Map集合可以保存鍵值映射關系,這非常適合本實例所需要的數據結構,所有省份信息可以保存為Map集合的鍵,而每個鍵可以保存對應的城市信息,本實例就是利用Map集合實現了省市級聯選擇框,當選擇省份信息時,將改變城市下拉選擇框對應的內容。
思路分析:
1. 創建全國(省,直轄市,自治區)映射集合,即LinkedHashMap對象,使用Map接口的put()方法向集合中添加指定的省與城市的映射關系,其中值為String型一維數組。
代碼如下:
CityMap.java
代碼如下:
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CityMap {
/**
* 全國(省,直轄市,自治區)映射集合
*/
public static Map<String,String[]> model=new LinkedHashMap<String, String[]>();
static{
model.put("北京", new String[]{"北京"});
model.put("上海", new String[]{"上海"});
model.put("天津", new String[]{"天津"});
model.put("重慶", new String[]{"重慶"});
model.put("黑龍江", new String[]{"哈爾濱","齊齊哈爾","牡丹江","大慶","伊春","雙鴨山","鶴崗","雞西","佳木斯","七台河","黑河","綏化","大興安嶺"});
model.put("吉林", new String[]{"長春","延邊","吉林","白山","白城","四平","松原","遼源","大安","通化"});
model.put("遼寧", new String[]{"沈陽","大連","葫蘆島","旅順","本溪","撫順","鐵嶺","遼陽","營口","阜新","朝陽","錦州","丹東","鞍山"});
model.put("內蒙古", new String[]{"呼和浩特","呼倫貝爾","錫林浩特","包頭","赤峰","海拉爾","烏海","鄂爾多斯","通遼"});
model.put("河北", new String[]{"石家莊","唐山","張家口","廊坊","邢台","邯鄲","滄州","衡水","承德","保定","秦皇島"});
model.put("河南", new String[]{"鄭州","開封","洛陽","平頂山","焦作","鶴壁","新鄉","安陽","濮陽","許昌","漯河","三門峽","南陽","商丘","信陽","周口","駐馬店"});
model.put("山東", new String[]{"濟南","青島","淄博","威海","曲阜","臨沂","煙台","棗莊","聊城","濟寧","菏澤","泰安","日照","東營","德州","濱州","萊蕪","濰坊"});
model.put("山西", new String[]{"太原","陽泉","晉城","晉中","臨汾","運城","長治","朔州","忻州","大同","呂梁"});
model.put("江蘇", new String[]{"南京","蘇州","昆山","南通","太倉","吳縣","徐州","宜興","鎮江","淮安","常熟","鹽城","泰州","無錫","連雲港","揚州","常州","宿遷"});
model.put("安徽", new String[]{"合肥","巢湖","蚌埠","安慶","六安","滁州","馬鞍山","阜陽","宣城","銅陵","淮北","蕪湖","毫州","宿州","淮南","池州"});
model.put("陝西", new String[]{"西安","韓城","安康","漢中","寶雞","鹹陽","榆林","渭南","商洛","銅川","延安"});
model.put("寧夏", new String[]{"銀川","固原","中衛","石嘴山","吳忠"});
model.put("甘肅", new String[]{"蘭州","白銀","慶陽","酒泉","天水","武威","張掖","甘南","臨夏","平涼","定西","金昌"});
model.put("青海", new String[]{"西寧","海北","海西","黃南","果洛","玉樹","海東","海南"});
model.put("湖北", new String[]{"武漢","宜昌","黃岡","恩施","荊州","神農架","十堰","鹹寧","襄樊","孝感","隨州","黃石","荊門","鄂州"});
model.put("湖南", new String[]{"長沙","邵陽","常德","郴州","吉首","株洲","婁底","湘潭","益陽","永州","岳陽","衡陽","懷化","韶山","張家界"});
model.put("浙江", new String[]{"杭州","湖州","金華","寧波","麗水","紹興","雁蕩山","衢州","嘉興","台州","舟山","溫州"});
model.put("江西", new String[]{"南昌","萍鄉","九江","上饒","撫州","吉安","鷹潭","宜春","新余","景德鎮","贛州"});
