引言
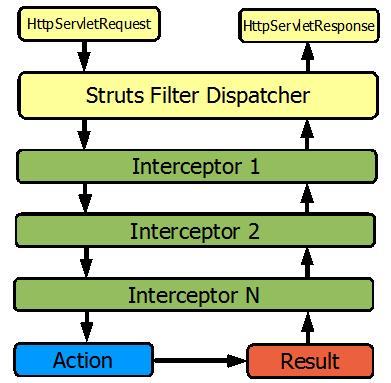
Apache Struts 作為最成功的 MVC Web 框架早已得到了廣泛的應用,但是其自身也暴露出不少缺點,從而引出了 Struts 2 。 Struts 2 摒棄了原來 Struts 1 的設計, 而是轉向了 webwork2,並結合 Struts 已有的優點,試圖打造出一個集眾家所長的完美 Web 框架。 Struts 2 因此也具備 webwork2 中的一個非常重要的特性 - 攔截器 (Interceptor) 。攔截器會在 Action 執行之前和之後被執行(如下圖),是一種典型 AOP 實現。
圖 1. Struts 2 的體系結構
Struts 2 本身提供了一個 org.apache.struts2.interceptor.RolesInterceptor 攔截器以方便開發人員來實現存取控制。但該攔截器的實現是建立在 J2EE 容器提供的存取控制機制之上的。容器提供的存取控制實現粒度較粗,往往無法滿足多數應用的需求。在許多項目中,用戶所應該具有的權限是由多種因素而決定,往往在不同的上下文中擁有不同的角色。例如在一個社交項目中,一個用戶會在不同的社團裡擁有不同的角色,如成員,管理員,來賓等。他的具體角色取決於當前所處社團的標識符。另外,用戶的角色還和他所要操作的資源類型有關。比如,在這個社交站點中,用戶可以創建自己的日程表,把這個日程表共享給其他用戶或者委托給其他人管理。這樣對日程表這種類型資源,就會有創建者,閱覽者和管理者三種角色。在更復雜應用中,用戶的角色可能還會受更多因素決定,這就要求存取控制要有更細的粒度,能夠處理更加復雜的邏輯。
為了滿足這個需求,在基於 Struts 2 的 Web 應用開發中,我們也可以利用攔截器來實現一個應用托管的基於角色的存取控制(RBAC, Role-Based Access Control)系統, 讓其能夠管理更細粒度的資源。該系統在 Struts 2 的配置文件中定義 Action 可以由那些角色來調用,即對角色進行授權。攔截器在 Action 調用之前,對當前用戶進行權限認證來決定 Action 是否應該被執行。
下面我們就基於 Hibernate+Spring+Struts2 框架來完成這個系統的實現。為了使系統結構更加清晰易於維護,我們將這個系統分為域模型層、持久層和服務層來實現。這種分層結構是目前 Web 開發廣為使用的一種模式。
模型層實現
這系統中我們只需要一個實體 UserRole, 用來定義用戶在不同的上下文中所具有的角色。在清單中,我們使用了 Java Persistence API (Hibernate 從 3.2 開始已經開始支持 JPA)中提供的 JDK 5.0 注解來對模型到數據庫表之間的映射進行定義。
清單 1.
@Entity
public class UserRole {
private Long id;
private User user;
private String objectType;
private Long objectId;
private String role;
public UserRole(Long userId, String role, String objectType, Long objectId) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(userId);
this.user = user;
this.role = role;
this.objectType = objectType;
this.objectId = objectId;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "userId", nullable = false)
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
public String getObjectType() {
return objectType;
}
public void setObjectType(String objectType) {
this.objectType = objectType;
}
public Long getObjectId() {
return objectId;
}
public void setObjectId(Long objectId) {
this.objectId = objectId;
}
public String getRole() {
return role;
}
public void setRole(String role) {
this.role = role;
}
}
注意這裡邊有兩個比較特殊的字段 objectType 和 objectId,它們用來表明用戶在具體哪個資源上擁有的角色。 objectType 指資源的類型,objectId 指資源的標識。比如我們要將用戶 Mike 加為某個日程表的管理員,則表中新增記錄的 user 字段為 Mike 在 user 表中的 ID,objectType 為“calendar”,objectID 為這個日程表 ID,role 為角色的名字“admin”。當然,如果您的應用中不同類型資源都使用唯一的全局 ID,objectType 這個字段也可以省略。
DAO 層實現
代碼清單 2 定義了對 UserRole 進行 CRUD 的 DAO 接口,代碼清單 3 則是它的實現。通過 @PersistenceContext 注解來讓容器注入 JPA 中的實體管理器 EntityManager 。 UserRoleDaoImpl 調用 EntityManager 來對 UserRole 進行持久化到數據庫中。
清單 2
public interface UserRoleDao {
public void create(UserRole userRole);
public void update(UserRole userRole);
public UserRole find(Long userId, String objectType, Long objectId);
}
清單 3
public class UserRoleDaoImpl implements UserRoleDao {
private EntityManager entityManager;
public EntityManager getEntityManager() {
return entityManager;
}
@PersistenceContext
public void setEntityManager(EntityManager entityManager) {
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
public void create(UserRole userRole) {
entityManager.persist(userRole);
}
public UserRole find(Long userId, String objectType, Long objectId) {
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(
"FROM UserRole ur WHERE ur.user.id=" +
userId +
" AND ur.objectType='" +
objectType +
"' AND ur.objectId=" +
objectId);
List result = query.getResultList();
if (result.size() == 0)
return null;
return (UserRole)result.get(0);
}
public void update(UserRole userRole) {
entityManager.merge(userRole);
}
}
服務層實現
創建一個 RoleService 接口 (清單 4) 作為 façade, 清單 5 是具體實現。 RoleServiceImpl 的實現很簡單,主要是封裝了為用戶分配角色和查詢用戶角色。注解 Transactional 用來將方法放置在一個事務中進行。在類聲明上的 @Transactional(readOnly = true) 表示默認的事務為只讀。 setUserRole 方法需要寫入數據到數據庫中,因此我們將其 readOnly 屬性設置成 false.
