本期開始講Model層的開發,整合iBatis框架,iBatis是Apache旗下Java數據持久層的框架,跟Hibernate是同一類型的框架。大家可到它的官方網站去下載http://ibatis.apache.org/java.cgi,如下圖:
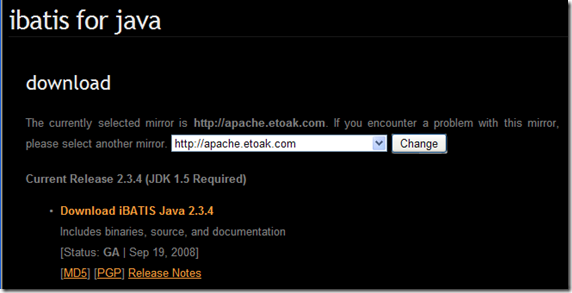
我這裡下載的是當前最新版本iBatis 2.3.4 , 下載之後,解壓包是這樣的:
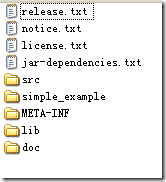
我們在lib目錄下,找到“ibatis-2.3.4.726.jar”文件,加入到我們項目的lib目錄下,就行。在這裡,我們先說下怎麼學習這個iBatis框架:上圖中,有個simple_example的文件夾,它裡面就包含了一個超級簡單且容易理解的例子,大家可以去學習一下。By the way,如果你學過Hibernate的話,你會發覺iBatis要比Hibernate好學很多。關於Hibernate和iBatis的爭論,網上有很多,大家有興趣可以去了解一下。
好,我們先建立數據庫和設計數據庫吧。我這項目用的是MySQL 5.0。生成數據庫和數據表的SQL語句如下:
create database simpledb;
create table article
(
ID int auto_increment not null primary key,
TITLE varchar(25),
AUTHOR varchar(25),
CONTENT text,
PUBTIME date
);
這是我們常見的新聞表及其中的字段。
接下來,寫一個與表對應的新聞類,Article.java,這個其實是POJO類,代碼如下:
package cn.simple.pojo;
import java.util.Date;
public class Article {
private int id;
private String title;
private String author;
private String content;
private Date pubtime;
/** *//***********getter和setter方法***********/
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Date getPubtime() {
return pubtime;
}
public void setPubtime(Date pubtime) {
this.pubtime = pubtime;
}
}
有了數據表和實體類,現在來寫兩者之間映射的配置文件Article.xml。代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE sqlMap
PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map 2.0//EN"
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-2.dtd">
<sqlMap namespace="Article">
<!-- Use type aliases to avoid typing the full classname every time. -->
<typeAlias alias="Article" type="cn.simple.pojo.Article" />
<!--
Result maps describe the mapping between the columns returned from a
query, and the class properties. A result map isn't necessary if the
columns (or aliases) match to the properties exactly.
-->
<resultMap id="ArticleResult" class="Article">
<result property="id" column="ID" />
<result property="title" column="TITLE"/>
<result property="author" column="AUTHOR"/>
<result property="content" column="CONTENT"/>
<result property="pubtime" column="PUBTIME"/>
</resultMap>
<!--
Select with no parameters using the result map for Account class.
-->
<select id="selectAllArticles" resultMap="ArticleResult">
select * from article
</select>
<!--
A simpler select example without the result map. Note the aliases to
match the properties of the target result class.
