很多的J2EE應用程序需要使用持久性數據(數據庫、文件等)。不同的程序,持久性存儲是各不相同的,並且用來訪問這些不同的持久性存儲機制的API也有很大的不同。如果應用程序要在不同的持久性存儲間遷移,這些訪問特定持久存儲層的代碼將面臨重寫。
如何解決這個問題?且看"DAO模式"
數據訪問對象(Data Acess Object) 模式
一.環境
根據數據源不同,數據訪問也不同。根據存儲的類型(關系數據庫、面向對象數據庫、文件等等)和供應商實現不同,持久性存儲(比如數據庫)的訪問差別也很大。
二.問題
許多真是的J2EE應用程序需要在一定程度上使用持久性數據。對於許多應用程序,持久性存儲是使用不同的機制實現的,並且用來訪問這些不同的持久性存儲機制的API也有很大的不同。
比如,應用程序使用實體bean(這裡應該是指BMP的bean,CMP的bean已大大降低了與RDBMS的耦合)的分布式組件來表示持久性數據,或者使用JDBC API來訪問駐留在某關系數據庫管理系統(RDBMS)中的數據,這些組件中包含連接性性和數據訪問代碼會引入這些組件與數據源實現之間的緊密耦合。組件中這類代碼依賴性使應用程序從某種數據源遷移到其他種類的數據源將變得非常麻煩和困難。當數據源變化時,組件也需要改變,以便於能夠處理新類型的數據源。
(舉個例子來說,我們UPTEL系統是使用JDBC API對 ORACLE數據庫進行連接和數據訪問的,這些JDBC API與SQL語句散布在系統中,當我們需要將UPTEL遷移到其他RDBMS時,比如曾經遷移到INFORMIX,就面臨重寫數據庫連接和訪問數據的模塊。)
三.作用力
1.諸如bean管理的實體bean、會話bean、servlet等組件往往需要從持久性存儲數據源中檢索數據,以及進行數據存儲等操作。
2.根據產品供應商的不同,持久性存儲API差別也很大,這些API和其能力同樣根據存儲的類型不同也有差別,這樣存在以下缺點,即訪問這些獨立系統的API很不統一。
3.組件需要透明於實際的持久性存儲或者數據源實現,以便於提供到不同供應商產品、不同存儲類型和不同數據源類型的更容易的移植性。
四.解決方案
使用數據訪問對象(DAO)模式來抽象和封裝所有對數據源的訪問。DAO管理著與數據源的連接以便檢索和存儲數據。
DAO實現了用來操作數據源的訪問機制。數據源可以時RDBMS,LDAP,File等。依賴於DAO的業務組件為其客戶端使用DAO提供更簡單的接口。DAO完全向客戶端隱藏了數據源實現細節。由於當低層數據源實現變化時,DAO向客戶端提供的接口不會變化,所有該模式允許DAO調整到不同的存儲模式,而不會影響其客戶端或者業務組件。重要的是,DAO充當組件和數據源之間的適配器。
(按照這個理論,如果我們UPTEL系統使用了DAO模式,就可以無縫的從ORACLE遷移到任何一個RDBMS了。夢想總是很完美的,且看看DAO模式如何實現)
1.結構,圖1是表示DAO模式中各種關系的類圖。
此主題相關圖片如下:
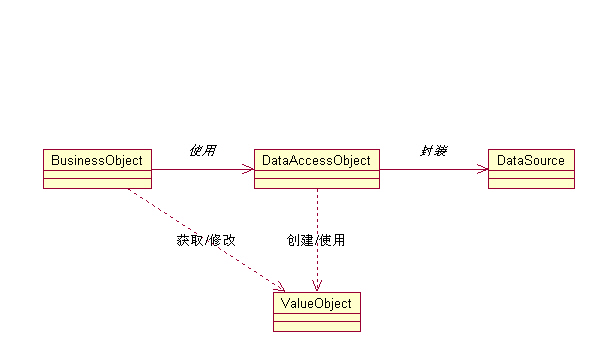
2.參與者和職責