清單 4
public interface RoleService {
public void setUserRole(Long userId, String role, String objectType, Long objectId);
public String findRole(Long userId, String objectType, Long objectId);
}
清單 5
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleService {
private UserRoleDao userRoleDao;
public void setUserRoleDao(UserRoleDao userRoleDao) {
this.userRoleDao = userRoleDao;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = false)
public void setUserRole(Long userId, String role, String objectType, Long objectId) {
UserRole userRole = new UserRole(userId, role, objectType, objectId);
UserRole userRoleInDB = userRoleDao.find(userId, objectType, objectId);
if (null == userRoleInDB) {
userRoleDao.create(userRole);
} else {
userRole.setId(userRoleInDB.getId());
userRoleDao.update(userRole);
}
}
public String findRole(Long userId, String objectType, Long objectId) {
UserRole userRole = userRoleDao.find(userId, objectType, objectId);
if (userRole == null) {
return null;
}
return userRole.getRole();
}
}
攔截器的實現
攔截器會在 Action 被執行之前被 Struts 2 框架所調用,我們利用這個特性來完成對用戶身份的認證,只有用戶具有正確角色方能執行 Action 。具體哪些角色可以執行 Action,需要在 Struts 2 的配置文件中指定,將在下一小節中詳細闡述。這一點和 Struts 2 內置的 RolesInterceptor 類似,但我們的攔截器可以通過 objectType 和 objectId 來實現更加細粒度的認證。
要創建一個用於用戶角色認證的攔截器。需要讓其實現 com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor 接口並對 String intercept(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) throws Exception 方法進行實現。 如清單 6 。成員變量 roleService 是通過 Spring 的依賴注入被賦予 RoleServiceImpl 。 allowedRoles 和 disallowedRoles 分別存儲了允許和不允許執行 Action 的角色,兩者不能同時存在。 objectType 和 objectIdKey 分別表示資源的類型和資源 ID 在 HTTP 請求中的參數名。它們是做為 Interceptor 的參數在 Struts 2 配置文件中進行設置,會自動由 Struts 2 框架填充進來。
清單 6
public class RBACInterceptor implements Interceptor {
public static final String FORBIDDEN = "forbidden";
private List<String> allowedRoles = new ArrayList<String>();
private List<String> disallowedRoles = new ArrayList<String>();
private RoleService roleService;
private String objectType;
private String objectIdKey;
public void setRoleService(RoleService roleService) {
this.roleService = roleService;
}
public void setObjectType(String objectType) {
this.objectType = objectType;
}
public void setObjectIdKey(String objectIdKey) {
this.objectIdKey = objectIdKey;
}
public void setAllowedRoles(String roles) {
if (roles != null)
allowedRoles = Arrays.asList(roles.split("[ ]*,[ ]*"));
}
public void setDisallowedRoles(String roles) {
if (roles != null)
disallowedRoles = Arrays.asList(roles.split("[ ]*,[ ]*"));
}
public void init() {
}
public void destroy() {
}
public String intercept(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
// Get object id
Long objectId = Long.valueOf(request.getParameter(objectIdKey));
Map session = actionInvocation.getInvocationContext().getSession();
// Get current user id
Long userId = (Long) session.get(Constant.KEY_CURRENT_USER);
// Get the user role
String userRole = roleService.findRole(userId, objectType, objectId);
if (!isAllowed(userRole)) {
// forbid invoking the action
return FORBIDDEN;
} else {
// allow invoking the action
return actionInvocation.invoke();
}
}
// Check if the current user has correct role to invoke the action