model.put("福建", new String[]{"福州","廈門","龍巖","南平","寧德","莆田","泉州","三明","漳州"});
model.put("貴州", new String[]{"貴陽","安順","赤水","遵義","銅仁","六盤水","畢節","凱裡","都勻"});
model.put("四川", new String[]{"成都","泸州","內江","涼山","阿壩","巴中","廣元","樂山","綿陽","德陽","攀枝花","雅安","宜賓","自貢","甘孜州","達州","資陽","廣安","遂寧","眉山","南充"});
model.put("廣東", new String[]{"廣州","深圳","潮州","韶關","湛江","惠州","清遠","東莞","江門","茂名","肇慶","汕尾","河源","揭陽","梅州","中山","德慶","陽江","雲浮","珠海","汕頭","佛山"});
model.put("廣西", new String[]{"南寧","桂林","陽朔","柳州","梧州","玉林","桂平","賀州","欽州","貴港","防城港","百色","北海","河池","來賓","崇左"});
model.put("雲南", new String[]{"昆明","保山","楚雄","德宏","紅河","臨滄","怒江","曲靖","思茅","文山","玉溪","昭通","麗江","大理"});
model.put("海南", new String[]{"海口","三亞","儋州","瓊山","通什","文昌"});
model.put("新疆", new String[]{"烏魯木齊","阿勒泰","阿克蘇","昌吉","哈密","和田","喀什","克拉瑪依","石河子","塔城","庫爾勒","吐魯番","伊寧"});
}
}
2. 定義獲取省份的方法,創建一個Map集合,將上一步得到的映射集合賦值給它,使用Map集合的keySet()方法獲取該集合中的所有鍵對象組成的Set集合,即為省分集合,創建一個Object型一維數組,使用Set接口的toArray()方法將Set集合轉換為數組,返回此數組作為省份選擇下拉列表的參數。
3. 使用JComboBox類的setModel()方法為省份下拉列表添加省份信息,參數即為上一步中的獲取省份方法。
4. 定義根據省份獲取市/縣的方法,創建一個Map集合,將步驟1中得到的映射集合賦值給它,使用Map集合的get()方法獲取指定鍵的值,即為市/縣集合,創建一個String[]型一維數組,將市/縣集合賦值給該數組。
5. 定義省份下拉列表的選項狀態更改事件,在該事件中通過JComboBox類的getSelectedItem()方法獲取選中的省份,默認為省份集合中的第一個值,然後使用JComboBox類的removeAllItems()方法清空市/縣列表,根據選中的省份獲取市/縣數組,最後使用JComboBox的setModel()方法重新添加市/縣列表的值。
代碼如下:
BackgroundPanel.java
代碼如下:
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* 帶背景的面板組件
*
* @author ZhongWei Lee
*/
public class BackgroundPanel extends JPanel {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7758689434195492602L;
/**
* 背景圖片
*/
private Image image;
/**
* 構造方法
*/
public BackgroundPanel() {
super();
setOpaque(false);
setLayout(null);
}
/**
* 設置圖片的方法
*/
public void setImage(Image image) {
this.image = image;
}
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {// 重寫繪制組件外觀
if (image != null) {
int width = getWidth();// 獲取組件大小
int height = getHeight();
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, width, height, this);// 繪制圖片與組件大小相同
}
super.paintComponent(g);// 執行超類方法
}
}
SwingResourceManager.java
代碼如下:
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
/**
* Utility class for managing resources such as colors, fonts, images, etc.
*
* This class may be freely distributed as part of any application or plugin.
