在很多大型應用中都會對數據進行切分,並且采用多個數據庫實例進行管理,這樣可以有效提高系統的水平伸縮性。而這樣的方案就會不同於常見的單一數據實例的方案,這就要程序在運行時根據當時的請求及系統狀態來動態的決定將數據存儲在哪個數據庫實例中,以及從哪個數據庫提取數據。
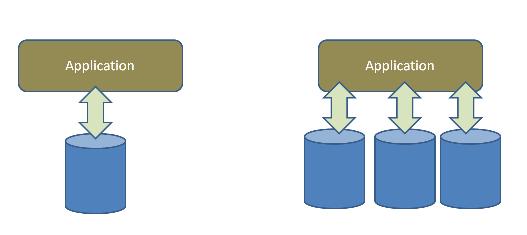
Figure 1 數據分割及多數據庫架構
通常這種多數據源的邏輯會滲透到業務邏輯中,同時也會給我們使用的數據訪問API諸如Hibernate和iBatis等帶來不便(需要指定多個SessionFactory或SqlMapClient實例來對應多個DataSource)。
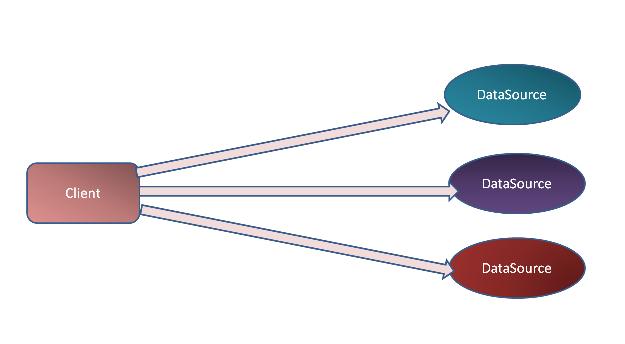
Figure 2 多數據源的選擇邏輯滲透至客戶端
解決方案
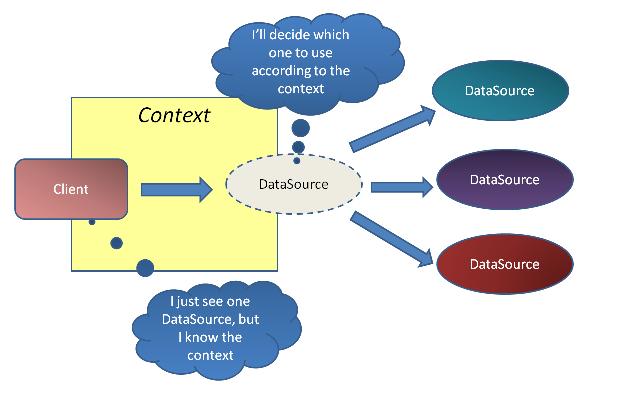
Figure 3 采用Proxy模式來封裝數據源選擇邏輯
通過采用Proxy模式我們在方案中實現一個虛擬的數據源,並且用它來封裝數據源選擇邏輯,這樣就可以有效地將數據源選擇邏輯從Client中分離出來。
Client提供選擇所需的上下文(因為這是Client所知道的),由虛擬的DataSource根據Client提供的上下文來實現數據源的選擇。
Spring2.x的版本中提供了實現這種方式的基本框架,虛擬的DataSource僅需繼承AbstractRoutingDataSource實現determineCurrentLookupKey()在其中封裝數據源的選擇邏輯。
實例:
publicclass DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
static Logger log = Logger.getLogger("DynamicDataSource");
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
String userId=(String)DbContextHolder.getContext();
Integer dataSourceId=getDataSourceIdByUserId(userId);
return dataSourceId;
}
}
實例中通過UserId來決定數據存放在哪個數據庫中。
配置文件示例:
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.bitfone.smartdm.datasource.DynamicDataSource">
<property name="targetDataSources">
<map key-type="java.lang.Integer">
<entry key="0" value-ref="dataSource0"/>
<entry key="1" value-ref="dataSource1"/>
<entry key="2" value-ref="dataSource2"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource0"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlMapClient" class="org.springframework.orm.ibatis.SqlMapClientFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:com/bitfone/smartdm/dao/sqlmap/sql-map-config.xml"/>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="UserInfoDAO" class="com.bitfone.smartdm.dao.impl.UserInfoDAO">
<property name="sqlMapClient" ref="sqlMapClient"/>
</bean>