還是來整體看一下HashMap的結構吧. 如下圖所示(圖沒畫好),方框代表Hash桶,橢圖代表 桶內的元素,在這裡就是Key-value對所組成Map.Entry對像.
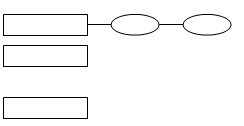
如果有多個元索被Hash函數定位到同一個桶內,我們稱之為hash沖突,桶內的元素組成單向 鏈表.讓我們看一下hashMap JDK源碼(因篇幅關系,刪除了部分代碼與注釋,感興可以查看 JDK1.6源碼):
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry[] table;
transient int size;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
transient volatile int modCount;
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
table = new Entry[capacity];
init();
}
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
private V getForNullKey() {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
}
先介紹一下負載因子(loadFactor)和容量(capacity)的屬性。其實一個 HashMap 的實際 容量就因子*容量,其默認值是 16(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)×0.75=12;這個很重要, 當存入HashMap的對象超過這個容量時,HashMap 就會重新構造存取表.
最重要的莫過於Put與Get方法.
我們先看put. 這裡先說一下,HashMap的hash函數是對key對像的hashCode進行hash,並把 Null keys always map to hash 0.這裡也正好證明了為什麼基本類型(int之類) 不能做KEY 值。
參考put方法源碼,首選判斷Key是否為null,若為NULL,剛從0號散列桶內去尋找key為null 的Entry,找到則用新的Value替換舊的 Value值,並返回舊值.反之把當前Entry放入0號桶,0號 桶內的其他Entry鏈接到當前Entry後面(參考Entry的next屬性).
如果是非NULL值,其實已經很簡單,根把hash結果找到相應的hash桶(當前桶),遍歷桶內 鏈表,如果找到與當前KEY值相同Entry, 則替抱該Entry的value值為當前value值。否則用當 前key-value構建Entry對像,並入當前桶內,桶內元素鏈到新Entry後面.與null思路相同.
到這裡get方法,就不用多說了,首先用key的hashCode 進行hash(參考HashMap的hash方 法),用所得值定位桶號.遍歷桶內鏈表,找到該KEY值的Entry對像,返回VALUE.反不到,則返回 NULL,簡單著呢.
回到網友貼子上來,如何快速查找KEY? hashMap通示計算得的HASH值快速定位到元素所在 的桶,這樣就排除了絕大部分元素,遍歷其內的小鏈表就很快了.如果用鏈表把所有元素鏈起來 ,時間可想而知.
HashMap唯一高明之處在於他的Hash算法(不太明白):
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}.
另外 transient Entry[] table中的transient是什麼意思,下一篇再說吧,歡迎拍磚.