每次提到有關Eclipse插件啟動的問題的時候,腦子中自然的反應就是:可以設定為預先啟動 (org.eclipse.ui.startup),否則默認的情況下是懶啟動(Lazy Start),只有當插件中的功能被真正 調用的時候,插件才會被啟動。可能是人也跟著變懶了,也一直沒有去留心Eclipse底層是怎麼實現這種 懶加載的,只是有個大致的猜測,估計又是用hook機制了。昨天閒著具體看了一下實現,果然是類似的實 現。下面就大致和大家分享一下,說的不一定准確,僅供參考 ~_~。
直接進入主題,我們的Eclipse實例啟動肯定要構造工作區,那麼ResourcesPlugin肯定會被啟動,我 們就在ResourcesPlugin.startup方法設置一個斷點,調試棧如下:
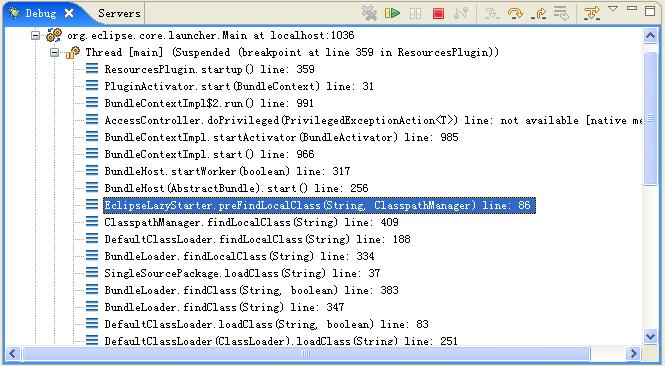
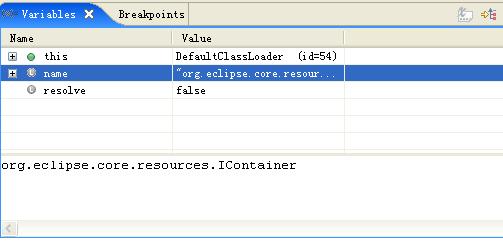
假設我們對插件類型加載細節不知道,猜測大致過程如下:
1、DefaultClassLoader加載類型(org.eclipse.core.resources.IContainer)
2、EclipseLazyStarter.preFindLocalClass
3、啟動資源插件:ResourcesPlugin.startup
補充說明:
1、org.eclipse.osgi.internal.baseadaptor.DefaultClassLoader是Eclipse針對OSGI類加載實現的 核心角色,也是eclipse插件默認的類加載器類型,當然,每個插件有自己獨立的類加載器實例來負責類 型加載。
2、DefaultClassLoader、BundleLoader、ClasspathManager三者協作,處理類型加載請求(為什麼一 個類加載過程要搞的這麼復雜呢?Eclipse的考慮是什麼呢? 大家思考吧~_~)
【EclipseLazyStarter調用分析】
我們先大致看一下EclipseLazyStarter.preFindLocalClass方法的代碼實現:
1 public class EclipseLazyStarter implements ClassLoadingStatsHook, HookConfigurator {
2 public void preFindLocalClass(String name, ClasspathManager manager) throws ClassNotFoundException {
3 //首先判斷,如果不需要啟動則返回
4
5 //如果插件正在啟動,則設定5000ms超時等待;如果超時,直接報錯返回
6
7 //啟動插件
8 }
9 }
加載類型之前為什麼要給回調一下EclipseLazyStarter. preFindLocalClass,又hook了?我們看了一 下EclipseLazyStarter繼承了ClassLoadingStatsHook接口,ClassLoadingStatsHook接口的類型API文檔 說明了它的作用:
A ClassLoadingStatsHook hooks into the <code>ClasspathManager</code> class.
