在處理異常時,應該區分checked異常和unchecked異常。對於checked異常,我們應該提供健壯的異常恢復機制,而對於unchecked異常,這就是編程錯誤即bug,應該在調試階段很好的發現和處理它們。
1. Java異常層次結構
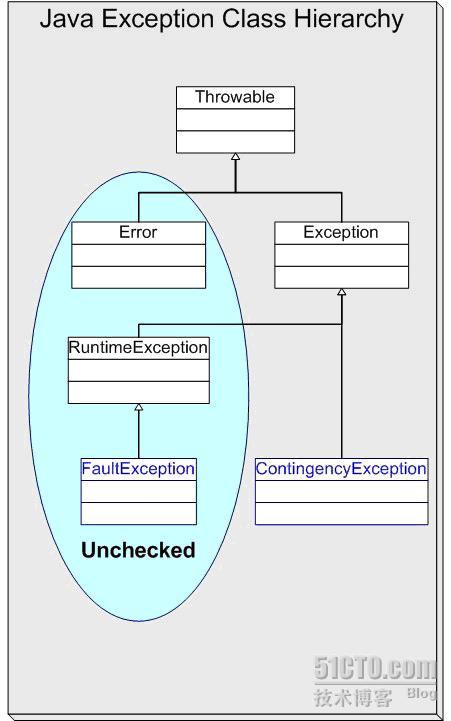
上圖(注:該圖引自http://dev2dev.bea.com.cn/techdoc/200702364792.html)標出了Java異常層次結構,也指出了哪些異常是unchecked,哪些異常是checked。下面給出幾段常見的異常處理代理,試圖總結日常開發中應該如何處理異常。
2.針對checked異常的恢復機制
checked異常並不是編程錯誤,它的出現是軟件運行階段所不可避免的。最常見的這類異常如socket連接超時。
對於此類異常,我們應該在程序的運行態下試圖從異常中恢復過來。下面這段代碼(Recover.java)的主要邏輯是,對目標值protected int current進行判斷,如果該值大於2則成功,否則拋出NotBigEnoughException異常。
在執行程序的過程中,在每次catch到NotBigEnoughException異常時,我們對current值遞增,試圖從異常中恢復過來。
NotBigEnoughException.java
package com.zj.exception.types;
public class NotBigEnoughException extends Exception {
public NotBigEnoughException() {
super();
}
public NotBigEnoughException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
Recover.java
package com.zj.exception;
import com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException;
public class Recover {
protected int current = 0;
protected boolean accept = false;
public Recover() {}
public Recover(int cur) {
current = cur;
}
public void increment() {
++current;
}
public boolean passed() {
return accept;
}
public void passing() throws NotBigEnoughException {
if (current > 2) {
accept = true;
System.out.println("accept " + current);
} else
throw new NotBigEnoughException("reject " + current);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Recover re = new Recover();
while (!re.passed()) {
try {
re.passing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
System.out.println(e);
re.increment();
}
}
}
}
結果:
com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 0
com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 1
com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 2
accept 3
3.繼承異常
在子類繼承父類的情況下,子類override方法的異常聲明只能取自(小於等於)父類該方法的異常聲明;對於子類構造方法的異常聲明必須包含(大於等於)父類構造方法的異常聲明。
類Inheritor繼承自類Recover,它的方法passing()試圖聲明一個父類沒有的異常UnknowException,這樣做是不允許的。
UnknowException.java
package com.zj.exception.types;
public class UnknowException extends Exception {
public UnknowException() {
super();
}
public UnknowException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
error in: Inheritor.java
//couldn't throws new exceptions where not found in its base class
public void passing() throws NotBigEnoughException, UnknowException {
if (current > 2) {
accept = true;
System.out.println("accept " + current);
} else if (current >= 0)
throw new NotBigEnoughException("reject " + current);
else
throw new UnknowException("i don't know how to deal with "
+ current);
}
之所以覆蓋這個方法的目的是對父類的passing()方法做進一步擴展,對0<=current<=2的情況拋出NotBigEnoughException,而對current<0的情況則拋出一個新的異常UnknowException。
此時,提供兩種解決方法。
方法一,使用恢復異常機制,overrding passing()方法,這樣可以處理掉所有的異常,因此不需要異常聲明。
ok in: Inheritor.java
//sure passing(),so not have to throw exceptions
public void passing(){
while (!passed()) {
try {
super.passing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
increment();
}
}
}
方法二,寫一個加強的passing()方法,即fortifiedPassing(),對於在父類passing()中捕獲的異常,進行再判斷。如果是0<=current<=2的情況則重新拋出NotBigEnoughException,如果是current<0的情況則拋出一個新的異常UnknowException。
ok in: Inheritor.java
public void fortifiedPassing() throws NotBigEnoughException, UnknowException{
try {
super.passing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
if(current>=0)
throw e;
else
throw new UnknowException("i don't know how to deal with "
+ current);
}
}
Inheritor.java
package com.zj.exception;
import com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException;