1)BusinessObject(業務對象)
代表數據客戶端。正是該對象需要訪問數據源以獲取和存儲數據。
2)DataAccessObject(數據訪問對象)
是該模式的主要對象。DataAccessObject抽取該BusinessObject的低層數據訪問實現,以保證對數據源的透明訪問。BusinessObject也可以把數據加載和存儲操作委托給DataAccessObject。
3)DataSource(數據源)
代表數據源實現。數據源可以是各RDBMSR數據庫,OODBMS,XML文件等等。
4)valueObject(值對象)
代表用做數據攜帶著的值對象。DataAccessObject可以使用值對象來把數據返回給客戶端。
DataAccessObject也許會接受來自於客戶端的數據,其中這些用於更新數據源的數據存放於值對象中來傳遞。
3.策略
1).自動DAO代碼產生策略
因為每個BusinessObject對應於一個特殊的DAO,因此有可能建立BusinessObject,DAO和低層實現(比如RDBMS中的表)之間的關系(映射)。一點這些關系(映射)已經建立,我們就可以編寫與應用程序有館的代碼生成的簡單工具了(什麼?自己寫GP程序?用ORM的附帶工具自動生成不就完了,最多自己寫幾個Adapter,牛人就是不同,啥都要自己寫...),其中的工具可以產生該應用程序需要的所有DAO代碼。
如果DAO需求很復雜,我們可以采用第三方工具,其中這些工具提供對象到RDBMS數據庫的關系映射(這裡指的是前面提到的ORM工具,全稱是Object Relation Mapping,目前成熟的ORM工具有很多:Hibernate,OJB,Torque,TopLink等等)。
這些工具通常包含GUI工具來把業務對象映射到持久性存儲對象,並且因而定義中間DAO。一旦這些映射完成,這些工具會自動地生成代碼,並且也許會提供其他增值功能,比如結果緩沖、查詢緩沖、與應用程序集成,以及與其他第三方產品(比如分布式緩沖)地繼承,等等。
(增值服務:Torque提供了結果緩沖,Hibernate提供了對Oracle數據庫SQL指令的優化,OJB提供JDO API、OMDB API)
2).數據訪問對象的工廠策略
通過調整抽象工廠和工廠方法模式,DAO模式可以達到很高的靈活度。
當低層存儲不會隨著實現變化而變化時,該策略可以使用工廠方法模式來實現該策略。以產生應用程序需要的大量DAO。圖2是這種情況下的類圖。
此主題相關圖片如下:
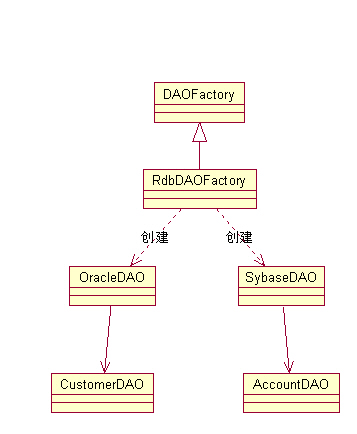
當低層存儲隨著實現變化而變化時,該策略可以使用抽象工廠方法模式而實現。
圖3是這種情況下的類圖。
此主題相關圖片如下:
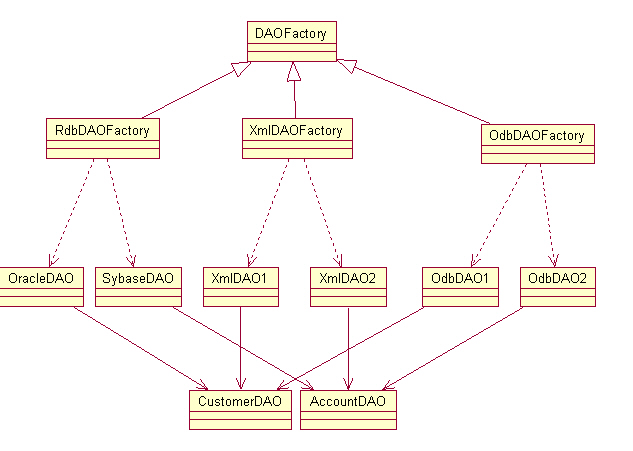
5.結果
1).啟用透明性
業務對象可以是使用數據源,而無須了解該數據源實現的具體細節。訪問是透明的,原因是實現被隱藏在DAO的內部。
2).啟用更容易的遷移