追蹤前面的調用棧,ClassLoadingStatsHook是在ClasspathManager.findLocalClass中被調用的:
1 public Class findLocalClass(String classname) throws ClassNotFoundException {
2 Class result = null;
3 ClassLoadingStatsHook[] hooks = data.getAdaptor().getHookRegistry ().getClassLoadingStatsHooks();
4 try {
5 for (int i = 0; i < hooks.length; i++)
6 hooks[i].preFindLocalClass(classname, this);
7 result = findLocalClassImpl(classname, hooks);
8 return result;
9 } finally {
10 for (int i = 0; i < hooks.length; i++)
11 hooks[i].postFindLocalClass(classname, result, this);
12 }
13 }
再接著往下看之前,我們大致已經知道來的Eclipse的插件lazy start是怎麼回事了:
EclipseLazyStarter hook到了插件類加載器的類型加載過程中了,在類型被加載之前會回調 EclipseLazyStarter. preFindLocalClass方法:如果類型所在插件還沒啟動,啟動它;如果正在啟動, 則設置5000ms的超時,限時不能完成啟動,則報錯返回!
(附加說明:頭一段時間在另外一篇隨筆中,寫了一些編寫插件啟動類應該注意的點,其中有一條就 是避免在插件啟動方法中干耗時的事情。這裡真正告訴我們了原因:如果超過5000ms不能完成啟動--注 意這其中還不包含所依賴插件的啟動時間,那麼肯定會出現類加載超時的錯誤了:
While loading class "{1}", thread "{0}" timed out waiting ({4}ms) for thread "{2}" to finish starting bundle "{3}". To avoid deadlock, thread "{0}" is proceeding but "{1}" may not be fully initialized.
)
【EclipseLazyStarter是如何完成注冊過程的?】
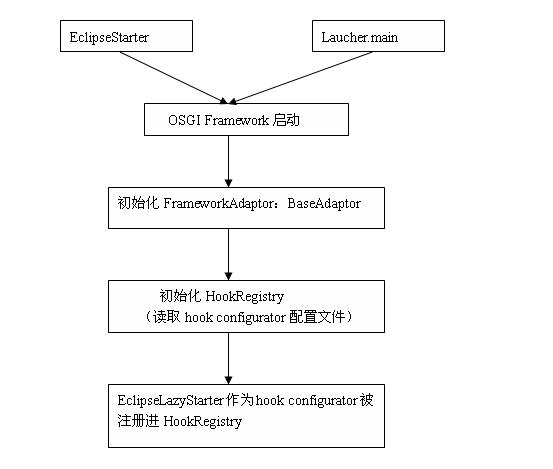
過程簡要解釋如下:
1、啟動osgi framework,兩種啟動方式:如果想利用Eclipse的一些特性,則就以EclipseStarter為 入口點啟動;否則,可以用命令行的方式,以Laucher.main為入口點啟動
2、初始化FrameworkAdaptor(對應eclipse實現是BaseAdaptor)看一下接口說明:
/**
* FrameworkAdaptor interface to the osgi framework. This class is used to provide
* platform specific support for the osgi framework.
*
* <p>The OSGi framework will call this class to perform platform specific functions.
*
* Classes that implement FrameworkAdaptor MUST provide a constructor that takes as a
* parameter an array of Strings. This array will contain arguments to be
* handled by the FrameworkAdaptor. The FrameworkAdaptor implementation may define the format
* and content of its arguments.
*
* The constructor should parse the arguments passed to it and remember them.
* The initialize method should perform the actual processing of the adaptor
* arguments.
* <p>
* Clients may implement this interface.
* </p>
* @since 3.1
*/
顯而易見,FrameworkAdaptor其實是osgi framework的後門,提供平台附加支持。
看一下BaseAdaptor的構造函數:
1 /**
2 * Constructs a BaseAdaptor.
3 * @param args arguments passed to the adaptor by the framework.