* <p>
* Copyright (c) 2003 - 2004, Instantiations, Inc. <br>All Rights Reserved
*
* @author scheglov_ke
*/
public class SwingResourceManager {
/**
* Maps image names to images
*/
private static HashMap<String, Image> m_ClassImageMap = new HashMap<String, Image>();
/**
* Returns an image encoded by the specified input stream
* @param is InputStream The input stream encoding the image data
* @return Image The image encoded by the specified input stream
*/
private static Image getImage(InputStream is) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte buf[] = new byte[1024 * 4];
while (true) {
int n = is.read(buf);
if (n == -1)
break;
baos.write(buf, 0, n);
}
baos.close();
return Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().createImage(baos.toByteArray());
} catch (Throwable e) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the image
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
String key = clazz.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
if ((path.length() > 0) && (path.charAt(0) == '/')) {
String newPath = path.substring(1, path.length());
image = getImage(new BufferedInputStream(clazz.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(newPath)));
} else {
image = getImage(clazz.getResourceAsStream(path));
}
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
}
return image;
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String path) {
return getImage("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an image stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the image file
* @return Image The image stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static Image getImage(String section, String path) {
String key = section + '|' + SwingResourceManager.class.getName() + '|' + path;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
if (image == null) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
image = getImage(fis);
m_ClassImageMap.put(key, image);
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
return image;
}
/**
* Clear cached images in specified section
* @param section the section do clear
*/
public static void clearImages(String section) {
for (Iterator<String> I = m_ClassImageMap.keySet().iterator(); I.hasNext();) {
String key = I.next();
if (!key.startsWith(section + '|'))
continue;
Image image = m_ClassImageMap.get(key);
image.flush();
I.remove();
}
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path relative to the specified class
* @param clazz Class The class relative to which to find the icon
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Class<?> clazz, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(clazz, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String path) {
return getIcon("default", path); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
/**
* Returns an icon stored in the file at the specified path
* @param section String The storage section in the cache
* @param path String The path to the icon file
* @return Icon The icon stored in the file at the specified path
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(String section, String path) {
return getIcon(getImage(section, path));
}
/**
* Returns an icon based on the specified image
* @param image Image The original image
* @return Icon The icon based on the image
*/
public static ImageIcon getIcon(Image image) {
if (image == null)
return null;
return new ImageIcon(image);
}
}
MainFrame.java
代碼如下:
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;
import java.awt.event.ItemListener;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.swing.DefaultComboBoxModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
import javax.swing.border.TitledBorder;
public class MainFrame extends JFrame {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4595347311922711984L;
private JTextField textField_3;
private JTextField textField_1;
private JComboBox comboBox_1;
private JTextField textField;
private JComboBox cityComboBox;
private JComboBox comboBox;
/**
* Launch the application
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel("com.sun.java.swing.plaf.nimbus.NimbusLookAndFeel");