DAO層使應用程序更加容易地遷移到一個不同的數據庫實現。業務對象不了解低層數據實現。因而,該遷移只涉及對DAO層的變化。更進一步說,如果使用工廠策略,則有可能為每一個低層存儲實現提供一個具體工廠實現。在這種情況下,遷移到不同的遷移實現意味著給應用程序提供一個新的工廠實現。
3).減少業務對象中代碼復雜度
由於DAO管理所有的數據訪問復雜性,它可以簡化業務對象和其他使用DAO的客戶端中的代碼。所有與實現有關的代碼(比如sql語句)都被包含在DAO中,而不是包含在業務對象中。這樣做提高了代碼的可讀性,已經代碼生產效率。
4).把所有的數據訪問集中到一個獨立的層。
因為所有的數據訪問操作現在被委托給DAO,所有單獨的數據訪問層可以被看作把數據訪問實現與應用程序中的其他代碼相隔離的。這種集中化使應用程序更容易地維護和管理。
5).不適用於容器管理的持久性
由於EJB容器用容器管理的持久性(CMP)來管理實體bean,該容器會自動地服務所有的持久性存儲訪問。使用容器管理的實體bean的應用程序不需要DAO層,因為該應用程序服務器透明地提供該功能。然而,當需要組合使用CMP和BMP時,DAO仍舊有用處。
6).添加其他層
DAO會在數據客戶端和數據源之間創建其他的對象層,其中該數據源需要被設計和實現以便於權衡該模式的好處。但是選擇本方法也會帶來額外的開銷。
7).需要類層次設計
在使用工廠策略時,我們需要設計和實現具體工廠的層次,以及這些工廠產生的具體產品層次。如果能夠確保這種靈活性,則有必要考慮這種額外的工作。這樣做會增加設計的復雜性。然而,在實現該工廠策略時,你可以首先考慮工廠方法模式,然後再根據需要過渡到抽象工廠。
六.范例代碼
1.實現數據訪問對象模式
范例9-4時表示Customer信息的持久性對象的DAO范例代碼。當findCustomer()被調用時,CloudscapeCustomerDAO創建一個Customer值對象。
范例9-6是使用DAO的范例代碼。
2.實現數據訪問對象的工廠策略
1)使用工廠方法模式
2)使用抽象工廠模式
范例代碼9-2是CloudscapeDAOFactory的范例代碼。
范例代碼9-3中的CustomerDAO接口為Customer持久性對象定義了DAO方法,這些接口是被所有具體DAO實現來實現的,比如CloudscapeCustomerDAO、OracleCustomerDAO、已經SybaseCustomerDAO。Account和OrederDAO接口也與此類似。
Example 9.1 Abstract DAOFactory Class
// Abstract class DAO Factory
public abstract class DAOFactory {
// List of DAO types supported by the factory
public static final int CLOUDSCAPE = 1;
public static final int ORACLE = 2;
public static final int SYBASE = 3;
...
