Java的一大優勢是能完成多線程任務,對線程的封裝和調度非常好,那麼它又是如何實現的呢?
jdk的包下和線程相關類的類圖。
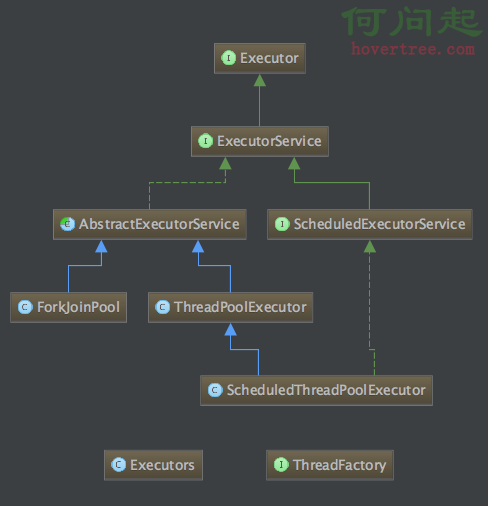
從上面可以看出Java的線程池主的實現類主要有兩個類ThreadPoolExecutor和ForkJoinPool。
ForkJoinPool是Fork/Join框架下使用的一個線程池,一般情況下,我們使用的比較多的就是ThreadPoolExecutor。我們大多數時候創建線程池是通過Executors類的幾個方法實現的:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}這裡看到基本上這幾個方法都是返回了ThreadPoolExecutor這個對象。以下是ThreadPoolExecutor的構造方法:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)幾個參數的含義:
線程池用的最多的是execute(),它的執行實際上分了三步:
corePoolSize,那麼啟用新的線程來執行新任務。corePoolSize,那麼嘗試把任務緩存起來,然後二次檢查線程池的狀態,看這個時候是否能添加一個額外的線程,來執行這個任務。如果這個檢查到線程池關閉了,就拒絕任務。public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}線程池把每個線程都封裝成一個對象Worker,以上有一個關鍵的函數addWorker():
addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core)
firstTask代表這個線程池首先要執行的任務,core代表是否使用corePoolSize來做為線程池線程的最大標記。
以上就是對線程池的一個基本解析。