MainFrame frame = new MainFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame
*/
public MainFrame() {
getContentPane().setLayout(null);
setBounds(100, 100, 518, 379);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//獲取默認的市/縣
String province=(String)getProvince()[0];
setTitle("輸入指定省/直轄市查詢對應的市縣");
final BackgroundPanel backgroundPanel = new BackgroundPanel();
backgroundPanel.setImage(SwingResourceManager.getImage(MainFrame.class, "/images/background.jpg"));
backgroundPanel.setBounds(0, 0, 510, 380);
getContentPane().add(backgroundPanel);
final JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.setOpaque(false);
panel.setBounds(36, 126, 438, 70);
backgroundPanel.add(panel);
panel.setLayout(null);
panel.setBorder(new TitledBorder(null, "居住地", TitledBorder.DEFAULT_JUSTIFICATION, TitledBorder.DEFAULT_POSITION, null, null));
cityComboBox = new JComboBox();
cityComboBox.setBounds(245, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(cityComboBox);
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getCity(province)));
comboBox = new JComboBox();
comboBox.setBounds(25, 25, 124, 27);
panel.add(comboBox);
comboBox.addItemListener(new ItemListener() {
public void itemStateChanged(final ItemEvent e) { // 選項狀態更改事件
itemChange();
}
});
comboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(getProvince())); // 添加省份信息
final JLabel label = new JLabel();
label.setText("省/直轄市");
label.setBounds(155, 30, 66, 18);
panel.add(label);
final JLabel label_1 = new JLabel();
label_1.setText("市/縣");
label_1.setBounds(375, 30, 37, 18);
panel.add(label_1);
final JLabel label_2 = new JLabel();
label_2.setBounds(36, 43, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_2);
label_2.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_2.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_2.setText("姓 名:");
textField = new JTextField();
textField.setBounds(113, 38, 154, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField);
final JLabel label_3 = new JLabel();
label_3.setBounds(36, 84, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_3);
label_3.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_3.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_3.setText("性 別:");
comboBox_1 = new JComboBox();
comboBox_1.setBounds(113, 81, 66, 25);
backgroundPanel.add(comboBox_1);
comboBox_1.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(new String[] {"男", "女"}));
final JLabel label_4 = new JLabel();
label_4.setBounds(36, 212, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4);
label_4.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4.setText("詳細地址:");
textField_1 = new JTextField();
textField_1.setBounds(113, 208, 367, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_1);
final JLabel label_4_1 = new JLabel();
label_4_1.setBounds(36, 252, 65, 18);
backgroundPanel.add(label_4_1);
label_4_1.setHorizontalTextPosition(SwingConstants.LEADING);
label_4_1.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
label_4_1.setText("E-mail:");
textField_3 = new JTextField();
textField_3.setBounds(113, 248, 367, 27);
backgroundPanel.add(textField_3);
final JButton button = new JButton();
button.setBounds(159, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button);
button.setText("保存");
final JButton button_1 = new JButton();
button_1.setBounds(265, 289, 75, 28);
backgroundPanel.add(button_1);
button_1.setText("重置");
//
}
/**
* 獲取省、直轄市,自治區
*
* @return
*/
public Object[] getProvince() {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model;// 獲取省份信息保存到Map中
Set<String> set = map.keySet(); // 獲取Map集合中的鍵,並以Set集合返回
Object[] province = set.toArray(); // 轉換為數組
return province; // 返回獲取的省份信息
}
/**
* 獲取指定省對應的市/縣
*
* @param selectProvince
* @return
*/
public String[] getCity(String selectProvince) {
Map<String, String[]> map = CityMap.model; // 獲取省份信息保存到Map中
String[] arrCity = map.get(selectProvince); // 獲取指定鍵的值
return arrCity; // 返回獲取的市/縣
}
private void itemChange() {
String selectProvince = (String) comboBox.getSelectedItem();
cityComboBox.removeAllItems(); // 清空市/縣列表
String[] arrCity = getCity(selectProvince); // 獲取市/縣
cityComboBox.setModel(new DefaultComboBoxModel(arrCity)); // 重新添加市/縣列表的值
}
}
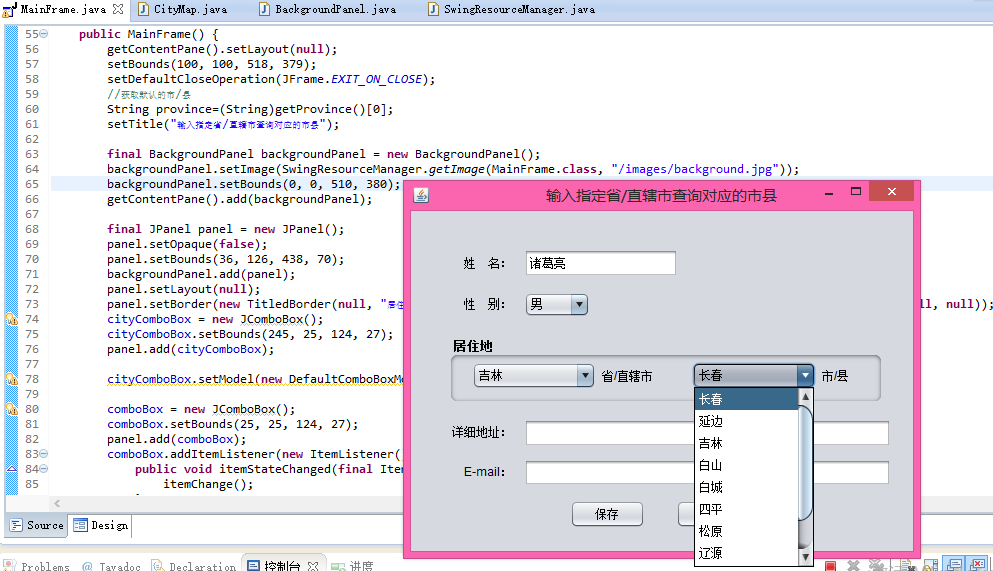
效果如圖: