GUI 和 AWT
GUI:Graphics User Interface 圖形用戶界面
AWT:Abstract Window Toolkit 抽象窗口工具集
之前的程序輸出結果均在控制台上顯示,現在學習AWT後,可以編程顯示圖形用戶界面。
抽象窗口工具包AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) 是 API為Java 程序提供的建立圖形用戶界面GUI (Graphics User Interface)工具集,之所以叫抽象窗口工具集,是因為該圖形用戶界面可以與系統無關,可以跨平台AWT可用於Java的applet和applications中,它支持圖形用戶界面編程。
用戶界面組件;
事件處理模型;
圖形和圖像工具,包括形狀、顏色和字體類;
布局管理器,可以進行靈活的窗口布局而與特定窗口的尺寸和屏幕分辨率無關;
數據傳送類,可以通過本地平台的剪貼板來進行剪切和粘貼。
java.awt包中提供了GUI設計所使用的類和接口。
java.awt包提供了基本的java程序的GUI設計工具。主要包括下述三個概念:
組件--Component
容器--Container
布局管理器--LayoutManager
組件
Java的圖形用戶界面的最基本組成部分是組件(Component),組件是一個可以以圖形化的方式顯示在屏幕上並能與用戶進行交互的對象,例如一個按鈕,一個標簽等。組件不能獨立地顯示出來,必須將組件放在一定的容器中才可以顯示出來。
常用組件:
Button 按鈕:
label 標簽 :顯示文字內容
TextField 文本框 :接受用戶輸入
這些組件都被封裝成類,編程時進行實例化被直接調用。
類java.awt.Component是許多組件類的父類,Component類中封裝了組件通用的方法和屬性,如圖形的組件對象、大小、顯示位置、前景色和背景色、邊界、可見性等,因此許多組件類也就繼承了Component類的成員方法和成員變量,相應的成員方法包括:
getComponentAt(int x, int y)
getFont()
getForeground()
getName()
getSize()
paint(Graphics g)
repaint()
update()
setVisible(boolean b)
setSize(Dimension d)
setName(String name)等
容器
容器(Container)也是一個類,實際上是Component的子類,因此容器本身也是一個組件,具有組件的所有性質,但是它的主要功能是容納其它組件和容器。
常用容器
容器java.awt.Container是Component的子類,一個容器可以容納多個組件,並使它們成為一個整體。容器可以簡化圖形化界面的設計,以整體結構來布置界面。所有的容器都可以通過add()方法向容器中添加組件。
有三種類型的容器:Window、Panel、ScrollPane,常用的有Panel, Frame, Applet。
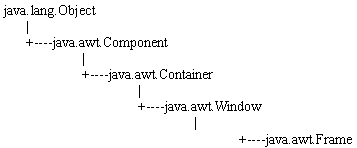
1.Frame 窗口
繼承關系
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("我的第一個窗口");
frame.setBounds(50, 50, 300, 200);//設置Frame 的大小,距離windows界面上左均為50,寬和高分別為300 200
frame.setBackground(Color.PINK);
frame.setVisible(true);//設置Frame為可見
}
}
Output:
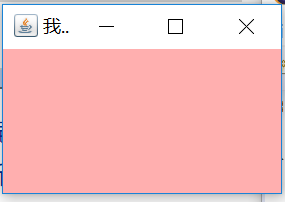
一般我們要生成一個窗口,通常是用Window的子類Frame來進行實例化,而不是直接用到Window類。Frame的外觀就像我們平常在windows系統下見到的窗口,有標題、邊框、菜單、大小等等。每個Frame的對象實例化以後,都是沒有大小和不可見的,因此必須調用setSize( )來設置大小,調用setVisible(true)來設置該窗口為可見的。
另外,AWT在實際的運行過程中是調用所在平台的圖形系統,因此同樣一段AWT程序在不同的操作系統平台下運行所看到的圖形系統是不一樣的。例如在windows下運行,則顯示的窗口是windows風格的窗口;而在UNIX下運行時,則顯示的是UNIX風格的窗口。
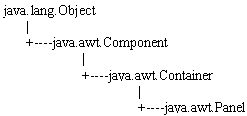
2. Panel 面板
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("我的panel 界面");
frame.setBounds(50, 50, 500, 300);
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.setBackground(Color.pink);
//panel.setBounds(0, 0, 200, 100); 如果要用 panel將整個窗口分塊,則要用到布局管理器,不可直接調用實現
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
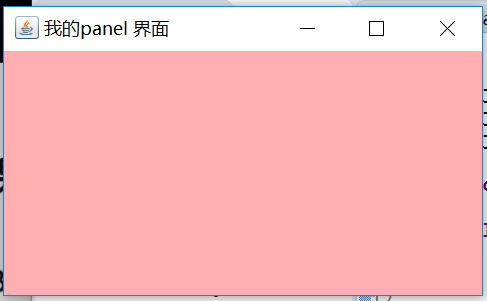
Panel 可以作為容器容納其他組件,但不可以像Frame 一樣獨立存在,必須將其添加到其他容器其中。
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("用戶登入窗口");
frame.setBounds(50, 50, 400, 100);
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.setBackground(Color.pink);
frame.add(panel);
Label lable = new Label("用戶名");
TextField textField = new TextField("請輸入用戶名",20);//20為文本框長度
Button loginbtn = new Button("確定");
panel.add(lable);
panel.add(textField);
