖2 t_checkingaccount表
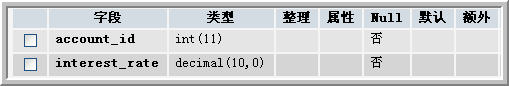
圖3 t_savingsaccount表
在t_checkingaccount和t_savingsaccount表中都有一個account_id,這個account_id的值依賴於 t_myaccounts表中的account_id。
下面先來編寫與t_myaccounts對應的實體Bean,代碼如下:
package entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorColumn;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_myaccounts")
@Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.JOINED)
public class Account
{
protected String id;
protected float balance;
protected String type;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="account_id")
public String getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public float getBalance()
{
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(float balance)
{
this.balance = balance;
}
@Column(name="account_type")
public String getType()
{
return type;
}
public void setType(String type)
{
this.type = type;
}
}
從上面的代碼可以看出,只使用了@Inheritance對實體Bean進行注釋。
下面編寫MyCheckingAccount和MySavingsAccount類的代碼:
MyCheckingAccount類的代碼:
package entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_checkingaccount")
// 指定與Account類共享的主鍵名
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name="account_id")
public class MyCheckingAccount extends Account
{
private double overdraftLimit;
public MyCheckingAccount()
{
// 為account_type字段賦默認值
setType("C");
}
@Column(name="overdraft_limit")
public double getOverdraftLimit()
{
return overdraftLimit;
}
public void setOverdraftLimit(double overdraftLimit)
{
this.overdraftLimit = overdraftLimit;
}
}
MySavingsAccount類的代碼:
package entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_savingsaccount")
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn(name="account_id")
public class MySavingsAccount extends Account
{
private double interestRate;
public MySavingsAccount()
{
// 為account_type字段賦默認值
setType("S");
}
@Column(name="interest_rate")
public double getInterestRate()
{
return interestRate;
}
public void setInterestRate(double interestRate)
{
this.interestRate = interestRate;
}
}
在上面的代碼中使用構造方法來初始化了t_myaccounts表的account_type字段的值。
可以使用下面的代碼進行測試:
System.out.println(((MyCheckingAccount)em.createQuery("from MyCheckingAccount where
id=12")
.getSingleResult()).getBalance());
MyCheckingAccount ca = new MyCheckingAccount();
ca.setBalance(342);
ca.setOverdraftLimit(120);
em.persist(ca);
MySavingsAccount sa = new MySavingsAccount();
sa.setBalance(200);
sa.setInterestRate(321);
em.persist(sa);