-->
<select id="selectArticleById" parameterClass="int" resultClass="Article">
select
ID as id,
TITLE as title,
AUTHOR as author,
CONTENT as content,
PUBTIME as pubtime
from Article
where ID=#id#
</select>
<!-- Insert example, using the Account parameter class -->
<insert id="insertArticle" parameterClass="Article">
insert into article (
TITLE,
AUTHOR,
CONTENT,
PUBTIME
) values (
#title#,
#author#,
#content#,
#pubtime#
)
</insert>
<!-- Update example, using the Account parameter class -->
<update id="updateArticle" parameterClass="Article">
update article set
TITLE = #title#,
AUTHOR = #author#,
CONTENT = #content#,
PUBTIME = #pubtime#
where
ID = #id#
</update>
<!-- Delete example, using an integer as the parameter class -->
<delete id="deleteArticleById" parameterClass="int">
delete from article where ID = #id#
</delete>
</sqlMap>
大家不要覺得這個映射文件很復雜,其實,這挺容易理解的,如果大家賴得寫的話,可復制iBatis自帶的simple_example下的例子的映射文件,然後修改一下就行。
有了表、實體類、表與實體之間的映射文件,之後,該做什麼呢?學過Hibernate的朋友會想到那個數據庫連接信息的配置文件,當然,iBatis也需要類似的文件,即SqlMapConfig.xml,代碼如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE sqlMapConfig
PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD SQL Map Config 2.0//EN"
"http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/sql-map-config-2.dtd">
<sqlMapConfig>
<!-- Configure a built-in transaction manager. If you're using an
app server, you probably want to use its transaction manager
and a managed datasource -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" commitRequired="false">
<dataSource type="SIMPLE">
<property name="JDBC.Driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="JDBC.ConnectionURL" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/simpledb"/>
<property name="JDBC.Username" value="root"/>
<property name="JDBC.Password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</transactionManager>
<!-- List the SQL Map XML files. They can be loaded from the
classpath, as they are here (com.domain.data) -->
<sqlMap resource="cn/simple/pojo/Article.xml"/>
<!-- List more here
<sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Order.xml"/>
<sqlMap resource="com/mydomain/data/Documents.xml"/>
-->
</sqlMapConfig>
一看這代碼,也有點復雜,我的說法同上,大不了COPY,再略作修改,呵呵
好了,來寫我們的業務邏輯層:
package cn.simple.manager;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import cn.simple.pojo.Article;
import com.ibatis.common.resources.Resources;
import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClient;
import com.ibatis.sqlmap.client.SqlMapClientBuilder;
public class ArticleManager {
/** *//**
* SqlMapClient instances are thread safe, so you only need one. In this
* case, we'll use a static singleton. So sue me. ;-)
*/
private static SqlMapClient sqlMapper;
/** *//**
* It's not a good idea to put code that can fail in a class initializer,
* but for sake of argument, here's how you configure an SQL Map.
*/
static {
try {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("SqlMapConfig.xml");
sqlMapper = SqlMapClientBuilder.buildSqlMapClient(reader);
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Fail fast.
throw new RuntimeException(
"Something bad happened while building the SqlMapClient instance."
+ e, e);
}
}
/** *//**
* 查詢列表
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static List<Article> selectAllArticles() throws SQLException {
return sqlMapper.queryForList("selectAllArticles");
}
/** *//**
* 插入數據
* @param article
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void insertArticle(Article article) throws SQLException {
sqlMapper.insert("insertArticle", article);
}
/** *//**
* 更新數據
* @param article
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void updateArticle(Article article) throws SQLException {
sqlMapper.update("updateArticle", article);
}
/** *//**
* 刪除數據
* @param id
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void deleteArticle(int id) throws SQLException {
sqlMapper.delete("deleteArticleById", id);
}
/** *//**
* 單查數據
* @param id
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Article queryArticleById(int id) throws SQLException {
Article article = (Article)sqlMapper.queryForObject("selectArticleById", id);
return article;
}
}
寫一個Junit測試類來測試一下吧,代碼如下:
package cn.simple.manager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import cn.simple.pojo.Article;
public class ArticleManagerTest {
@Test
public void testSelectAllArticles() throws SQLException {
List<Article> list = ArticleManager.selectAllArticles();
for(Article a : list){
System.out.println(a.getTitle() + a.getAuthor() + a.getContent() + a.getPubtime());
}
}
@Test
public void testInsertArticle() throws SQLException {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
Article article = new Article();
article.setTitle("title-" + i);
article.setAuthor("author-" + i);
article.setContent("content-" + i);
article.setPubtime(new Date());
ArticleManager.insertArticle(article);
}
}
@Test
public void testUpdateArticle() throws SQLException {
Article article = new Article();
article.setId(3);
article.setTitle("title-title");
article.setAuthor("author-author");
ArticleManager.updateArticle(article);
}
@Test
public void testDeleteArticle() throws SQLException {
ArticleManager.deleteArticle(5);
}
}
到此,我們的項目文件列表截圖如下:
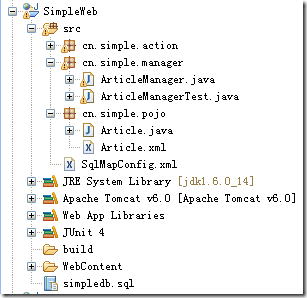
新聞管理的Model層開發完畢,可以供我們的Action調用了,好,Struts 2.1.6 精簡實例系列教程,敬請大家期待下文!