panel.add(loginbtn);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
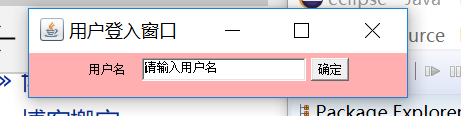
需要注意的是,Lebel 、TextField、 Button這些組件的添加是有順序的,以上是一個簡單的界面,比較復雜的情況則要使用布局管理器來實現。 並且以上的代碼比較簡單,實現的只是最基本的顯示功能,並不能進行實際的登陸與關閉操作。
布局管理器(LayoutManager):每個容器都有一個布局管理器,當容器需要對某個組件進行定位或判斷其大小尺寸時,就會調用其對應的布局管理器。
為了使我們生成的圖形用戶界面具有良好的平台無關性,Java語言中,提供了布局管理器這個工具來管理組件在容器中的布局,而不使用直接設置組件位置和大小的方式。
布局管理器主要包括:FlowLayout,BorderLayout,GridLayout,CardLayout,GridBagLayout
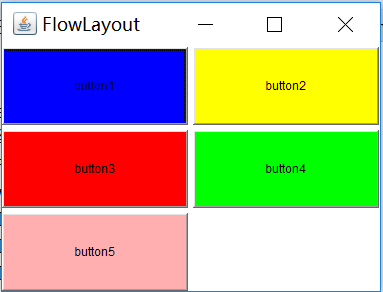
1. FlowLayout(流布局)
FlowLayout 是Panel,Applet的缺省布局管理器(默認布局管理器)。其組件的放置規律是從上到下、從左到右進行放置,如果容器足夠寬,第一個組件先添加到容器中第一行的最左邊,後續的組件依次添加到上一個組件的右邊,如果當前行已放置不下該組件,則放置到下一行的最左邊。
FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT,20,40);
/*第一個參數表示組件的對齊方式,指組件在這一行中的位置是居中對齊、居右對齊還是居左對齊,第二個參數是組件之間的橫向間隔,第三個參數是組件之間的縱向間隔,單位是象素。*/
FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT);
//居左對齊,橫向間隔和縱向間隔都是缺省值5個象素
FlowLayout();
//缺省的對齊方式居中對齊,橫向間隔和縱向間隔都是缺省值5個象素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("FlowLayout");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 400, 300);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
Button but1 = new Button("button1");
Button but2 = new Button("button2");
Button but3 = new Button("button3");
Button but4 = new Button("button4");
Button but5 = new Button("button5");
but1.setBackground(Color.blue);
but2.setBackground(Color.yellow);
but3.setBackground(Color.red);
but4.setBackground(Color.green);
but5.setBackground(Color.pink);
frame.add(but1);
frame.add(but2);
frame.add(but3);
frame.add(but4);
frame.add(but5);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
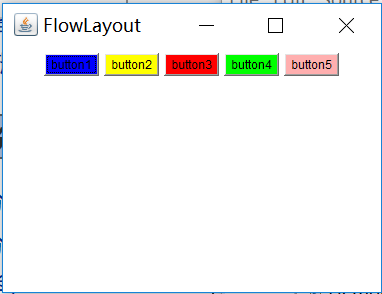
流布局與麻將布局的不同在於麻將布局要自己設置東西南北中的位置布局,而流布局則是按照按鈕的調用先後順序依次排列。默認居中排列,如果要設置為居左或居右排列,只需實例化FlowLayout ,用其實例對象 fl 調用設置隊列的方法,將其設置為居左。
即FlowLayout fl = new FlowLayout();
fl.setAlignment(FlowLayout.LEFT);
frame.setLayout(fl);
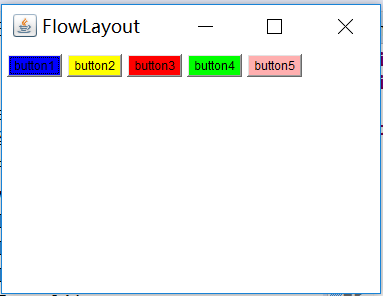
上圖為居左放置。
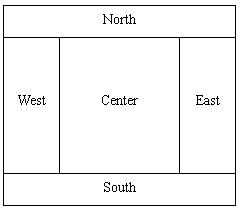
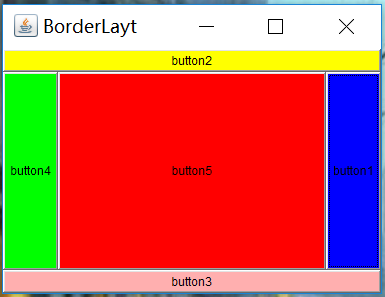
2. BorderLayout(麻將布局)
BorderLayout 是Window,Frame和Dialog的缺省(默認)布局管理器。BorderLayout布局管理器把容器分成5個區域:North,South,East,West和Center,每個區域只能放置一個組件。各個區域的位置及大小如下圖所示:
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("BorderLayt");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 400, 300);
//設置 frame 的布局為BorderLayout
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
Button btn1 = new Button("button1");
Button btn2 = new Button("button2");
Button btn3 = new Button("button3");
Button btn4 = new Button("button4");
Button btn5 = new Button("button5");
btn1.setBackground(Color.blue);
btn2.setBackground(Color.yellow);
btn3.setBackground(Color.pink);
btn4.setBackground(Color.green);
btn5.setBackground(Color.red);