// There will be a method for each DAO that can be
// created. The concrete factories will have to
// implement these methods.
public abstract CustomerDAO getCustomerDAO();
public abstract AccountDAO getAccountDAO();
public abstract OrderDAO getOrderDAO();
...
public static DAOFactory getDAOFactory(
int whichFactory) {
switch (whichFactory) {
case CLOUDSCAPE:
return new CloudscapeDAOFactory();
case ORACLE :
return new OracleDAOFactory();
case SYBASE :
return new SybaseDAOFactory();
...
default :
return null;
}
}
}
Example 9.2 Concrete DAOFactory Implementation for Cloudscape
// Cloudscape concrete DAO Factory implementation
import java.sql.*;
public class CloudscapeDAOFactory extends DAOFactory {
public static final String DRIVER="COM.cloudscape.core.RmiJdbcDriver";
public static final String DBURL="jdbc:cloudscape:rmi://localhost:1099/CoreJ2EEDB";
// method to create Cloudscape connections
public static Connection createConnection() {
// Use DRIVER and DBURL to create a connection
// Recommend connection pool implementation/usage
}
public CustomerDAO getCustomerDAO() {
// CloudscapeCustomerDAO implements CustomerDAO
return new CloudscapeCustomerDAO();
}
public AccountDAO getAccountDAO() {
// CloudscapeAccountDAO implements AccountDAO
return new CloudscapeAccountDAO();
}
public OrderDAO getOrderDAO() {
// CloudscapeOrderDAO implements OrderDAO
return new CloudscapeOrderDAO();
}
...
}
Example 9.3 Base DAO Interface for Customer
// Interface that all CustomerDAOs must support
public interface CustomerDAO {
public int insertCustomer(...);
public boolean deleteCustomer(...);
public Customer findCustomer(...);
public boolean updateCustomer(...);
public RowSet selectCustomersRS(...);
public Collection selectCustomersVO(...);
...
}
Example 9.4 Cloudscape DAO Implementation for Customer
// CloudscapeCustomerDAO implementation of the
// CustomerDAO interface. This class can contain all
// Cloudscape specific code and SQL statements.
// The client is thus shielded from knowing
// these implementation details.
import java.sql.*;
public class CloudscapeCustomerDAO implements
CustomerDAO {
public CloudscapeCustomerDAO() {
// initialization
}
// The following methods can use
// CloudscapeDAOFactory.createConnection()
// to get a connection as required
public int insertCustomer(...) {
// Implement insert customer here.
// Return newly created customer number
// or a -1 on error
}
public boolean deleteCustomer(...) {
// Implement delete customer here
// Return true on success, false on failure
}
public Customer findCustomer(...) {
// Implement find a customer here using supplied
// argument values as search criteria
// Return a value object if found,
// return null on error or if not found
}
public boolean updateCustomer(...) {
// implement update record here using data
// from the customerData value object
// Return true on success, false on failure or
// error
}
public RowSet selectCustomersRS(...) {
// implement search customers here using the
// supplied criteria.
// Return a RowSet.
}
public Collection selectCustomersVO(...) {
// implement search customers here using the
// supplied criteria.
// Alternatively, implement to return a Collection
// of value objects.
}
...
}
Example 9.5 Customer value Object
public class Customer implements java.io.Serializable {
// member variables
int CustomerNumber;
String name;
String streetAddress;
String city;
...
// getter and setter methods...
...
}
Example 9.6 Using a DAO and DAO Factory ?Client Code
...
// create the required DAO Factory
DAOFactory cloudscapeFactory =
DAOFactory.getDAOFactory(DAOFactory.DAOCLOUDSCAPE);
// Create a DAO
CustomerDAO custDAO = cloudscapeFactory.getCustomerDAO();
// create a new customer
int newCustNo = custDAO.insertCustomer(...);
// Find a customer object. Get the value object.
Customer cust = custDAO.findCustomer(...);
// modify the values in the value object.
cust.setAddress(...);
cust.setEmail(...);
// update the customer object using the DAO
custDAO.updateCustomer(cust);
// delete a customer object
custDAO.deleteCustomer(...);
// select all customers in the same city
Customer criteria=new Customer();
criteria.setCity("廣州");
Collection customersList =
custDAO.selectCustomersVO(criteria);
// returns customersList - collection of Customer
// value objects. iterate through this collection to
// get values.
...