4 */
5 public BaseAdaptor(String[] args) {
6 if (LocationManager.getConfigurationLocation() == null)
7 LocationManager.initializeLocations();
8 hookRegistry = new HookRegistry(this);
9 FrameworkLogEntry[] errors = hookRegistry.initialize();
10 if (errors.length > 0)
11 for (int i = 0; i < errors.length; i++)
12 getFrameworkLog().log(errors[i]);
13 // get the storage after the registry has been initialized
14 storage = getStorage();
15 // TODO consider passing args to BaseAdaptorHooks
16 }
我們看到,調用了HookRegistry.initialize進行初始化
3、初始化HookRegistry,我們直接看一下HookRegistry.initialize方法實現
1 /**
2 * Initializes the hook configurators. The following steps are used to initialize the hook configurators. <p>
3 * 1. Get a list of hook configurators from all hook configurators properties files on the classpath,
4 * add this list to the overall list of hook configurators, remove duplicates. <p>
5 * 2. Get a list of hook configurators from the ("osgi.hook.configurators.include") system property
6 * and add this list to the overall list of hook configurators, remove duplicates. <p>
7 * 3. Get a list of hook configurators from the ("osgi.hook.configurators.exclude") system property
8 * and remove this list from the overall list of hook configurators. <p>
9 * 4. Load each hook configurator class, create a new instance, then call the {@link HookConfigurator#addHooks(HookRegistry)} method <p>
10 * 5. Set this HookRegistry object to read only to prevent any other hooks from being added. <p>
11 * @return an array of error log entries that occurred while initializing the hooks
12 */
13 public FrameworkLogEntry[] initialize() {
14 ArrayList configurators = new ArrayList(5);
15 ArrayList errors = new ArrayList(0); // optimistic that no errors will occur
16 mergeFileHookConfigurators(configurators, errors);
17 mergePropertyHookConfigurators(configurators);
18 loadConfigurators(configurators, errors);
19 // set to read-only
20 readonly = true;
21 return (FrameworkLogEntry[]) errors.toArray(new FrameworkLogEntry[errors.size ()]);
22 }
其中的mergeFileHookConfigurators方法調用,讀取了一個名為hookconfigurators.properties的屬 性配置文件,在org.eclipse.osgi插件中。看一下裡面的內容:
1 ###############################################################################
2 # Copyright (c) 2005, 2006 IBM Corporation and others.
3 # All rights reserved. This program and the accompanying materials
4 # are made available under the terms of the Eclipse Public License v1.0
5 # which accompanies this distribution, and is available at
6 # http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v10.html
7 #
8 # Contributors:
9 # IBM Corporation - initial API and implementation
10 ###############################################################################
11 hook.configurators= \
12 org.eclipse.osgi.internal.baseadaptor.BaseHookConfigurator,\
13 org.eclipse.osgi.internal.baseadaptor.DevClassLoadingHook,\
14 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseStorageHook,\
15 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseLogHook,\
16 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseErrorHandler,\
17 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseAdaptorHook,\
18 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseClassLoadingHook,\
19 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseLazyStarter,\
20 org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.stats.StatsManager,\
21 org.eclipse.osgi.internal.verifier.SignedBundleHook
22
^_^,我們的EclipseLazyStarter赫然在列!!!
回過頭來看一下EclipseLazyStarter(繼承ClassLoadingStatsHook)的使用方式:
BaseAdaptor.getHookRegistry().getClassLoadingStatsHooks()
前面已經看了ClasspathManager中findLocalClass方法的代碼,就是這麼調用ClassLoadingStatsHook policy的(我們的EclipseLazyStarter...)
【總結】
hook了,osgi framework留了個後門,Eclipse好好的利用了這個後門~_~
【附加說明】
1、EclipseLazyStarter只是ClassLoadingStatsHook policy的實現,其實HookRegsitry中還有其他的 hook policy,例如:
org.eclipse.osgi.baseadaptor.hooks.ClassLoadingHook
org.eclipse.osgi.baseadaptor.hooks.BundleFileWrapperFactoryHook
org.eclipse.osgi.baseadaptor.hooks.BundleFileFactoryHook
org.eclipse.osgi.baseadaptor.hooks.StorageHook
org.eclipse.osgi.baseadaptor.hooks.AdaptorHook
2、大家可以順帶詳細的看一下HookRegistry、HookConfigurator、BaseAdaptor等
3、hook這種手法在Eclipse的資源管理中也有比較成功的應用,可以看一下
org.eclipse.core.resources.team.IMoveDeleteHook
例如cvs、ClearCase等團隊開發管理工具中,都實現了這種hook,通過擴展點 org.eclipse.core.resources.moveDeleteHook動態掛入。大家有興趣可以深入看看,看過之後應該就明 白了為什麼cvs、ClearCase等一些團隊開發管理工具功能有一些不同了~_~
4、對osgi感興趣的同學,可以看一下org.eclipse.osgi插件中的代碼,質量很高~_~
亂轟轟的,湊合著看吧