frame.add(btn1,BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(btn2,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(btn3,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(btn4,BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(btn5);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
3. GridLayout(表格布局)
使容器中各個組件呈網格狀布局,平均占據容器的空間。
在程序中安排組件的位置和大小時,應該注意以下兩點:
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("FlowLayout");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 400, 300);
GridLayout gl = new GridLayout(3,2,5,5); //設置表格為3行兩列排列,表格橫向間距為5個像素,縱向間距為5個像素
frame.setLayout(gl);
Button but1 = new Button("button1");
Button but2 = new Button("button2");
Button but3 = new Button("button3");
Button but4 = new Button("button4");
Button but5 = new Button("button5");
but1.setBackground(Color.blue);
but2.setBackground(Color.yellow);
but3.setBackground(Color.red);
but4.setBackground(Color.green);
but5.setBackground(Color.pink);
frame.add(but1);
frame.add(but2);
frame.add(but3);
frame.add(but4);
frame.add(but5);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
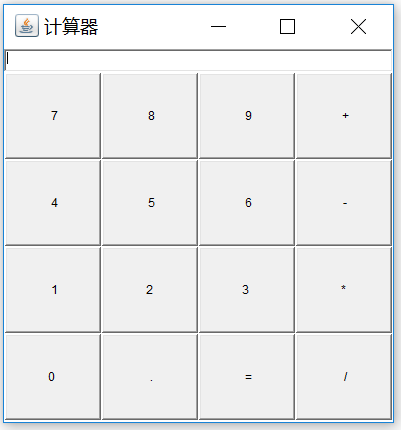
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame("計算器");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 300, 420);
/*因為Frame 的默認布局為BorderLayout 所以這兩句代碼可以省略。
BorderLayout bl = new BorderLayout();
frame.setLayout(bl);
*/
//創建一個文本輸入框,然後將其添加到 North 位置
TextField tf = new TextField();
frame.add(tf, BorderLayout.NORTH);
//創建一個Panel 面板,並設置布局為 GridLayout
Panel panel = new Panel();
GridLayout gl = new GridLayout(4,4,1,1);//創建Panel 面板,大小為4*4,行距與列距均為1 個像素點
panel.setLayout(gl);
//將 panel 添加到 frame 的 Center 位置
frame.add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
Button btn1 = new Button (" 7");
Button btn2 = new Button (" 8");
Button btn3 = new Button (" 9");
Button btn4 = new Button (" +");
Button btn5 = new Button (" 4");
Button btn6 = new Button (" 5");
Button btn7 = new Button (" 6");
Button btn8 = new Button (" -");
Button btn9 = new Button (" 1");
Button btn10 = new Button ("2");
Button btn11 = new Button ("3 ");
Button btn12 = new Button ("*");
Button btn13 = new Button ("0 ");
Button btn14 = new Button (" .");
Button btn15 = new Button (" =");
Button btn16 = new Button (" /");
//將按鈕添加到 Panel 面板
panel.add(btn1);
panel.add(btn2);
panel.add(btn3);
panel.add(btn4);
panel.add(btn5);
panel.add(btn6);
panel.add(btn7);
panel.add(btn8);
panel.add(btn9);
panel.add(btn10);
panel.add(btn11);
panel.add(btn12);
panel.add(btn13);
panel.add(btn14);
panel.add(btn15);
panel.add(btn16);
frame.setVisible( true);
}
}
Output:
1.Frame是一個頂級窗口。Frame的缺省布局管理器為BorderLayout。
2.Panel 無法單獨顯示,必須添加到某個容器中。 Panel 的缺省布局管理器為FlowLayout。
3.當把Panel 作為一個組件添加到某個容器中後,該Panel 仍然可以有自己的布局管理器。因此,可以利用Panel 使得BorderLayout 中某個區域顯示多個組件,達到設計復雜用戶界面的目的 。
4.如果采用無布局管理器 setLayout(null),則必須使用setLocation(),setSize(),setBounds()等方法手工設置組件的大小和位置,此方法會導致平台相關,不鼓勵使用。