protected boolean isAllowed(String userRole) {
if (allowedRoles.size() > 0) {
if (userRole == null)
return false;
return allowedRoles.contains(userRole);
} else if (disallowedRoles.size() > 0) {
if (userRole == null)
return true;
return !disallowedRoles.contains(userRole);
}
return true;
}
}
在 intercept 方法中我們根據當前用戶的 ID,HTTP 請求參數中獲得資源的 ID,所存取的資源類型來調用 RoleService 獲得用戶的角色。 然後再判斷該角色是否在 allowedRoles 和 disallowedRoles 中來確定用戶是否有權限調用 Action 。如果用戶沒權限,則將請求發送到名為“forbidden”的 result 。從這裡可以看出,用戶的角色驗證與身份驗證的作用完全不同。身份驗證是驗證用戶是否網站注冊用戶,而角色認證是在用戶為注冊用戶的前提下對用戶相對於站內各種資源扮演的角色的辨別。
上面代碼中用到了判斷用戶是否具有運行 Action 所要求的角色的函數 isAllowed()。它首先根據用戶 ID 和 Action 作用於的對象的類型和 ID 從數據庫查詢到用戶對應的角色,然後將用戶角色與允許角色的列表逐個比較。如果允許角色列表包含用戶實際角色則返回真,否則返回假;如果允許角色列表為空,則將用戶角色與禁止角色的列表比較,如果用戶的角色被禁止,則返回假,否則返回真。如果兩個列表都為空,也返回真。這樣既可以對某個 Action 配置允許訪問角色列表,也可以配置拒絕訪問列表。
使用
首先我需要在 Spring 的配置文件中添加系統中所涉及到各個 POJO,如清單 7 。
清單 7
<!-- Data Access Objects -->
<bean id="userRoleDao" class="com.sample.security.dao.impl.UserRoleDaoImpl"/>
<!-- Service Objects -->
<bean id="roleService"
class="com. sample.security.service.impl.RoleServiceImpl" >
<property name="userRoleDao" ref="userRoleDao" />
</bean>
<!-- Interceptor Objects -->
<bean id="RBACInterceptor" scope="prototype"
class="com. sample.security.interceptor. RBACInterceptor ">
<property name="roleService" ref="roleService" />
</bean>
然後需要在 Struts 配置文件中對需要進行存取控制的 Action 進行配置。首先定義我們實現的攔截器,並把其加到攔截器棧中。在 <interceptors> …… </interceptors> 中添加下面的代碼。
<interceptor name="RBAC ” class="RBACInterceptor" />
現在我們可以將 RBAC 攔截器添加到任意的 interceptor-stack 中,或者直接配置到任意的 Action 。添加下面清單中的內容到 Struts 2 配置文件中,將能夠對在一個日程表中刪除會議進行控制。
清單 8
<action name="deleteMeeting" class="com.demo.action.DeleteMeetingAction">
<result>/WEB-INF/jsp/deleteMeetingResult.jsp</result>
<result name="forbidden">/WEB-INF/jsp/forbidden.jsp</result>
<interceptor-ref name="RBAC">
<param name="allowedRoles">admin, owner</param>
<param name="objectType">calendar</param>
<param name="objectIdKey">id</param>
</interceptor-ref>
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack" />
</action>
至於用戶角色的分配,我們可以定義一個 Action 通過 RoleService 來創建。如下面清單 9 的配置和清單 10 的代碼實現了一個 Action 允許日程表的創建者來分配角色給其它人。
清單 9
<action name="assignCalendarRole" class="com.demo.action.AssignCalendarRoleAction">
<result>/WEB-INF/jsp/deleteMeetingResult.jsp</result>
<result name="forbidden">/WEB-INF/jsp/forbidden.jsp</result>
<interceptor-ref name="RBAC">
<param name="allowedRoles">owner</param>
<param name="objectType">calendar</param>
<param name="objectIdKey">id</param>
</interceptor-ref>
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack" />
</action>
清單 10
public class AssignCalendarRoleAction extends ActionSupport {
private RoleService roleService;
private Long userId = 0;
private String userRole = "reader";
private Long id = 0;
public AssignCalendarRoleAction (RoleService roleService) {
this.roleService = roleService;
}
public String execute() {
roleService.setUserRole(userId, userRole, "calendar", id);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
結束語
本文介紹了如何在 Spring+Hibernate+Struts2 框架中實現一個應用托管的 RBAC 系統,不同於容器提供的 RBAC,它能夠更加細粒度地對各種資源進行存取控制。這裡的實現非常簡單,還需要許多地方可以進行擴展和完善(比如對用戶組的支持),希望能對讀者起到拋磚引玉的作用。