import com.zj.exception.types.UnknowException;
public class Inheritor extends Recover {
public Inheritor(int cur) {
super(cur);
}
//couldn't throws new exceptions where not found in its base class
/**
public void passing() throws NotBigEnoughException, UnknowException {
if (current > 2) {
accept = true;
System.out.println("accept " + current);
} else if (current >= 0)
throw new NotBigEnoughException("reject " + current);
else
throw new UnknowException("i don't know how to deal with "
+ current);
}*/
//sure passing(),so not have to throw exceptions
public void passing(){
while (!passed()) {
try {
super.passing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
increment();
}
}
}
public void fortifiedPassing() throws NotBigEnoughException, UnknowException{
try {
super.passing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
if(current>=0)
throw e;
else
throw new UnknowException("i don't know how to deal with "
+ current);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// not required try-catch
new Inheritor(3).passing();
new Inheritor(1).passing();
new Inheritor(-1).passing();
//no exceptions
try {
new Inheritor(3).fortifiedPassing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnknowException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
//NotBigEnoughException:
try {
new Inheritor(1).fortifiedPassing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnknowException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
//UnknownException:
try {
new Inheritor(-1).fortifiedPassing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnknowException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
結果:
accept 3
accept 3
accept 3
accept 3
com.zj.exception.types.UnknowException: i don't know how to deal with -1
com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 1
at com.zj.exception.Recover.passing(Recover.java:28)
at com.zj.exception.Inheritor.fortifiedPassing(Inheritor.java:38)
at com.zj.exception.Inheritor.main(Inheritor.java:63)
4.RuntimeException與包裝異常
RuntimeException是unhecked異常,它們由JVM拋出(你也可以拋出它),並且不必在異常聲明(throws)中列出。
如果RuntimeException沒有被catch而到達mian()方法時,那麼在程序退出前會自動調用該異常的printStackTrace()方法,打印該異常。
RuntimeException代表的是編程錯誤(如0除數,數組越界),是應該在調試階段解決的。
當你在捕獲某些異常,而不知道該如果處理時,你可以將它包裝為RuntimeException,這樣在後續的方法調用過程中就不用聲明(throws)該方法了。
在類Wrapper中,我們override fortifiedPassing()方法,並將它可能拋出的異常包裝為RuntimeException。
Wrapper.java
package com.zj.exception;
import com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException;
import com.zj.exception.types.UnknowException;
public class Wrapper extends Inheritor {
public Wrapper(int cur) {
super(cur);
}
public void fortifiedPassing() {
try {
super.fortifiedPassing();
} catch (NotBigEnoughException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (UnknowException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// not required try-catch
new Wrapper(3).fortifiedPassing();
new Wrapper(1).fortifiedPassing();
new Wrapper(-1).fortifiedPassing();
}
}
結果:
accept 3
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 1
at com.zj.exception.Wrapper.fortifiedPassing(Wrapper.java:14)
at com.zj.exception.Wrapper.main(Wrapper.java:23)
Caused by: com.zj.exception.types.NotBigEnoughException: reject 1
at com.zj.exception.Recover.passing(Recover.java:28)
at com.zj.exception.Inheritor.fortifiedPassing(Inheritor.java:38)
at com.zj.exception.Wrapper.fortifiedPassing(Wrapper.java:12)
... 1 more
本文出自 “子 孑” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto.com/113473/70681